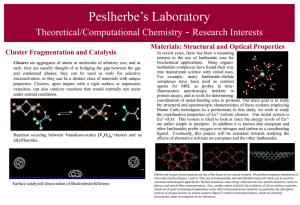
Cluster Fragmentation and Catalysis
... agents for MRI, as probes in timefluorescence spectroscopy, markers in protein assays, and as tools for determining coordination of metal-binding sites in proteins. Our main goal is to study the structural and spectroscopic characteristics of these systems employing Monte Carlo techniques.As a preli ...
... agents for MRI, as probes in timefluorescence spectroscopy, markers in protein assays, and as tools for determining coordination of metal-binding sites in proteins. Our main goal is to study the structural and spectroscopic characteristics of these systems employing Monte Carlo techniques.As a preli ...
High School Physical Science Glossary
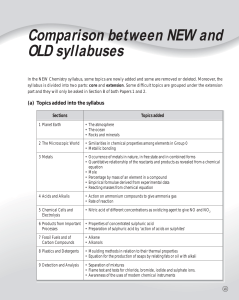
... chemical reaction- a process in which the atoms of one or more substances are rearranged into new substances coefficient- whole numbers written in front of individual compounds or atoms within a chemical equation indicating the relative amounts of each for the purpose of balancing the equation comb ...
... chemical reaction- a process in which the atoms of one or more substances are rearranged into new substances coefficient- whole numbers written in front of individual compounds or atoms within a chemical equation indicating the relative amounts of each for the purpose of balancing the equation comb ...
Bio Boot Camp - Tredyffrin/Easttown School District
... Water • The cohesive forces between liquid molecules are responsible for the phenomenon known as surface tension. The molecules at the surface do not have other like molecules on all sides of them and consequently they cohere more strongly to those directly associated with them on the surface. This ...
... Water • The cohesive forces between liquid molecules are responsible for the phenomenon known as surface tension. The molecules at the surface do not have other like molecules on all sides of them and consequently they cohere more strongly to those directly associated with them on the surface. This ...
exo and endo experiments
... The Law of Conservation of Mass The Law of Conservation of Mass was officially established in the year 1789 by the French Chemist, Antoine Lavoisier. The Law of Conservation of Mass states that mass is neither lost nor gained in chemical reactions, it states that it simply changes form. For that rea ...
... The Law of Conservation of Mass The Law of Conservation of Mass was officially established in the year 1789 by the French Chemist, Antoine Lavoisier. The Law of Conservation of Mass states that mass is neither lost nor gained in chemical reactions, it states that it simply changes form. For that rea ...
The Chemical Context of Life Chapter 2 Notes
... Atomic number: # of protons Mass number: sum of protons + neutrons Isotopes: different atomic forms of an element. -ex. Carbon-12 (99%), Carbon-13 (1%), Carbon-14 (<1%) ...
... Atomic number: # of protons Mass number: sum of protons + neutrons Isotopes: different atomic forms of an element. -ex. Carbon-12 (99%), Carbon-13 (1%), Carbon-14 (<1%) ...
01.CN_Other pages/p1-9
... (b) (i) Which particle(s) is / are the ions? Hint 2 (ii) What is the relationship between P and Q? (iii) Do particles of P and Q have the same chemical properties? Explain your answer. (c) (i) Suggest a term to indicate the relationship between S and T. (ii) Explain why S and T have the same chemica ...
... (b) (i) Which particle(s) is / are the ions? Hint 2 (ii) What is the relationship between P and Q? (iii) Do particles of P and Q have the same chemical properties? Explain your answer. (c) (i) Suggest a term to indicate the relationship between S and T. (ii) Explain why S and T have the same chemica ...
Document
... Summarizing Limiting Reactant and Yield • The limiting reactant (or limiting reagent) is the reactant that is completely consumed in a chemical reaction and limits the amount of product. • The reactant in excess is any reactant that occurs in a quantity greater than is required to completely react ...
... Summarizing Limiting Reactant and Yield • The limiting reactant (or limiting reagent) is the reactant that is completely consumed in a chemical reaction and limits the amount of product. • The reactant in excess is any reactant that occurs in a quantity greater than is required to completely react ...
Oregon State University, Summer 2009 Chemistry 121 Midterm
... This exam consists of 20 multiple-choice questions. Each multiple-choice question has 5 points associated with it. Select the best answer by filling in the corresponding circle on the rear page of the answer sheet. If you have any questions before the exam, please ask. If you have any questions duri ...
... This exam consists of 20 multiple-choice questions. Each multiple-choice question has 5 points associated with it. Select the best answer by filling in the corresponding circle on the rear page of the answer sheet. If you have any questions before the exam, please ask. If you have any questions duri ...
1 - mvhs-fuhsd.org
... 3. What is chemistry? 4. What branch of chemistry is most concerned with the study of carbon compounds? 5. What does the word chemical, as used by scientists, mean? 6. Briefly describe the differences between basic research, applied research, and technological development. Provide an example of each ...
