Alternative Electron Flows (Water–Water Cycle and Cyclic Electron
... (Asada 1996, Asada 1999). The first is the monodehydroascorbate radical (MDA) reductase (MDAR) (Hossain and Asada 1985). MDAR reduces the primary oxidation product of Asc, MDA, produced in the APX reaction to Asc using NAD(P)H. NAD(P)H + 2 MDA → NAD(P) + + 2 Asc (MDAR reaction) Second is dehydroascor ...
... (Asada 1996, Asada 1999). The first is the monodehydroascorbate radical (MDA) reductase (MDAR) (Hossain and Asada 1985). MDAR reduces the primary oxidation product of Asc, MDA, produced in the APX reaction to Asc using NAD(P)H. NAD(P)H + 2 MDA → NAD(P) + + 2 Asc (MDAR reaction) Second is dehydroascor ...
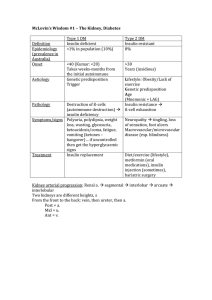
McLovin`s Wisdom #1 – The Kidney, Diabetes Type 1 DM Type 2
... 10 H+ inside from NADH and 6+ inside from FADH2. Each ATP needs a total of H+ to be produced. Electron transport chain ...
... 10 H+ inside from NADH and 6+ inside from FADH2. Each ATP needs a total of H+ to be produced. Electron transport chain ...
BCHM 562, Biochemistry II
... to the FADH2, whereby it accepts two H atoms. 3. FMN functions as prosthetic group of various oxidoreductases such as NADH dehydrogenase. 4. During catalytic cycle, the reversible interconversion of oxidized (FMN), semiquinone (FMNH•) and reduced (FMNH2) forms occurs. 5. FMN is a stronger oxidizing ...
... to the FADH2, whereby it accepts two H atoms. 3. FMN functions as prosthetic group of various oxidoreductases such as NADH dehydrogenase. 4. During catalytic cycle, the reversible interconversion of oxidized (FMN), semiquinone (FMNH•) and reduced (FMNH2) forms occurs. 5. FMN is a stronger oxidizing ...
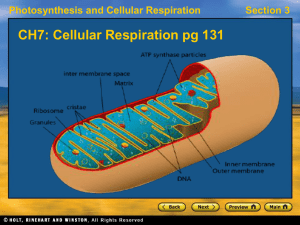
CH7Cellular-Respiration
... • In the 2nd stage, pyruvate EITHER passes through the Krebs cycle OR undergoes fermentation. – Fermentation recycles NAD+ but does not produce ATP. ...
... • In the 2nd stage, pyruvate EITHER passes through the Krebs cycle OR undergoes fermentation. – Fermentation recycles NAD+ but does not produce ATP. ...
15.2 Electrons and Chemical Bonds
... c. the number of electrons involved in a chemical bond 6. Name three elements that have an oxidation number of 3+. 7. What is the oxidation number for the elements shown in Figure 15.16? 8. When elements form a molecule, what is TRUE about the oxidation numbers of the atoms in the molecule? a. The s ...
... c. the number of electrons involved in a chemical bond 6. Name three elements that have an oxidation number of 3+. 7. What is the oxidation number for the elements shown in Figure 15.16? 8. When elements form a molecule, what is TRUE about the oxidation numbers of the atoms in the molecule? a. The s ...
4.1 PPT- Atomic Theory and Bonding
... up end to end = 1 cm An atom = proton(s) + neutron(s) + electron(s) ...
... up end to end = 1 cm An atom = proton(s) + neutron(s) + electron(s) ...
File - Groby Bio Page
... This includes photosynthetic organisms – they are unique as they both respire and photosynthesise. Unlike photosynthesis, respiration is exothermic. Both photosynthesis and respiration are interrelated and are important in cycling carbon dioxide and oxygen in the atmosphere. Why is it that plants ca ...
... This includes photosynthetic organisms – they are unique as they both respire and photosynthesise. Unlike photosynthesis, respiration is exothermic. Both photosynthesis and respiration are interrelated and are important in cycling carbon dioxide and oxygen in the atmosphere. Why is it that plants ca ...
