Chemistry
... Specific conductance, equivalent conductance, measurement of equivalent conductance. Variation of equivalent conductance with dilution. Migration of ions, Kohlrausch’s law. Arrhenius theory of electrolyte dissociation and its limitations. Ostwald’s dilution law. Debye-Huckel-Onsagar’s equation for s ...
... Specific conductance, equivalent conductance, measurement of equivalent conductance. Variation of equivalent conductance with dilution. Migration of ions, Kohlrausch’s law. Arrhenius theory of electrolyte dissociation and its limitations. Ostwald’s dilution law. Debye-Huckel-Onsagar’s equation for s ...
Test #5 Review
... bromine (For the same reason – more energy levels.) Why do elements in the same family behave the same? They all have the same number of valence electrons. ...
... bromine (For the same reason – more energy levels.) Why do elements in the same family behave the same? They all have the same number of valence electrons. ...
Chemistry Final Exam Test Yourself I
... A chemical reaction is at this when the concentrations of reactants and products remain constant. (Forward reaction rate = Reverse reaction rate.) (Equilibrium) Branch of chemistry that can be used to determine how fast a reaction occurs (Kinetics) ...
... A chemical reaction is at this when the concentrations of reactants and products remain constant. (Forward reaction rate = Reverse reaction rate.) (Equilibrium) Branch of chemistry that can be used to determine how fast a reaction occurs (Kinetics) ...
Advanced Placement (AP) Chemistry 2012 – 2013 Ramsay High
... 2. Methods of expressing concentration (the use of normality is not tested) 3. Raoult’s law and colligative properties (nonvolatile solutes); osmosis 4. Non-ideal behavior (qualitative aspects) ...
... 2. Methods of expressing concentration (the use of normality is not tested) 3. Raoult’s law and colligative properties (nonvolatile solutes); osmosis 4. Non-ideal behavior (qualitative aspects) ...
examples of chemical and physical reactions.
... called _______________. The substances that are present at the end of the reaction are called the _____________. Example: If we take a paper, the reactant is the paper. If we burn the paper the reaction is burning. At the end of the reaction i.e. when the paper completely burns, the product is ash. ...
... called _______________. The substances that are present at the end of the reaction are called the _____________. Example: If we take a paper, the reactant is the paper. If we burn the paper the reaction is burning. At the end of the reaction i.e. when the paper completely burns, the product is ash. ...
A = 27
... #28)Which Isotope will decay spontaneously and emit a particle with a charge of +2? A) Fe-53 b) Cs-137 c) Au-198 d) Fr-220 Radiation of +2 charge is an alpha particle, and table “N” lists natural decay. Find the alpha emitter on table n from the choices. The answer is Fr-220 d), the only alpha emitt ...
... #28)Which Isotope will decay spontaneously and emit a particle with a charge of +2? A) Fe-53 b) Cs-137 c) Au-198 d) Fr-220 Radiation of +2 charge is an alpha particle, and table “N” lists natural decay. Find the alpha emitter on table n from the choices. The answer is Fr-220 d), the only alpha emitt ...
Chemistry Exam 2 Specifications and Sample Exam
... A. no reaction at all because the process is endothermic. B. a colourless gas at the cathode and a metallic coating on the anode. C. a coloured liquid at the anode and a metallic coating on the cathode. D. a colourless gas at the anode and a coloured liquid at the cathode. Question 11 Information su ...
... A. no reaction at all because the process is endothermic. B. a colourless gas at the cathode and a metallic coating on the anode. C. a coloured liquid at the anode and a metallic coating on the cathode. D. a colourless gas at the anode and a coloured liquid at the cathode. Question 11 Information su ...
Elementary my dear Watson review
... For example, carbon dioxide (CO2) is made up of 1 atom of carbon and two atoms of oxygen. ...
... For example, carbon dioxide (CO2) is made up of 1 atom of carbon and two atoms of oxygen. ...
Sample Exercise 20.1 Identifying Oxidizing and Reducing Agents
... is spontaneous. A solution containing K2Cr2O7 and H2SO4 is poured into one beaker, and a solution of KI is poured into another. A salt bridge is used to join the beakers. A metallic conductor that will not react with either solution (such as platinum foil) is suspended in each solution, and the two ...
... is spontaneous. A solution containing K2Cr2O7 and H2SO4 is poured into one beaker, and a solution of KI is poured into another. A salt bridge is used to join the beakers. A metallic conductor that will not react with either solution (such as platinum foil) is suspended in each solution, and the two ...
Worked out problems
... is spontaneous. A solution containing K2Cr2O7 and H2SO4 is poured into one beaker, and a solution of KI is poured into another. A salt bridge is used to join the beakers. A metallic conductor that will not react with either solution (such as platinum foil) is suspended in each solution, and the two ...
... is spontaneous. A solution containing K2Cr2O7 and H2SO4 is poured into one beaker, and a solution of KI is poured into another. A salt bridge is used to join the beakers. A metallic conductor that will not react with either solution (such as platinum foil) is suspended in each solution, and the two ...
Science24-UnitA-Section3.1-3.2
... Types of Reactions When you study for school, do you put things that are similar together? Do you look for patterns when you try solving a mathematics problem? Similarly, in chemistry, you can group chemical reactions together according to particular patterns in which the reactions occur. The most c ...
... Types of Reactions When you study for school, do you put things that are similar together? Do you look for patterns when you try solving a mathematics problem? Similarly, in chemistry, you can group chemical reactions together according to particular patterns in which the reactions occur. The most c ...
Ch 19 test_take-home
... 19) Which one of the following processes produces a decrease in the entropy of the system? A) boiling water to form steam B) dissolution of solid KCl in water C) mixing of two gases into one container D) freezing water to form ice E) melting ice to form water 20) For a reaction to be spontaneous und ...
