- thevignanam
... fall into three categories: 1) Anabolic pathways are those involved in the synthesis of compounds. Anabolic pathways are endergonic. (2) Catabolic pathways are involved in the breakdown of larger molecules, commonly involving oxidative reactions; they are exergonic, producing reducing equivalents an ...
... fall into three categories: 1) Anabolic pathways are those involved in the synthesis of compounds. Anabolic pathways are endergonic. (2) Catabolic pathways are involved in the breakdown of larger molecules, commonly involving oxidative reactions; they are exergonic, producing reducing equivalents an ...
Jordan University of Science and Technology Faculty of Medicine
... a. Does the Michaelis-Menten model describe the behavior of allosteric enzymes? b. What are the models for the behavior of allosteric enzymes? (Concerted Model) c. How does phosphorylation of specific residues regulate enzyme activity? d. What are zymogens, and how do they control enzyme activity? e ...
... a. Does the Michaelis-Menten model describe the behavior of allosteric enzymes? b. What are the models for the behavior of allosteric enzymes? (Concerted Model) c. How does phosphorylation of specific residues regulate enzyme activity? d. What are zymogens, and how do they control enzyme activity? e ...
AP BIOLOGY Ch. 2 Objectives “Chemistry”
... 13. Explain how a peptide bond forms between two amino acids. 14. List and describe the four major components of an amino acid. Explain how amino acids may be grouped according to the physical and chemical properties of the R group. 15. Explain what determines protein conformation and why it is impo ...
... 13. Explain how a peptide bond forms between two amino acids. 14. List and describe the four major components of an amino acid. Explain how amino acids may be grouped according to the physical and chemical properties of the R group. 15. Explain what determines protein conformation and why it is impo ...
123 - Jordan University of Science and Technology
... a. Does the Michaelis-Menten model describe the behavior of allosteric enzymes? b. What are the models for the behavior of allosteric enzymes? (Concerted Model) c. How does phosphorylation of specific residues regulate enzyme activity? d. What are zymogens, and how do they control enzyme activity? e ...
... a. Does the Michaelis-Menten model describe the behavior of allosteric enzymes? b. What are the models for the behavior of allosteric enzymes? (Concerted Model) c. How does phosphorylation of specific residues regulate enzyme activity? d. What are zymogens, and how do they control enzyme activity? e ...
123 biochemistry - Jordan University of Science and Technology
... a. Does the Michaelis-Menten model describe the behavior of allosteric enzymes? b. What are the models for the behavior of allosteric enzymes? (Concerted Model) c. How does phosphorylation of specific residues regulate enzyme activity? d. What are zymogens, and how do they control enzyme activity? e ...
... a. Does the Michaelis-Menten model describe the behavior of allosteric enzymes? b. What are the models for the behavior of allosteric enzymes? (Concerted Model) c. How does phosphorylation of specific residues regulate enzyme activity? d. What are zymogens, and how do they control enzyme activity? e ...
U4L21 fuel oxidation - The University of Sydney
... • There are specific transporters for FA – CD36 moves to the cell surface whenever there is a need to take up FA at a rapid rate • FA is carried on FABP (fatty acid binding protein) in cytoplasm ...
... • There are specific transporters for FA – CD36 moves to the cell surface whenever there is a need to take up FA at a rapid rate • FA is carried on FABP (fatty acid binding protein) in cytoplasm ...
photosynthesis
... The glucose produced in photosynthesis may be converted to insoluble starch. Start does not attract water by osmosis. Plant cells use some of the photosynthetic glucose for respiration. In addition, nitrates, absorbed by the roots, are needed for healthy growth. Any 1 of light, temperature and carbo ...
... The glucose produced in photosynthesis may be converted to insoluble starch. Start does not attract water by osmosis. Plant cells use some of the photosynthetic glucose for respiration. In addition, nitrates, absorbed by the roots, are needed for healthy growth. Any 1 of light, temperature and carbo ...
factors in photosynthesis
... The glucose produced in photosynthesis may be converted to insoluble starch. Start does not attract water by osmosis. Plant cells use some of the photosynthetic glucose for respiration. In addition, nitrates, absorbed by the roots, are needed for healthy growth. Any 1 of light, temperature and carbo ...
... The glucose produced in photosynthesis may be converted to insoluble starch. Start does not attract water by osmosis. Plant cells use some of the photosynthetic glucose for respiration. In addition, nitrates, absorbed by the roots, are needed for healthy growth. Any 1 of light, temperature and carbo ...
Exam 3 Review
... pyruvate oxidation, citric acid cycle, and electron transport chain/oxidative phosphorylation). Also, be able to determine the ATP yield from a molecule of pyruvate and a molecule of acetyl-CoA. 9. Explain why glucose is immediately phosphorylated to become glucose-6-phosphate when it enters a ...
... pyruvate oxidation, citric acid cycle, and electron transport chain/oxidative phosphorylation). Also, be able to determine the ATP yield from a molecule of pyruvate and a molecule of acetyl-CoA. 9. Explain why glucose is immediately phosphorylated to become glucose-6-phosphate when it enters a ...
04_Sports_training
... In general, there is an inverse relationship between a given energy system’s maximum rate of ATP production (i.e., ATP produced per unit of time) and the total amount of ATP it is capable of producing over a long time. As a result, the phosphagen energy system primarily supplies ATP for highintensit ...