... 3. What is chemistry? 4. What branch of chemistry is most concerned with the study of carbon compounds? 5. What does the word chemical, as used by scientists, mean? 6. Briefly describe the differences between basic research, applied research, and technological development. Provide an example of each ...
syllabus for screening test (mcq type)
... a) Electrical conductance, weak and strong electrolytes, variation of equivalent conductance with dilution, Kohlrausch’s law, transport number, determination of transport number by moving boundary method, theory of strong electrolytes, applications of conductance measurements. b) Galvanic cells, the ...
... a) Electrical conductance, weak and strong electrolytes, variation of equivalent conductance with dilution, Kohlrausch’s law, transport number, determination of transport number by moving boundary method, theory of strong electrolytes, applications of conductance measurements. b) Galvanic cells, the ...
Honors Chemistry II Review 1. Express the following in scientific
... Which reactant is limiting if there are 80kg of water to be removed and 65kg of Li2O available? How many kg of the excess reactant remain? 20. After lithium hydroxide is produced aboard the space shuttle, it is used to remove exhaled carbon dioxide from the air supply according to the following equa ...
... Which reactant is limiting if there are 80kg of water to be removed and 65kg of Li2O available? How many kg of the excess reactant remain? 20. After lithium hydroxide is produced aboard the space shuttle, it is used to remove exhaled carbon dioxide from the air supply according to the following equa ...
Unit 7: Chemical Equations & Reactions
... 1. Identify the most complex substance. 2. Beginning with that substance, choose an element that appears in only one reactant and one product. • Adjust the coefficients to obtain the same number of atoms of this element on both sides. • Balance polyatomic ions as a unit (if possible). • Re-write H2 ...
... 1. Identify the most complex substance. 2. Beginning with that substance, choose an element that appears in only one reactant and one product. • Adjust the coefficients to obtain the same number of atoms of this element on both sides. • Balance polyatomic ions as a unit (if possible). • Re-write H2 ...
unit 7 – writing and balancing chemical equations
... There are four physical state symbols which are used as subscripts immediately following substances whose physical states are known or given. (s) – solid, which is used for solids or precipitates () – liquid, which is used only for “true” liquids such as elements which are liquids at room temperatu ...
... There are four physical state symbols which are used as subscripts immediately following substances whose physical states are known or given. (s) – solid, which is used for solids or precipitates () – liquid, which is used only for “true” liquids such as elements which are liquids at room temperatu ...
2. Essential Chemistry
... o Participates in chemical reactions o Water has a high specific heat which moderates temperature - absorbs and releases heat very slowly, minimizes temperature fluctuations to within limits that permit life Heat is absorbed when hydrogen bonds break Heat is released when hydrogen bonds form o R ...
... o Participates in chemical reactions o Water has a high specific heat which moderates temperature - absorbs and releases heat very slowly, minimizes temperature fluctuations to within limits that permit life Heat is absorbed when hydrogen bonds break Heat is released when hydrogen bonds form o R ...
Final Analysis – Exam Review
... c. The number of electrons that pass through the wire in a specific time interval d. Measured in a circuit using a voltmeter 2. Electric potential (Voltage) is: a. The number of electrons that pass through a wire in a specific time interval b. The ability of an object to conduct protons c. The amoun ...
... c. The number of electrons that pass through the wire in a specific time interval d. Measured in a circuit using a voltmeter 2. Electric potential (Voltage) is: a. The number of electrons that pass through a wire in a specific time interval b. The ability of an object to conduct protons c. The amoun ...
The Thomas Hardye School Summer Preparation Task Chemistry AS
... Formulae of Ionic compounds Ionic compounds contain positive and negative ions. The number of positive charges must equal the number of negative charges so that the compound has no charge overall. Brackets Watch out for compound ions, e.g. ammonium, hydrogencarbonate, hydroxide, nitrate, sulphate an ...
... Formulae of Ionic compounds Ionic compounds contain positive and negative ions. The number of positive charges must equal the number of negative charges so that the compound has no charge overall. Brackets Watch out for compound ions, e.g. ammonium, hydrogencarbonate, hydroxide, nitrate, sulphate an ...
Gateway Chemistry Review (Answer Key) Structure and Properties
... Two atoms contain the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. Isotopes are atoms of the same element, but have different masses. Isotopes with an unstable nucleus will tend to breakdown or decay; these atoms are called radioactive and will release energy in the form of nuclea ...
... Two atoms contain the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. Isotopes are atoms of the same element, but have different masses. Isotopes with an unstable nucleus will tend to breakdown or decay; these atoms are called radioactive and will release energy in the form of nuclea ...
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry that studies chemical reactions which take place at the interface of an electrode, usually a solid metal or a semiconductor, and an ionic conductor, the electrolyte. These reactions involve electric charges moving between the electrodes and the electrolyte (or ionic species in a solution). Thus electrochemistry deals with the interaction between electrical energy and chemical change.When a chemical reaction is caused by an externally supplied current, as in electrolysis, or if an electric current is produced by a spontaneous chemical reaction as in a battery, it is called an electrochemical reaction. Chemical reactions where electrons are transferred directly between molecules and/or atoms are called oxidation-reduction or (redox) reactions. In general, electrochemistry describes the overall reactions when individual redox reactions are separate but connected by an external electric circuit and an intervening electrolyte.