... 19) Which one of the following processes produces a decrease in the entropy of the system? A) boiling water to form steam B) dissolution of solid KCl in water C) mixing of two gases into one container D) freezing water to form ice E) melting ice to form water 20) For a reaction to be spontaneous und ...
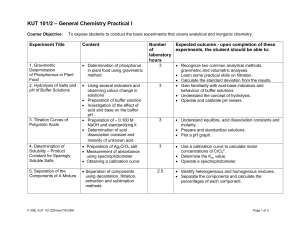
KUT 101/2 – General Chemistry Practical I
... • Recognise coordination compounds, wherein the metal is a Lewis acid and the atoms or molecules joined to the metal are Lewis base or ligands. • Calculate the percentage yield. ...
... • Recognise coordination compounds, wherein the metal is a Lewis acid and the atoms or molecules joined to the metal are Lewis base or ligands. • Calculate the percentage yield. ...
Molar Heat of Reaction
... Expressed in kilojoules per mole (kJ/mol) of dissolved solute In this reaction heat can be either released or absorbed ...
... Expressed in kilojoules per mole (kJ/mol) of dissolved solute In this reaction heat can be either released or absorbed ...
PHT-224 Lectures 7
... Toxicity and safety study: Urea is diuretic. In aqueous solution, 1% degradation gives very toxic ammonia (increase pH) and CO2, which can cause ampoule to explode due to limited solubility in water. Therefore shelf life is based on 1% not 10% degradation. Product elegance: Solution of epinephri ...
... Toxicity and safety study: Urea is diuretic. In aqueous solution, 1% degradation gives very toxic ammonia (increase pH) and CO2, which can cause ampoule to explode due to limited solubility in water. Therefore shelf life is based on 1% not 10% degradation. Product elegance: Solution of epinephri ...
Example - cloudfront.net
... 5) ______________ Displacement: A reaction between _________________ that are dissolved in water that produces ________________, one of which is ___________. Water or a gas may be one of the two compounds being produced. General Form: AX (aq) + BY(aq) AY(aq) + BX (s) A solid produced during a che ...
... 5) ______________ Displacement: A reaction between _________________ that are dissolved in water that produces ________________, one of which is ___________. Water or a gas may be one of the two compounds being produced. General Form: AX (aq) + BY(aq) AY(aq) + BX (s) A solid produced during a che ...
Chapter 12 Oxidation-Reduction Reactions
... spontaneously. 3. Make a simple redox table similar to Table 12.1 that contains all the metal atoms and metal ions that you analyzed in this investigation. Note that the ion that was able to oxidize all other metal atoms is placed at the top of the left column. In the next row, place the ion that ox ...
... spontaneously. 3. Make a simple redox table similar to Table 12.1 that contains all the metal atoms and metal ions that you analyzed in this investigation. Note that the ion that was able to oxidize all other metal atoms is placed at the top of the left column. In the next row, place the ion that ox ...
Class 10 - Department of Physics | Oregon State
... and Electric Potential (“voltage”) (V) In the study and harnessing of electrical energy, it is convenient to express the electrical potential energy on a per-unit-charge basis. This is called the electric potential or voltage, and is denoted by V. Electric potential is a field—a point-by-point descr ...
... and Electric Potential (“voltage”) (V) In the study and harnessing of electrical energy, it is convenient to express the electrical potential energy on a per-unit-charge basis. This is called the electric potential or voltage, and is denoted by V. Electric potential is a field—a point-by-point descr ...
Introduction
... This unit introduces some general types of reactions such as acid-base and redox reactions. Such reactions are neatly described by their balanced chemical equations. And since many of these reactions occur in water as the solvent, we have considered the nature of the species in solution. Remember th ...
... This unit introduces some general types of reactions such as acid-base and redox reactions. Such reactions are neatly described by their balanced chemical equations. And since many of these reactions occur in water as the solvent, we have considered the nature of the species in solution. Remember th ...
Document
... Covalent compounds are typically formed from nonmetals and we call them molecules Molecules is the single unit of compounds characterized by covalent bonding They tend to have low melting and boiling points. Exist as discrete molecules in the solid, liquid, and gas states. Their bonds can be charact ...
... Covalent compounds are typically formed from nonmetals and we call them molecules Molecules is the single unit of compounds characterized by covalent bonding They tend to have low melting and boiling points. Exist as discrete molecules in the solid, liquid, and gas states. Their bonds can be charact ...
Chap. 4 - Chemical Reactions
... molecular equation for the reaction. Although this equation shows the reactants and products of the reaction, it does not give a very clear picture of what truly occurs in solution. In fact, such an aqueous solution actually contains individual IONS, not molecules, in solution. By looking at the afo ...
... molecular equation for the reaction. Although this equation shows the reactants and products of the reaction, it does not give a very clear picture of what truly occurs in solution. In fact, such an aqueous solution actually contains individual IONS, not molecules, in solution. By looking at the afo ...
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry that studies chemical reactions which take place at the interface of an electrode, usually a solid metal or a semiconductor, and an ionic conductor, the electrolyte. These reactions involve electric charges moving between the electrodes and the electrolyte (or ionic species in a solution). Thus electrochemistry deals with the interaction between electrical energy and chemical change.When a chemical reaction is caused by an externally supplied current, as in electrolysis, or if an electric current is produced by a spontaneous chemical reaction as in a battery, it is called an electrochemical reaction. Chemical reactions where electrons are transferred directly between molecules and/or atoms are called oxidation-reduction or (redox) reactions. In general, electrochemistry describes the overall reactions when individual redox reactions are separate but connected by an external electric circuit and an intervening electrolyte.