CHEMICAL REACTIONS
... ________ 19. Among the elements listed, which one could replace all of the rest as an ion from a compound in aqueous solution? a. Cu c. Fe b. Ca d. Ag ...
... ________ 19. Among the elements listed, which one could replace all of the rest as an ion from a compound in aqueous solution? a. Cu c. Fe b. Ca d. Ag ...
Chemistry Comes Alive: Part A
... • Ions are formed by transfer of valence shell electrons between atoms • Anions (– charge) have gained one or more electrons • Cations (+ charge) have lost one or more electrons ...
... • Ions are formed by transfer of valence shell electrons between atoms • Anions (– charge) have gained one or more electrons • Cations (+ charge) have lost one or more electrons ...
File
... Coulomb's Law is one of the basic ideas of electricity in physics. The law looks at the forces created between two charged objects. Coulomb’s Law states that the strength of the force exerted between two charged particles depends on the strength of the charges on the objects and the distance between ...
... Coulomb's Law is one of the basic ideas of electricity in physics. The law looks at the forces created between two charged objects. Coulomb’s Law states that the strength of the force exerted between two charged particles depends on the strength of the charges on the objects and the distance between ...
Key Points Formulae
... through a differential equation • A surface where all points are on the same electric potential is defined as an equipotential surface; these lines are parallel to electric field lines • There is also ...
... through a differential equation • A surface where all points are on the same electric potential is defined as an equipotential surface; these lines are parallel to electric field lines • There is also ...
matter crct/final exam review
... 41. Why do atoms share valence electrons or transfer valence electrons? 42. What is the difference between a compound and an element? ...
... 41. Why do atoms share valence electrons or transfer valence electrons? 42. What is the difference between a compound and an element? ...
Slide 1
... Ion separation and analysis using MS/MS technique AHB+ ions are separated and further analyzed by MS/MS. ...
... Ion separation and analysis using MS/MS technique AHB+ ions are separated and further analyzed by MS/MS. ...
Chemical Reactions
... Don’t forget about the diatomic elements! (BrINClHOF) For example, Oxygen is O2 as an element. In a compound, it can’t be a diatomic element because it’s not an element anymore, it’s a compound! ...
... Don’t forget about the diatomic elements! (BrINClHOF) For example, Oxygen is O2 as an element. In a compound, it can’t be a diatomic element because it’s not an element anymore, it’s a compound! ...
Document
... 5. Halogens: The oxidation number of fluorine is -1. Each of the other halogens (Cl, Br, I) has an oxidation number of -1 in binary compounds, except when the other element is another halogen above it in the periodic table or the other element is oxygen. 6. Compounds and ions: The sum of the oxidat ...
... 5. Halogens: The oxidation number of fluorine is -1. Each of the other halogens (Cl, Br, I) has an oxidation number of -1 in binary compounds, except when the other element is another halogen above it in the periodic table or the other element is oxygen. 6. Compounds and ions: The sum of the oxidat ...
Dear 3EFG, Refer to your notes for the formula and other data. But
... about 30 billion years it is nearly gone. Strontium -90 formed by nuclear reactions that occur in nuclear weapons testing is essentially gone after several hundred years. 2) Example of a nuclear bombardment reaction is the fusion that goes on in the sun which is essentially four protons and electron ...
... about 30 billion years it is nearly gone. Strontium -90 formed by nuclear reactions that occur in nuclear weapons testing is essentially gone after several hundred years. 2) Example of a nuclear bombardment reaction is the fusion that goes on in the sun which is essentially four protons and electron ...
Nuclear Astrophysics (1)
... The chemical potential obtained from the total number density n provides information on energy/momentum distributions of particles. It is only determined up to a constant. If energy generation due to mass differences in reactions is involved, the above equation is correct, if ...
... The chemical potential obtained from the total number density n provides information on energy/momentum distributions of particles. It is only determined up to a constant. If energy generation due to mass differences in reactions is involved, the above equation is correct, if ...
H 2 O
... • Volume – Temperature Relationship – At constant pressure, the volume is directly proportional to temperature ...
... • Volume – Temperature Relationship – At constant pressure, the volume is directly proportional to temperature ...
Answers to Final Exam Review
... 49. Write a balanced chemical equation for each reaction (include phases). Identify the type of reaction. a. Sodium metal dropped into a beaker of water. Na (s) + 2H2O (l) Na+ (aq) + 2OH- (aq) + H2 (g) b. Silver nitrate is added to sodium chloride. AgNO3 (s) + NaCl (s) AgCl (s) + NaNO3 (s) (doubl ...
