Types of Chemical Reactions Name_________________________
... How does the aluminum bromide precipitate become deposited on the watch glass covering the beaker since it does not come in contact with the bromine liquid? ...
... How does the aluminum bromide precipitate become deposited on the watch glass covering the beaker since it does not come in contact with the bromine liquid? ...
Click Here To File
... -There are 4 unpaired electrons. -Water is a weak ligand. Thus the hybridisation involved is sp3d2 (marks to be granted if hybridisation is depicted diagrammatically) (ii) The ionisation isomer is [Co(NH3)5SO4]Br. The IUPAC name is pentaamminesulphatocobalt(III)bromide. Chemical test to distinguish ...
... -There are 4 unpaired electrons. -Water is a weak ligand. Thus the hybridisation involved is sp3d2 (marks to be granted if hybridisation is depicted diagrammatically) (ii) The ionisation isomer is [Co(NH3)5SO4]Br. The IUPAC name is pentaamminesulphatocobalt(III)bromide. Chemical test to distinguish ...
09 Stoichiometry WS Stoichiometry WS
... container with excess P4O10. Water is absorbed by the following reaction: P4O10 + 6H2O 4H3PO4 a. What mass of water can be absorbed by 100. g of P4O10? b. If the P4O10 in the container absorbs 0.614 mol of water, what mass of H3PO4 is produced? c. If the mass of the container of P4O10 increases from ...
... container with excess P4O10. Water is absorbed by the following reaction: P4O10 + 6H2O 4H3PO4 a. What mass of water can be absorbed by 100. g of P4O10? b. If the P4O10 in the container absorbs 0.614 mol of water, what mass of H3PO4 is produced? c. If the mass of the container of P4O10 increases from ...
Questions - Unified Council
... (A) lower air pressure, higher acceleration due to gravity. (B) higher air pressure, lower acceleration due to gravity. (C) higher air pressure, higher acceleration due to gravity. (D) lower air pressure, lower acceleration due to gravity. ...
... (A) lower air pressure, higher acceleration due to gravity. (B) higher air pressure, lower acceleration due to gravity. (C) higher air pressure, higher acceleration due to gravity. (D) lower air pressure, lower acceleration due to gravity. ...
Practice Exam #2
... 25) 7, 5, 3, 1. HClO4 has the highest. 26) Li3 PO4 27) The salt contains insoluble compounds to prevent the grains of salt from sticking together in humid weather. 28) increases the concentration of H+ ions in aqueous solutions 29) a0 Yes, b) Yes, c) No ...
... 25) 7, 5, 3, 1. HClO4 has the highest. 26) Li3 PO4 27) The salt contains insoluble compounds to prevent the grains of salt from sticking together in humid weather. 28) increases the concentration of H+ ions in aqueous solutions 29) a0 Yes, b) Yes, c) No ...
4.IonicCompounds - Gleneaglesunit1and2chemistry2012
... state they are not free to move. – When an ionic compound melts, however, the particles are free to move and the compound will conduct electricity. ...
... state they are not free to move. – When an ionic compound melts, however, the particles are free to move and the compound will conduct electricity. ...
Types of Chemical Reactions
... • For example, when ammonia and hydrogen chloride vapours combine, they form a white smoke as solid particles of ammonium chloride are formed. ...
... • For example, when ammonia and hydrogen chloride vapours combine, they form a white smoke as solid particles of ammonium chloride are formed. ...
Chap 2.3 notes
... • The unit of electric charge is the coulomb (C). • The fundamental charge on an electron is 1.6 X 10-19 C. • 1 C = 1/ 1.6 X 10-19 = 6.25 X 1018 electrons or 6,250,000,000,000,000,000 electrons. ...
... • The unit of electric charge is the coulomb (C). • The fundamental charge on an electron is 1.6 X 10-19 C. • 1 C = 1/ 1.6 X 10-19 = 6.25 X 1018 electrons or 6,250,000,000,000,000,000 electrons. ...
1b-Redox FIB notes and practice
... On the other hand, copper is ______________ in this reaction from Cu 0 to Cu +2. These results agree with those obtained by analyzing the reaction by using electron transfer. Example: Use the change in oxidation number to identify which elements are oxidized and reduced in each of these reactions. ...
... On the other hand, copper is ______________ in this reaction from Cu 0 to Cu +2. These results agree with those obtained by analyzing the reaction by using electron transfer. Example: Use the change in oxidation number to identify which elements are oxidized and reduced in each of these reactions. ...
Chemical Reactions Mr. Campbell
... water is boiled and bubbles form, is it a chemical change? ► No ► Electrolysis of water produces H2 gas and O2 gas. Is this a chemical change? ► Yes ► Color change in leaves because chlorophyll is being produced. Is this a chemical change? ► Yes ...
