updated chem cp final review key
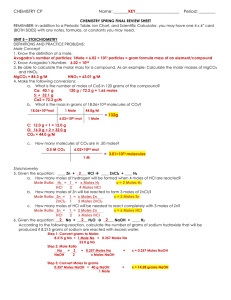
... SOLVENT: the substance that does the dissolving SOLUTE: the substance that is dissolved Examples of solutions include steel, Kool-Aid, and air. A mixture that is not a solution is oil and water. 70. Give an example of a solid, liquid, and gas solution. Identify the solute and solvent. Solid: Steel. ...
... SOLVENT: the substance that does the dissolving SOLUTE: the substance that is dissolved Examples of solutions include steel, Kool-Aid, and air. A mixture that is not a solution is oil and water. 70. Give an example of a solid, liquid, and gas solution. Identify the solute and solvent. Solid: Steel. ...
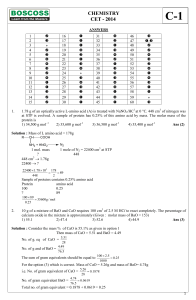
CHEMISTRY CET
... The statement that is NOT correct is 1) Energies of stationary states in hydrogen like atoms is inversely proportional to the square of the principal quantum number. 2) The radius of the first orbit of He is half that of the first orbit of hydrogen atom. 3) Angular quantum number signifies the shape ...
... The statement that is NOT correct is 1) Energies of stationary states in hydrogen like atoms is inversely proportional to the square of the principal quantum number. 2) The radius of the first orbit of He is half that of the first orbit of hydrogen atom. 3) Angular quantum number signifies the shape ...
幻灯片 1
... way different orbitals are filled is controlled by their energies (and hence their An atom consists of a very small positively charged nucleus, Electron and Nuclei different screening by other electrons) and by the Pauli exclusion principle. surrounded by negative electrons held by electrostatic att ...
... way different orbitals are filled is controlled by their energies (and hence their An atom consists of a very small positively charged nucleus, Electron and Nuclei different screening by other electrons) and by the Pauli exclusion principle. surrounded by negative electrons held by electrostatic att ...
Full-Text PDF
... where, ∆Go is standard Gibbs free energy change, n is the number of electrons, F is Faraday’s constant and ∆Eo is the standard electrical potential of the reaction. The electromotive force or EMF (∆E) is defined as the maximum potential difference of an electrochemical reaction [3]. The Gibbs free e ...
... where, ∆Go is standard Gibbs free energy change, n is the number of electrons, F is Faraday’s constant and ∆Eo is the standard electrical potential of the reaction. The electromotive force or EMF (∆E) is defined as the maximum potential difference of an electrochemical reaction [3]. The Gibbs free e ...
Regents Review Live
... tells you how many covalent bonds that atom can form with other nonmetals or how many electrons it wants to gain from metals to form an ion. The number of valence electrons in a metal tells you how many electrons the metal will lose to nonmetals to form an ion. Caution: May not work with transitio ...
... tells you how many covalent bonds that atom can form with other nonmetals or how many electrons it wants to gain from metals to form an ion. The number of valence electrons in a metal tells you how many electrons the metal will lose to nonmetals to form an ion. Caution: May not work with transitio ...
Ni recovery using KOH, NaOH, and NH4OH in the presence of
... data found in the Pourbaix diagrams. Thermodynamic considerations play an important role in leaching processes by providing basic guidance in the choice of combination of reagents and their concentration in order to obtain a favorable free energy ΔG associated with any proposed reaction. Paying part ...
... data found in the Pourbaix diagrams. Thermodynamic considerations play an important role in leaching processes by providing basic guidance in the choice of combination of reagents and their concentration in order to obtain a favorable free energy ΔG associated with any proposed reaction. Paying part ...
Worked solutions to the problems
... supervision. We have also not included specific details for handling or disposal of the products of these lab exercises, as these will vary greatly from country to country, but we know that you will employ best-practice to responsibly dispose or recycle the materials that your students use and produ ...