... 49. Write a balanced chemical equation for each reaction (include phases). Identify the type of reaction. a. Sodium metal dropped into a beaker of water. Na (s) + 2H2O (l) Na+ (aq) + 2OH- (aq) + H2 (g) b. Silver nitrate is added to sodium chloride. AgNO3 (s) + NaCl (s) AgCl (s) + NaNO3 (s) (doubl ...
PSC1341 Chapter 3
... ability to hold or give up electrons. Under ideal conditions, if two materials are rubbed together, the one higher on the list should give up electrons and become positively charged. As electrons collect on an object, it becomes negatively charged. As electrons leave an object it attains a positive ...
... ability to hold or give up electrons. Under ideal conditions, if two materials are rubbed together, the one higher on the list should give up electrons and become positively charged. As electrons collect on an object, it becomes negatively charged. As electrons leave an object it attains a positive ...
chapter2 - AlvarezHChem
... atoms minus their electrons) • Expected to see the particles pass through the foil • Found that some of the alpha particles were deflected by the foil • Led to the discovery of a region of heavy mass at the center of the atom = nucleus ...
... atoms minus their electrons) • Expected to see the particles pass through the foil • Found that some of the alpha particles were deflected by the foil • Led to the discovery of a region of heavy mass at the center of the atom = nucleus ...
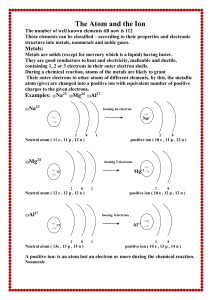
The Atom and the Ion
... Some of nonmetals are solids, others are gases and only there is one liquid element which is bromine. They have no luster, not malleable or ductile (brittle), they are bad conductors to heat and electricity, except graphite which is good conductor to electricity. Most of nonmetals contain 5,6 or 7 ...
... Some of nonmetals are solids, others are gases and only there is one liquid element which is bromine. They have no luster, not malleable or ductile (brittle), they are bad conductors to heat and electricity, except graphite which is good conductor to electricity. Most of nonmetals contain 5,6 or 7 ...
Balancing Equations
... Steps to Balancing Equations There are four basic steps to balancing a chemical equation. 1. Write the correct formula for the reactants and the ...
... Steps to Balancing Equations There are four basic steps to balancing a chemical equation. 1. Write the correct formula for the reactants and the ...
Week 7 - Acid-base, redox
... the charge (or oxidation number) will increase. Another atom gains one or more electrons, so the oxidation number will decrease. The term “redox” comes from the terms reduction and oxidation. If a substance gets oxidized (or loses electrons), then another substance gets reduced (or gains electrons). ...
... the charge (or oxidation number) will increase. Another atom gains one or more electrons, so the oxidation number will decrease. The term “redox” comes from the terms reduction and oxidation. If a substance gets oxidized (or loses electrons), then another substance gets reduced (or gains electrons). ...
Electricity
... negative to positive – An electric current will occur in a conductive metal when an electric potential exists – Electric potential is the difference between the charge at the – end and the + end – Electricity does work when the electrons flow in an electric current along a wire ...
... negative to positive – An electric current will occur in a conductive metal when an electric potential exists – Electric potential is the difference between the charge at the – end and the + end – Electricity does work when the electrons flow in an electric current along a wire ...
Homework Exercises
... Copper chloride can be made by reacting excess copper (II) carbonate with hydrochloric acid. Copper (II) carbonate + hydrochloric acid ⟶ copper(II)chloride + water + X (a) (b) (c) (d) ...
... Copper chloride can be made by reacting excess copper (II) carbonate with hydrochloric acid. Copper (II) carbonate + hydrochloric acid ⟶ copper(II)chloride + water + X (a) (b) (c) (d) ...
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry that studies chemical reactions which take place at the interface of an electrode, usually a solid metal or a semiconductor, and an ionic conductor, the electrolyte. These reactions involve electric charges moving between the electrodes and the electrolyte (or ionic species in a solution). Thus electrochemistry deals with the interaction between electrical energy and chemical change.When a chemical reaction is caused by an externally supplied current, as in electrolysis, or if an electric current is produced by a spontaneous chemical reaction as in a battery, it is called an electrochemical reaction. Chemical reactions where electrons are transferred directly between molecules and/or atoms are called oxidation-reduction or (redox) reactions. In general, electrochemistry describes the overall reactions when individual redox reactions are separate but connected by an external electric circuit and an intervening electrolyte.