chapter 21
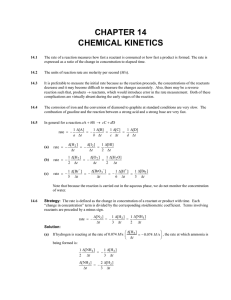
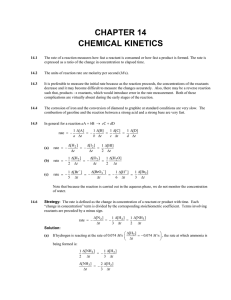
... Strategy: We are given a set of concentrations and rate data and asked to determine the order of the reaction and the initial rate for specific concentrations of X and Y. To determine the order of the reaction, we need to find the rate law for the reaction. We assume that the rate law takes the form ...
... Strategy: We are given a set of concentrations and rate data and asked to determine the order of the reaction and the initial rate for specific concentrations of X and Y. To determine the order of the reaction, we need to find the rate law for the reaction. We assume that the rate law takes the form ...
44. Find рН of formic acid solution with mass percent ω=5
... 15. Write electronic structures of Be and B atoms in the ground and excited states. What are the valences of these elements? 16. Name elements – organogens. 17. Define biogenic role of calcium and magnesium. 18. Write electronic structures of Cu and Ag atoms. What families of elements do they belong ...
... 15. Write electronic structures of Be and B atoms in the ground and excited states. What are the valences of these elements? 16. Name elements – organogens. 17. Define biogenic role of calcium and magnesium. 18. Write electronic structures of Cu and Ag atoms. What families of elements do they belong ...
Unit 6 Chemical Energy
... chemical energy from food keeps your body functioning. In each of these cases energy is transformed from one form to another. Energy transformations are the basis for all change, everywhere. Photosynthesis is a chemical process that takes radiant energy from the sun and stores it within molecules of ...
... chemical energy from food keeps your body functioning. In each of these cases energy is transformed from one form to another. Energy transformations are the basis for all change, everywhere. Photosynthesis is a chemical process that takes radiant energy from the sun and stores it within molecules of ...
Problem 1-2
... The top 15 of the 3rd round are the participants of the 4th round, a oneweek practical training. There are two written five-hour tests - one theoretical and one practical - under the same conditions as at the IChO. Here the team is selected. In this booklet all problems of the selection procedure an ...
... The top 15 of the 3rd round are the participants of the 4th round, a oneweek practical training. There are two written five-hour tests - one theoretical and one practical - under the same conditions as at the IChO. Here the team is selected. In this booklet all problems of the selection procedure an ...
Test bank questions
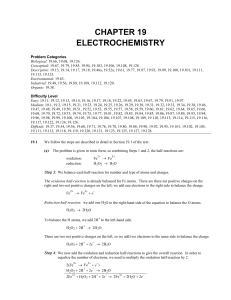
... At 250ºC, the equilibrium constant Kp for the reaction PCl5(g) PCl3(g) + Cl2(g) is 1.80. Sufficient PCl5 is put into a reaction vessel to give an initial pressure of 2.74 atm at 250ºC. Calculate the pressure of PCl5 after the system has reached equilibrium. A. 1.50 atm ...
... At 250ºC, the equilibrium constant Kp for the reaction PCl5(g) PCl3(g) + Cl2(g) is 1.80. Sufficient PCl5 is put into a reaction vessel to give an initial pressure of 2.74 atm at 250ºC. Calculate the pressure of PCl5 after the system has reached equilibrium. A. 1.50 atm ...
5 Steps
... exam there will be no surprises. Use this book in addition to your regular chemistry text. We have outlined three different study programs to prepare you for the exam. If you choose the year-long program, use it as you are taking your AP Chemistry course. It will provide additional problems in the A ...
... exam there will be no surprises. Use this book in addition to your regular chemistry text. We have outlined three different study programs to prepare you for the exam. If you choose the year-long program, use it as you are taking your AP Chemistry course. It will provide additional problems in the A ...
HW 19
... the text. Because the reactions are not run under standard-state conditions (concentrations are not 1 M), we need Nernst's equation [Equation (19.8) of the text] to calculate the emf (E) of a hypothetical galvanic cell. Remember that solids do not appear in the reaction quotient (Q) term in the Nern ...
... the text. Because the reactions are not run under standard-state conditions (concentrations are not 1 M), we need Nernst's equation [Equation (19.8) of the text] to calculate the emf (E) of a hypothetical galvanic cell. Remember that solids do not appear in the reaction quotient (Q) term in the Nern ...
Unit 4 - Chemical Equilibrium
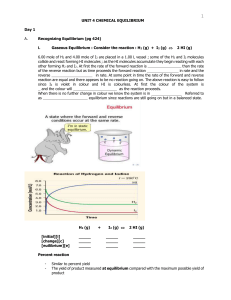
... Recognizing Equilibrium (pg 424) Gaseous Equilibrium : Consider the reaction : H2 (g) + I2 (g) ...
... Recognizing Equilibrium (pg 424) Gaseous Equilibrium : Consider the reaction : H2 (g) + I2 (g) ...
File - cpprashanths Chemistry
... Q29.Discuss oxides of nitrogen.Give structure and calculate the oxidation number of nitrogen in each of them.Arrange the oxides in order of increasing acid strength. Nitrogen forms a wide range of oxided .The oxidation number of nitrogen in these oxides varies from +1 to +5.The oxides are 1)N2O din ...