... supervision. We have also not included specific details for handling or disposal of the products of these lab exercises, as these will vary greatly from country to country, but we know that you will employ best-practice to responsibly dispose or recycle the materials that your students use and produ ...
Formation Mechanisms of Naphthalene and
... 3.1. Crossed Molecular Beam Setup. The crossed molecular beam technique represents an unprecedented approach to reveal the outcome of a reaction of two neutral molecules, radicals, and/or atoms in the single collision environment without wall effects.16−19 This is achieved by generating supersonic be ...
... 3.1. Crossed Molecular Beam Setup. The crossed molecular beam technique represents an unprecedented approach to reveal the outcome of a reaction of two neutral molecules, radicals, and/or atoms in the single collision environment without wall effects.16−19 This is achieved by generating supersonic be ...
chemistry - Textbooks Online
... drinking of which would endue the alchemist with immortality), and the search for the philosopher’s stone, which would turn base metals into gold. Improbable as these ideas might seem today, the alchemists continued their quests for around 2000 years and achieved some remarkable successes, even if t ...
... drinking of which would endue the alchemist with immortality), and the search for the philosopher’s stone, which would turn base metals into gold. Improbable as these ideas might seem today, the alchemists continued their quests for around 2000 years and achieved some remarkable successes, even if t ...
Unit 11 acids and bases part 1
... NH3, a BrØnsted-Lowry Base In the reaction of ammonia and water, • NH3 is the base that accept H+. • H2O is the acid that donates H+. ...
... NH3, a BrØnsted-Lowry Base In the reaction of ammonia and water, • NH3 is the base that accept H+. • H2O is the acid that donates H+. ...
DEMONSTRATION EXPERIMENTS IN PHYSICS
... topof the case andinsulated fromit with sulfuror otherdielectric. A convenient case may be made of a 3-in, length of brass tubing 4 in. in diameter, with glass windows cemented on the ends, and mountedon a suitable stand to fit the lantern. The instrument may be made into a vibrating electroscope of ...
... topof the case andinsulated fromit with sulfuror otherdielectric. A convenient case may be made of a 3-in, length of brass tubing 4 in. in diameter, with glass windows cemented on the ends, and mountedon a suitable stand to fit the lantern. The instrument may be made into a vibrating electroscope of ...
Problem Authors - PianetaChimica
... Preparatory Problems, Theoretical contaminations. The reaction of sulfuric acid with colemanite takes place in two steps: In the first step colemanite is dissolved in sulfuric acid forming the calcium(II) ion and boric acid. In the second step, calcium sulfate, formed from Ca2+ and SO42− ions, prec ...
... Preparatory Problems, Theoretical contaminations. The reaction of sulfuric acid with colemanite takes place in two steps: In the first step colemanite is dissolved in sulfuric acid forming the calcium(II) ion and boric acid. In the second step, calcium sulfate, formed from Ca2+ and SO42− ions, prec ...
Follow Along Notes - Jackson County School System
... Calculations involving equilibrium How to solve Equilibrium Problems: 1. Start with a balanced Chemical Equation 2. Write down the amounts (either concentration or pressure units) in an ICE table. 3. Shift the equilibrium by subtracting and adding x to either side to the equation. 4. Solve for x us ...
... Calculations involving equilibrium How to solve Equilibrium Problems: 1. Start with a balanced Chemical Equation 2. Write down the amounts (either concentration or pressure units) in an ICE table. 3. Shift the equilibrium by subtracting and adding x to either side to the equation. 4. Solve for x us ...
2003 AP Chemistry Form B Scoring Guidelines - AP Central
... These materials were produced by Educational Testing Service® (ETS®), which develops and administers the examinations of the Advanced Placement Program for the College Board. The College Board and Educational Testing Service (ETS) are dedicated to the principle of equal opportunity, and their progra ...
... These materials were produced by Educational Testing Service® (ETS®), which develops and administers the examinations of the Advanced Placement Program for the College Board. The College Board and Educational Testing Service (ETS) are dedicated to the principle of equal opportunity, and their progra ...
