7.1 CHEMICAL SYSTEMS IN EQUILIBRIUM: Dynamic Equilibrium in
... The Haber Process combines nitrogen from the air with hydrogen derived mainly from natural gas (methane) into ammonia. The reaction is reversible and the production of ammonia is exothermic. ...
... The Haber Process combines nitrogen from the air with hydrogen derived mainly from natural gas (methane) into ammonia. The reaction is reversible and the production of ammonia is exothermic. ...
Chemistry_Stoichiome..
... 80. 100 mL of 10 % NaOH (w/V) is added to 100 mL of 10 % HCl (w/V). The resultant solution becomes: a) alkaline b) strongly alkaline c) acidic d) neutral 81. Calculate the molality of 1 L solution of 80 % H2SO4 (w/V), given that the density of the solution is 1.80 g mL−1 . a) 9.18 b) 8.6 c) 1.02 d) ...
... 80. 100 mL of 10 % NaOH (w/V) is added to 100 mL of 10 % HCl (w/V). The resultant solution becomes: a) alkaline b) strongly alkaline c) acidic d) neutral 81. Calculate the molality of 1 L solution of 80 % H2SO4 (w/V), given that the density of the solution is 1.80 g mL−1 . a) 9.18 b) 8.6 c) 1.02 d) ...
General and Inorganic Chemistry – Laboratory Techniques
... Knowledge of students on Chemistry at the beginning of their graduate studies is rather different. Most of the students do not have proper laboratory expertise. This educational experience prompted the faculty of the institute to compile an educational material that can help students to make themsel ...
... Knowledge of students on Chemistry at the beginning of their graduate studies is rather different. Most of the students do not have proper laboratory expertise. This educational experience prompted the faculty of the institute to compile an educational material that can help students to make themsel ...
Chap18 - Bakersfield College
... is 0.0025 M. If the concentration of oxalate ion is 1.0 x 10-7 M, do you expect calcium oxalate to precipitate? Ksp for calcium oxalate is 2.3 x 10-9. – The ion product quotient, Qc, is: ...
... is 0.0025 M. If the concentration of oxalate ion is 1.0 x 10-7 M, do you expect calcium oxalate to precipitate? Ksp for calcium oxalate is 2.3 x 10-9. – The ion product quotient, Qc, is: ...
Contents and Concepts Learning Objectives
... is 0.0025 M. If the concentration of oxalate ion is 1.0 x 10-7 M, do you expect calcium oxalate to precipitate? Ksp for calcium oxalate is 2.3 x 10-9. ...
... is 0.0025 M. If the concentration of oxalate ion is 1.0 x 10-7 M, do you expect calcium oxalate to precipitate? Ksp for calcium oxalate is 2.3 x 10-9. ...
Grossmont College Chemistry 120 Laboratory Manual 6th Edition
... data, but do not clutter the calculation section with arithmetic details. Likewise, think through and answer important questions that are intended to give you an understanding of the principles in which the experimental procedure is based as you perform the experiment. Scientists learn much by discu ...
... data, but do not clutter the calculation section with arithmetic details. Likewise, think through and answer important questions that are intended to give you an understanding of the principles in which the experimental procedure is based as you perform the experiment. Scientists learn much by discu ...
Problem 28. TUNNELING IN CHEMISTRY
... The natural tendency of any chemical reaction to proceed in a certain direction at constant temperature and pressure is determined by the sign of the Gibbs energy of the reaction, G. This is the universal principle. If G < 0, the reaction can proceed predominantly in the forward direction (a produ ...
... The natural tendency of any chemical reaction to proceed in a certain direction at constant temperature and pressure is determined by the sign of the Gibbs energy of the reaction, G. This is the universal principle. If G < 0, the reaction can proceed predominantly in the forward direction (a produ ...
Chapter 14: Chemical Kinetics
... For a reaction to occur as a result of a specific collision, the collision must have enough energy to overcome the energy barrier (activation energy). As you saw in Gases (Unit 10) and Intermolecular Forces and the Liquid State (Unit 11), the molecules in a given sample have a Boltzmann distribution ...
... For a reaction to occur as a result of a specific collision, the collision must have enough energy to overcome the energy barrier (activation energy). As you saw in Gases (Unit 10) and Intermolecular Forces and the Liquid State (Unit 11), the molecules in a given sample have a Boltzmann distribution ...