... water is boiled and bubbles form, is it a chemical change? ► No ► Electrolysis of water produces H2 gas and O2 gas. Is this a chemical change? ► Yes ► Color change in leaves because chlorophyll is being produced. Is this a chemical change? ► Yes ...
Use the following to answer questions 1-14:
... Fill in the blank with the most appropriate term from the chapter, unit, or course. To summarize what happens to substances during a chemical reaction, scientists use a chemical _______________________. Arsenic has a total of 33 electrons. It has _______________________ electron shells around its nu ...
... Fill in the blank with the most appropriate term from the chapter, unit, or course. To summarize what happens to substances during a chemical reaction, scientists use a chemical _______________________. Arsenic has a total of 33 electrons. It has _______________________ electron shells around its nu ...
Chemistry DCA Review Sheet
... 12. What physical and chemical properties are determined by investigation the Periodic Table? ...
... 12. What physical and chemical properties are determined by investigation the Periodic Table? ...
Electricity and Magnetism
... there will be a potential difference or voltage (V) created across the resistance. Ohm’s law gives a relationship between the voltage (V), current (I), and resistance (R) as follows: ...
... there will be a potential difference or voltage (V) created across the resistance. Ohm’s law gives a relationship between the voltage (V), current (I), and resistance (R) as follows: ...
Chapter 3 Chemical Reactions
... equations must be balanced for mass! In other words, there must be the same number of atoms of the each kind on both sides of the equation. ...
... equations must be balanced for mass! In other words, there must be the same number of atoms of the each kind on both sides of the equation. ...
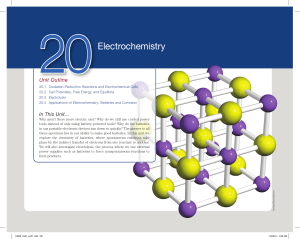
Chapter 20
... Charge buildup can be eliminated by adding a mechanism that allows counterions to flow between the two half-cells, the separated containers where oxidation and reduction take place. Two common options are the use of a porous disk or a salt bridge; a salt bridge is a stoppered tube containing an elec ...
... Charge buildup can be eliminated by adding a mechanism that allows counterions to flow between the two half-cells, the separated containers where oxidation and reduction take place. Two common options are the use of a porous disk or a salt bridge; a salt bridge is a stoppered tube containing an elec ...
Unit 6 Moles and Stoichiometry Short Answer Review
... 4. Determine the percent composition by mass of oxygen in the compound C6H12O6 5. A hydrated compound contains water molecules within its crystal structure. The percent composition by mass of water in the hydrated compound CaSO 4•2H 2O has an accepted value of 20.9%. A student did an experiment and ...
... 4. Determine the percent composition by mass of oxygen in the compound C6H12O6 5. A hydrated compound contains water molecules within its crystal structure. The percent composition by mass of water in the hydrated compound CaSO 4•2H 2O has an accepted value of 20.9%. A student did an experiment and ...
chemical reaction - Peoria Public Schools
... Write word and formula equations for the chemical reaction that occurs when solid sodium oxide is added to water at room temperature and forms sodium hydroxide (dissolved in water) ...
... Write word and formula equations for the chemical reaction that occurs when solid sodium oxide is added to water at room temperature and forms sodium hydroxide (dissolved in water) ...
Ionic Bonding
... This amount of energy can compensate for values as large as I3 for valence electrons (i.e. can strip away up to 3 electrons). Because most transition metals would require the removal of more than 3 electrons to attain a noble gas core, they are not found in ionic compounds with a noble gas core (thu ...
... This amount of energy can compensate for values as large as I3 for valence electrons (i.e. can strip away up to 3 electrons). Because most transition metals would require the removal of more than 3 electrons to attain a noble gas core, they are not found in ionic compounds with a noble gas core (thu ...
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry that studies chemical reactions which take place at the interface of an electrode, usually a solid metal or a semiconductor, and an ionic conductor, the electrolyte. These reactions involve electric charges moving between the electrodes and the electrolyte (or ionic species in a solution). Thus electrochemistry deals with the interaction between electrical energy and chemical change.When a chemical reaction is caused by an externally supplied current, as in electrolysis, or if an electric current is produced by a spontaneous chemical reaction as in a battery, it is called an electrochemical reaction. Chemical reactions where electrons are transferred directly between molecules and/or atoms are called oxidation-reduction or (redox) reactions. In general, electrochemistry describes the overall reactions when individual redox reactions are separate but connected by an external electric circuit and an intervening electrolyte.