... Q29.Discuss oxides of nitrogen.Give structure and calculate the oxidation number of nitrogen in each of them.Arrange the oxides in order of increasing acid strength. Nitrogen forms a wide range of oxided .The oxidation number of nitrogen in these oxides varies from +1 to +5.The oxides are 1)N2O din ...
Covert Chemical... 2_Couvertures English chimie 4
... Experimental Activity 1: Equilibrium Systems ..................................................... 1.13 1.2 CHEMICAL REACTIONS .......................................................................................... 1.14 Equilibrium of the Reaction N2O4(g) a 2 NO2(g) .............................. ...
... Experimental Activity 1: Equilibrium Systems ..................................................... 1.13 1.2 CHEMICAL REACTIONS .......................................................................................... 1.14 Equilibrium of the Reaction N2O4(g) a 2 NO2(g) .............................. ...
20. Chemical Equilibrium
... The formula for water is not included in the examples above because dissolving is not a chemical change and, therefore, water is not consider a reactant. When substances dissolve in water they do not chemically react with it. They merely come part in the water. Later in this chapter you will study r ...
... The formula for water is not included in the examples above because dissolving is not a chemical change and, therefore, water is not consider a reactant. When substances dissolve in water they do not chemically react with it. They merely come part in the water. Later in this chapter you will study r ...
Soluble - HCC Learning Web
... How does the solubility of silver phosphate in water compare to that of silver phosphate in an acidic solution (made by adding nitric acid to the solution)? Explain. The silver phosphate is more soluble in an acidic solution. Copyright © Cengage Learning. All rights reserved ...
... How does the solubility of silver phosphate in water compare to that of silver phosphate in an acidic solution (made by adding nitric acid to the solution)? Explain. The silver phosphate is more soluble in an acidic solution. Copyright © Cengage Learning. All rights reserved ...
5. Coenzyme HAD+ is derived
... - The student will be able to explain the effect of the structure of the main classes of natural organic compounds and biopolymers on their chemical properties. -The student will be able to explain the relationship between the chemical composition, structure, properties and biological activity of su ...
... - The student will be able to explain the effect of the structure of the main classes of natural organic compounds and biopolymers on their chemical properties. -The student will be able to explain the relationship between the chemical composition, structure, properties and biological activity of su ...
5 Steps to a 5 AP Chemistry, 2008-2009 Edition
... Both of us have many years of experience in teaching introductory general chemistry at the university level. John Moore is the author of Chemistry for Dummies and he and Richard “Doc” Langley have also written Chemistry for the Utterly Confused, a guide for college/high school students. Each of us h ...
... Both of us have many years of experience in teaching introductory general chemistry at the university level. John Moore is the author of Chemistry for Dummies and he and Richard “Doc” Langley have also written Chemistry for the Utterly Confused, a guide for college/high school students. Each of us h ...
EQUILIBRIUM - SCH4U1-CCVI
... (a) Line up five clean test tubes all of the same diameter, and label them. Add 5.0 mL of 0.002 mol/L potassium thiocyanate solution to each of these five test tubes. To test tube (1) add 5.0 mL of 0.2 mol/L iron (III) nitrate solution. This tube will be used as the standard. (b) Measure 10.0 mL of ...
... (a) Line up five clean test tubes all of the same diameter, and label them. Add 5.0 mL of 0.002 mol/L potassium thiocyanate solution to each of these five test tubes. To test tube (1) add 5.0 mL of 0.2 mol/L iron (III) nitrate solution. This tube will be used as the standard. (b) Measure 10.0 mL of ...
THESE DOCTORAT DE L`UNIVERSITE DE TOULOUSE ET
... shows a greater tendency of the Mo compound to be reduced. For the W complex, on the other hand, a reversible reaction gives rise to a simple Cp*WVI ligand exchange product. The corresponding reaction for thioglycolic acid resulted in an adduct having the same stoichiometry at low substrate/W ratio, ...
... shows a greater tendency of the Mo compound to be reduced. For the W complex, on the other hand, a reversible reaction gives rise to a simple Cp*WVI ligand exchange product. The corresponding reaction for thioglycolic acid resulted in an adduct having the same stoichiometry at low substrate/W ratio, ...
c00kieee - Ritter Illustration
... α-particle causes the radiolysis of water, producing H and OH radicals as well as hydrogen peroxide. In acidic conditions, these species reduce Pu4+ and PuO2 2+ ions to give Pu3+ and PuO2 + , respectively. The radiolysis along with the disproportionation and reproportionation reactions shown in Sche ...
... α-particle causes the radiolysis of water, producing H and OH radicals as well as hydrogen peroxide. In acidic conditions, these species reduce Pu4+ and PuO2 2+ ions to give Pu3+ and PuO2 + , respectively. The radiolysis along with the disproportionation and reproportionation reactions shown in Sche ...
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry that studies chemical reactions which take place at the interface of an electrode, usually a solid metal or a semiconductor, and an ionic conductor, the electrolyte. These reactions involve electric charges moving between the electrodes and the electrolyte (or ionic species in a solution). Thus electrochemistry deals with the interaction between electrical energy and chemical change.When a chemical reaction is caused by an externally supplied current, as in electrolysis, or if an electric current is produced by a spontaneous chemical reaction as in a battery, it is called an electrochemical reaction. Chemical reactions where electrons are transferred directly between molecules and/or atoms are called oxidation-reduction or (redox) reactions. In general, electrochemistry describes the overall reactions when individual redox reactions are separate but connected by an external electric circuit and an intervening electrolyte.