Olefin Metathesis by Molybdenum lmido Alkylidene Catalysts R2H
... metal, so the imido ligand must give up its 7r bond and bend in the transition state (equation 8). The ease of alkylidene rotation therefore varies significantly with the nature of the imido ligand. For example, although there is little difference between the rates of alkylidene ligand rotation in h ...
... metal, so the imido ligand must give up its 7r bond and bend in the transition state (equation 8). The ease of alkylidene rotation therefore varies significantly with the nature of the imido ligand. For example, although there is little difference between the rates of alkylidene ligand rotation in h ...
Fundamentals
... reactants and products. Identify any non-ionic substances and include state symbols in the equation. Cross out the spectator ions that appear on both sides of the equation and so do not take part in the reaction. Solution The full, balanced equation for the reaction is: Na2CO3 (aq) + 2HF (aq) 2NaF ...
... reactants and products. Identify any non-ionic substances and include state symbols in the equation. Cross out the spectator ions that appear on both sides of the equation and so do not take part in the reaction. Solution The full, balanced equation for the reaction is: Na2CO3 (aq) + 2HF (aq) 2NaF ...
Contents and Concepts Learning Objectives
... is 0.0025 M. If the concentration of oxalate ion is 1.0 x 10-7 M, do you expect calcium oxalate to precipitate? Ksp for calcium oxalate is 2.3 x 10-9. – The ion product quotient, Qc, is: ...
... is 0.0025 M. If the concentration of oxalate ion is 1.0 x 10-7 M, do you expect calcium oxalate to precipitate? Ksp for calcium oxalate is 2.3 x 10-9. – The ion product quotient, Qc, is: ...
Chapter 8 "Ionic versus Covalent Bonding"
... In Chapter 2 "Molecules, Ions, and Chemical Formulas", we defined a chemical bond as the force that holds atoms together in a chemical compound. We also introduced two idealized types of bonding: covalent bonding1, in which electrons are shared between atoms in a molecule or polyatomic ion, and ioni ...
... In Chapter 2 "Molecules, Ions, and Chemical Formulas", we defined a chemical bond as the force that holds atoms together in a chemical compound. We also introduced two idealized types of bonding: covalent bonding1, in which electrons are shared between atoms in a molecule or polyatomic ion, and ioni ...
g - mrnicholsscience
... • Butane gas(C4H10) burns in oxygen gas to form carbon dioxide gas and water vapor C4H10(g) + O2(g) CO2(g) + H2O(g) “forms” ...
... • Butane gas(C4H10) burns in oxygen gas to form carbon dioxide gas and water vapor C4H10(g) + O2(g) CO2(g) + H2O(g) “forms” ...
CHE 1402 Lab Manual
... Place 0.30 g of CaCO3 in a test tube and carefully insert another smaller test tube in it containing 5mL of 4 M HCl (be sure NOT to mix CaCO3 and HCl before the experiment). Assemble the apparatus illustrated in Figure 2.1 but do not attach the test tube. Be sure that tube B does not extend below th ...
... Place 0.30 g of CaCO3 in a test tube and carefully insert another smaller test tube in it containing 5mL of 4 M HCl (be sure NOT to mix CaCO3 and HCl before the experiment). Assemble the apparatus illustrated in Figure 2.1 but do not attach the test tube. Be sure that tube B does not extend below th ...
Word Pro
... This is the contents of a Quiz 1 from a few years ago in the days of Chemistry 1000. (It has been reformatted to save paper) Answer ALL of the questions in the spaces provided. The mark that you obtain for this test will be used in calculating your final grade for the course. 1. Name the following c ...
... This is the contents of a Quiz 1 from a few years ago in the days of Chemistry 1000. (It has been reformatted to save paper) Answer ALL of the questions in the spaces provided. The mark that you obtain for this test will be used in calculating your final grade for the course. 1. Name the following c ...
Chapter 3 Mass Relationships in Chemical Reactions
... 89. One way of obtaining pure sodium carbonate is through the decomposition of the mineral trona, Na5(CO3)2(HCO3)·2H2O, Na5(CO3)2(HCO3)·2H2O(s) → 5Na2CO3(s) + CO2(g) + 3H2O(g) When 1.00 metric ton (1 × 103 kg) of trona is decomposed, 0.74 metric ton of Na2CO3 is recovered. What is the percent yield ...
... 89. One way of obtaining pure sodium carbonate is through the decomposition of the mineral trona, Na5(CO3)2(HCO3)·2H2O, Na5(CO3)2(HCO3)·2H2O(s) → 5Na2CO3(s) + CO2(g) + 3H2O(g) When 1.00 metric ton (1 × 103 kg) of trona is decomposed, 0.74 metric ton of Na2CO3 is recovered. What is the percent yield ...