Chapter 7 How Cells Release Chemical energy
... and a few steps before it, occurs inside mitochondria. The 2 pyruvates are broken down to CO2, which leaves the cell. During the reactions, 8 NAD+ and 2 FAD pick up electrons and hydrogen atoms, so 8 NADH and 2 FADH2 form. 2 ATP also form. The third and final stage, electron transfer phosphorylation ...
... and a few steps before it, occurs inside mitochondria. The 2 pyruvates are broken down to CO2, which leaves the cell. During the reactions, 8 NAD+ and 2 FAD pick up electrons and hydrogen atoms, so 8 NADH and 2 FADH2 form. 2 ATP also form. The third and final stage, electron transfer phosphorylation ...
Cellular Respiration
... – Passes the electrons to the electron transport chain – Electrons are ultimately passed to a molecule of oxygen (Final electron acceptor) ...
... – Passes the electrons to the electron transport chain – Electrons are ultimately passed to a molecule of oxygen (Final electron acceptor) ...
ATP and Energy, Enzymes - Jocha
... Rate of product formation is defined by the enzyme characteristics With huge amounts of substrate present the rate of product generation can only be increased by adding more ...
... Rate of product formation is defined by the enzyme characteristics With huge amounts of substrate present the rate of product generation can only be increased by adding more ...
QM/MM Study of Cytochrome P450 BM3
... F87 plays a “gatekeeper” role in that its bulky side chain must be rotated in order to allow for substrate binding. ...
... F87 plays a “gatekeeper” role in that its bulky side chain must be rotated in order to allow for substrate binding. ...
Cellular Respiration
... ETC at different points; this is because the electrons in NADH have more energy than the electrons in FADH2 ...
... ETC at different points; this is because the electrons in NADH have more energy than the electrons in FADH2 ...
Cellular Respiration - Spokane Public Schools
... – Passes the electrons to the electron transport chain – Electrons are ultimately passed to a molecule of oxygen (Final electron acceptor) ...
... – Passes the electrons to the electron transport chain – Electrons are ultimately passed to a molecule of oxygen (Final electron acceptor) ...
ch_02 - studylib.net
... a watery environment will always self-assemble into forms that keep the fatty acid tails away from water like the lipid bilayers found in the membranes of nearly all cells. Waxes contain one long-chain fatty acid linked covalently to a long-chain alcohol by an ester bond. They are ...
... a watery environment will always self-assemble into forms that keep the fatty acid tails away from water like the lipid bilayers found in the membranes of nearly all cells. Waxes contain one long-chain fatty acid linked covalently to a long-chain alcohol by an ester bond. They are ...
Computational analysis on photo-electron transfer processes of
... Our earlier studies on carbazolo-carbazole derivatives had proven that they are efficient organic dye sensitizers for applications in molecular photovoltaics. Analysis on photonic -electron transfer mechanisms of these molecular structures were not found in the literature. Carbazolo -carbazole (CC) ...
... Our earlier studies on carbazolo-carbazole derivatives had proven that they are efficient organic dye sensitizers for applications in molecular photovoltaics. Analysis on photonic -electron transfer mechanisms of these molecular structures were not found in the literature. Carbazolo -carbazole (CC) ...
F214 Content checklist
... State that light energy is used during photosynthesis to produce complex organic molecules. Explain how respiration in plants and animals depends upon the products of photosynthesis. State that, in plants, photosynthesis is a two-stage process taking place in chloroplasts. Explain, with the aid of d ...
... State that light energy is used during photosynthesis to produce complex organic molecules. Explain how respiration in plants and animals depends upon the products of photosynthesis. State that, in plants, photosynthesis is a two-stage process taking place in chloroplasts. Explain, with the aid of d ...
chapter 9 cellular respiration: harvesting
... ATP accounting so far… • Glycolysis 2 ATP • Kreb’s cycle 2 ATP • Life takes a lot of energy to run, need to extract more energy than 4 ATP! There’s got to be a better way! I need a lot more ATP! ...