File
... N2O3, least common of nitrogen oxides, a blue liquid that readily dissociates into NO(g) and NO2(g); NO2: another odd electron species, dimerizes to form N2O4, plays a role in smog production; HNO3: important industrial chemical, used to form nitrogen-based explosives, strong acid and a very strong ...
... N2O3, least common of nitrogen oxides, a blue liquid that readily dissociates into NO(g) and NO2(g); NO2: another odd electron species, dimerizes to form N2O4, plays a role in smog production; HNO3: important industrial chemical, used to form nitrogen-based explosives, strong acid and a very strong ...
GCE Chemistry SAMs 2009 onwards pdf
... Here are his results Mass of ethanol before experiment Mass of ethanol after experiment Mass of water Temperature of water before experiment Temperature of water after experiment ...
... Here are his results Mass of ethanol before experiment Mass of ethanol after experiment Mass of water Temperature of water before experiment Temperature of water after experiment ...
Electric Potential - Little Shop of Physics
... When two quantities are proportional to each other, their ratio is constant. We can see this directly for the electric potential energy of a charged particle at point B by calculating the ratio ...
... When two quantities are proportional to each other, their ratio is constant. We can see this directly for the electric potential energy of a charged particle at point B by calculating the ratio ...
Chm 2
... b. the mass of the products is greater than the mass of reactants. c. the number of atoms in the reactants and products must change. d. energy as heat must be added to the reactants. 2. Which observation does not indicate that a chemical reaction has occurred? a. formation of a precipitate c. evolut ...
... b. the mass of the products is greater than the mass of reactants. c. the number of atoms in the reactants and products must change. d. energy as heat must be added to the reactants. 2. Which observation does not indicate that a chemical reaction has occurred? a. formation of a precipitate c. evolut ...
Personal Tutor - Macmillan Learning
... however, is the pascal (Pa). 1 atmosphere = 101, 325 Pa Since this is such a large number it is often the case that textbooks will give pressure in kilopascals (kPa). 1 atm = 101.325 kPa. ...
... however, is the pascal (Pa). 1 atmosphere = 101, 325 Pa Since this is such a large number it is often the case that textbooks will give pressure in kilopascals (kPa). 1 atm = 101.325 kPa. ...
Major 01 - KFUPM Faculty List
... Now the charge on the left is 6+, that on the right is only 3+, so to balance the charge we add 3 electrons to the left: CrO42- + 8H+ + 3e- Cr3+ + 4H2O In the oxidation we add 2H2O on the left to provide the 2 O needed on the right, which gives 4H+ on the right: Cl- + 2H2O ClO2- + 4H+ The charge ...
... Now the charge on the left is 6+, that on the right is only 3+, so to balance the charge we add 3 electrons to the left: CrO42- + 8H+ + 3e- Cr3+ + 4H2O In the oxidation we add 2H2O on the left to provide the 2 O needed on the right, which gives 4H+ on the right: Cl- + 2H2O ClO2- + 4H+ The charge ...
Chapter 12: Chemical Equilibrium • Chemical Equilibrium
... cB0 is a standard reference state = 1 mol L-1 (ideal conditions) ...
... cB0 is a standard reference state = 1 mol L-1 (ideal conditions) ...
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry that studies chemical reactions which take place at the interface of an electrode, usually a solid metal or a semiconductor, and an ionic conductor, the electrolyte. These reactions involve electric charges moving between the electrodes and the electrolyte (or ionic species in a solution). Thus electrochemistry deals with the interaction between electrical energy and chemical change.When a chemical reaction is caused by an externally supplied current, as in electrolysis, or if an electric current is produced by a spontaneous chemical reaction as in a battery, it is called an electrochemical reaction. Chemical reactions where electrons are transferred directly between molecules and/or atoms are called oxidation-reduction or (redox) reactions. In general, electrochemistry describes the overall reactions when individual redox reactions are separate but connected by an external electric circuit and an intervening electrolyte.