Document
... Fig.2 The direction of spontaneous change for a gas is toward filling its container. A gas that already fills its container does not collect spontaneously in a small region of the container. A glass cylinder containing a brown gas (upper piece of glassware in the left illustration) is attached to a ...
... Fig.2 The direction of spontaneous change for a gas is toward filling its container. A gas that already fills its container does not collect spontaneously in a small region of the container. A glass cylinder containing a brown gas (upper piece of glassware in the left illustration) is attached to a ...
Chapter 14 Review
... A. Increasing the system volume shifts the equilibrium to the right. B. Increasing the temperature shifts the equilibrium to the right. C. A catalyst speeds up the approach to equilibrium and shifts the position of equilibrium to the right. D. Decreasing the total pressure of the system shifts the e ...
... A. Increasing the system volume shifts the equilibrium to the right. B. Increasing the temperature shifts the equilibrium to the right. C. A catalyst speeds up the approach to equilibrium and shifts the position of equilibrium to the right. D. Decreasing the total pressure of the system shifts the e ...
equilibrium - chemistryatdulwich
... seemingly not starting at all, have a tendency to attain a position of equilibrium and have therefore a K value. If Kc 1 than [products] exceed [reactants] at equilibrium (products or forward reaction is favoured – equilibrium is towards the right); if Kc 1 than reaction goes almost to a vir ...
... seemingly not starting at all, have a tendency to attain a position of equilibrium and have therefore a K value. If Kc 1 than [products] exceed [reactants] at equilibrium (products or forward reaction is favoured – equilibrium is towards the right); if Kc 1 than reaction goes almost to a vir ...
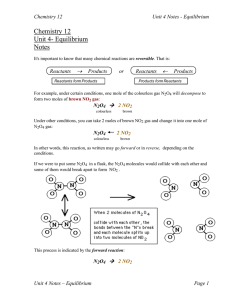
unit-4-notes-1_enthalpy-and-entropy
... the left (starting with reactants) or from the right (starting with products) Just a little term before we summarize: The word macroscopic means large scale or visible or observable. (The opposite is microscopic, which means too small to see eg. molecular level). Some macroscopic properties are tota ...
... the left (starting with reactants) or from the right (starting with products) Just a little term before we summarize: The word macroscopic means large scale or visible or observable. (The opposite is microscopic, which means too small to see eg. molecular level). Some macroscopic properties are tota ...
Chapter 12
... You are given moles of the reactant propane, and moles of the product carbon dioxide must be found. The balanced chemical equation must be written. Conversion from moles of C3H8 to moles of CO2 is required. The correct mole ratio has moles of unknown substance in the numerator and moles of known sub ...
... You are given moles of the reactant propane, and moles of the product carbon dioxide must be found. The balanced chemical equation must be written. Conversion from moles of C3H8 to moles of CO2 is required. The correct mole ratio has moles of unknown substance in the numerator and moles of known sub ...
Mole Concept - Shailendra Kumar Chemistry
... 1 g of dry green algae absorbs 4.7 × 10–3 mole of CO2 per hour by photosynthesis. If the fixed carbon atoms were all stored after photosynthesis as starch, (C6H10O5)n, how long would it take for the algae to double their own weight assuming photosynthesis takes place at a constant ...
... 1 g of dry green algae absorbs 4.7 × 10–3 mole of CO2 per hour by photosynthesis. If the fixed carbon atoms were all stored after photosynthesis as starch, (C6H10O5)n, how long would it take for the algae to double their own weight assuming photosynthesis takes place at a constant ...
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry that studies chemical reactions which take place at the interface of an electrode, usually a solid metal or a semiconductor, and an ionic conductor, the electrolyte. These reactions involve electric charges moving between the electrodes and the electrolyte (or ionic species in a solution). Thus electrochemistry deals with the interaction between electrical energy and chemical change.When a chemical reaction is caused by an externally supplied current, as in electrolysis, or if an electric current is produced by a spontaneous chemical reaction as in a battery, it is called an electrochemical reaction. Chemical reactions where electrons are transferred directly between molecules and/or atoms are called oxidation-reduction or (redox) reactions. In general, electrochemistry describes the overall reactions when individual redox reactions are separate but connected by an external electric circuit and an intervening electrolyte.