... ATP accounting so far… • Glycolysis 2 ATP • Kreb’s cycle 2 ATP • Life takes a lot of energy to run, need to extract more energy than 4 ATP! There’s got to be a better way! I need a lot more ATP! ...
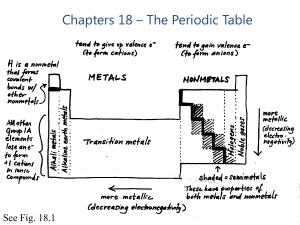
Chapters 18 – The Periodic Table
... from SO2 over V2O5 catalysts, is then converted to sulfuric acid. Sulfuric acid is the cheapest strong acid and is so widely used in industry that its production level is an indicator of a nation’s economic strength. Strong dehydrating agent that removes water from any organic source. 4. Sulfur hexa ...
... from SO2 over V2O5 catalysts, is then converted to sulfuric acid. Sulfuric acid is the cheapest strong acid and is so widely used in industry that its production level is an indicator of a nation’s economic strength. Strong dehydrating agent that removes water from any organic source. 4. Sulfur hexa ...
Solving Biochemistry`s Biggest Mystery: How We Produce Energy
... class. Oxidoreductases catalyze oxidation and reduction reactions. This class can be subdivided into reductases and oxidases. Enzymes called “dehydrogenases” are reductases. Their function is to catalyze the removal of a pair of electrons (and usually one or two protons) from another molecule. The n ...
... class. Oxidoreductases catalyze oxidation and reduction reactions. This class can be subdivided into reductases and oxidases. Enzymes called “dehydrogenases” are reductases. Their function is to catalyze the removal of a pair of electrons (and usually one or two protons) from another molecule. The n ...
1 - u.arizona.edu
... rate of flux in a particular direction is called the steady state - this is not the same as equilibrium, which is defined as the state in which the forward and backward reaction rates are the same; no net flux in either direction; no physiological free energy difference; ratio of products to substra ...
... rate of flux in a particular direction is called the steady state - this is not the same as equilibrium, which is defined as the state in which the forward and backward reaction rates are the same; no net flux in either direction; no physiological free energy difference; ratio of products to substra ...
(1/V m C) +
... enhancement is greatest when the Plasmon frequency is in resonance with the radiation. In order for scattering to occur, the plasmon oscillations must be perpendicular to the surface. If they are in plane with the surface, no scattering will occur. It is because of this requirement that roughened su ...
... enhancement is greatest when the Plasmon frequency is in resonance with the radiation. In order for scattering to occur, the plasmon oscillations must be perpendicular to the surface. If they are in plane with the surface, no scattering will occur. It is because of this requirement that roughened su ...
Ch. 07 PhotoSynthesis: Using Light to Make Food
... How Photosystems Harvest Light Energy • When a pigment molecule absorbs a photon, one of the pigment’s electrons gains energy: electrons has been raised from a ground state to an excited state • The excited state is very unstable, and generally the electron loses the excess energy and falls back to ...
... How Photosystems Harvest Light Energy • When a pigment molecule absorbs a photon, one of the pigment’s electrons gains energy: electrons has been raised from a ground state to an excited state • The excited state is very unstable, and generally the electron loses the excess energy and falls back to ...
Chapter 9: Cellular Respiration Notes
... • Before the cycle can begin, pyruvate must be converted to 2 carbon molecule, which links the cycle to glycolysis, releasing CO2, and making ATP from ADP and a phosphate group. • Electrons are extracted in a series of cycle reactions to be carried by NADH and FADH2 to the electron transport chain. ...
... • Before the cycle can begin, pyruvate must be converted to 2 carbon molecule, which links the cycle to glycolysis, releasing CO2, and making ATP from ADP and a phosphate group. • Electrons are extracted in a series of cycle reactions to be carried by NADH and FADH2 to the electron transport chain. ...
Cellular Respiration
... Oxidative phosphorylation • Electron-carrying redox molecules (NADH and FADH2) transfer their electrons to the e- transport chain • The e- transport chain uses the electrons to create a proton gradient across the ...
... Oxidative phosphorylation • Electron-carrying redox molecules (NADH and FADH2) transfer their electrons to the e- transport chain • The e- transport chain uses the electrons to create a proton gradient across the ...