... In general, there is an inverse relationship between a given energy system’s maximum rate of ATP production (i.e., ATP produced per unit of time) and the total amount of ATP it is capable of producing over a long time. As a result, the phosphagen energy system primarily supplies ATP for highintensit ...
Jordan University of Science and Technology Faculty of Medicine
... e. What is the Fluid-Mosaic model of membrane structure? f. What are some of the functions of membranes? g. What are the lipid-soluble vitamins, and what are their functions? h. What are prostaglandins and leukotrienes, and what do they have to do with lipids? ...
... e. What is the Fluid-Mosaic model of membrane structure? f. What are some of the functions of membranes? g. What are the lipid-soluble vitamins, and what are their functions? h. What are prostaglandins and leukotrienes, and what do they have to do with lipids? ...
Jordan University of Science and Technology
... e. What is the Fluid-Mosaic model of membrane structure? f. What are some of the functions of membranes? g. What are the lipid-soluble vitamins, and what are their functions? h. What are prostaglandins and leukotrienes, and what do they have to do with lipids? ...
... e. What is the Fluid-Mosaic model of membrane structure? f. What are some of the functions of membranes? g. What are the lipid-soluble vitamins, and what are their functions? h. What are prostaglandins and leukotrienes, and what do they have to do with lipids? ...
Active Transport of Amino Acids by Membrane
... The vesicle preparation described here was active primarily with the nonphysiological electron donors, ascorbate-TMPI) or ascorbate-PMS. Relatively little stimulation of transport was observed with any of the potentially physiological electron donors tested. The reason for this is not known. Effecti ...
... The vesicle preparation described here was active primarily with the nonphysiological electron donors, ascorbate-TMPI) or ascorbate-PMS. Relatively little stimulation of transport was observed with any of the potentially physiological electron donors tested. The reason for this is not known. Effecti ...
You Light Up My Life
... Electrons from first-stage reactions are delivered to NAD+ in mitochondria ...
... Electrons from first-stage reactions are delivered to NAD+ in mitochondria ...
Chapter 9b - Richsingiser.com
... Biological Membranes? • Transport processes are vital for all life forms • Cells must be able to import nutrients and export waste • All cells maintain concentration gradients of various metabolites across the plasma membrane and other intracellular membranes • Many transport processes involve movem ...
... Biological Membranes? • Transport processes are vital for all life forms • Cells must be able to import nutrients and export waste • All cells maintain concentration gradients of various metabolites across the plasma membrane and other intracellular membranes • Many transport processes involve movem ...
Cell Metabolism
... less than 1 cal of energy 1 to 2 cal of energy 7. 3 Kcal of energy 7. 3 cal of energy different amounts of energy depending on the cell ...
... less than 1 cal of energy 1 to 2 cal of energy 7. 3 Kcal of energy 7. 3 cal of energy different amounts of energy depending on the cell ...
Chapter 3: Energy, Catalysis, and Biosynthesis
... 13-29 For each of the following sentences, fill in the blanks with the best word or phrase selected from the list below. Not all words or phrases will be used; each word or phrase may be used more than once. Oxidative phosphorylation is a process that occurs in the __________________ of mitochondria ...
... 13-29 For each of the following sentences, fill in the blanks with the best word or phrase selected from the list below. Not all words or phrases will be used; each word or phrase may be used more than once. Oxidative phosphorylation is a process that occurs in the __________________ of mitochondria ...
Lecture 1 Course overview and intro to enzymes
... cycling electrons for H+ gradient harvesting electrons for reducing equivalents Chloroplast photosystem: the Z scheme system II water splitting and proton gradient system I making reducing equivalents cytb6f: linking photosystems II and I water splitting complex: where those e come from Chloroplast ...
... cycling electrons for H+ gradient harvesting electrons for reducing equivalents Chloroplast photosystem: the Z scheme system II water splitting and proton gradient system I making reducing equivalents cytb6f: linking photosystems II and I water splitting complex: where those e come from Chloroplast ...
Poster
... aspirin? The answers lie in a study of cytochrome P450s (CYP101), a family of enzymes that are responsible for the transformation of vitamins, pharmaceuticals and other foreign chemicals into soluble and readily excreted molecules. This goal is achieved primarily by hydroxylation reactions, which oc ...
... aspirin? The answers lie in a study of cytochrome P450s (CYP101), a family of enzymes that are responsible for the transformation of vitamins, pharmaceuticals and other foreign chemicals into soluble and readily excreted molecules. This goal is achieved primarily by hydroxylation reactions, which oc ...
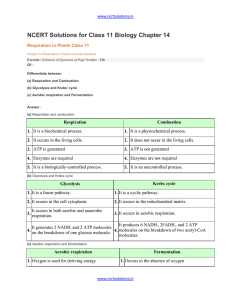
chapter_14_respiration_in_plants
... FMN. In a similar manner, FADH2 (complex II) generated during citric acid cycle gets transferred to ubiquinone. The electrons from ubiquinone are received by cytochrome bc1 (complex III) and further get transferred to cytochrome c. The cytochrome c acts as a mobile carrier between complex III and cy ...
... FMN. In a similar manner, FADH2 (complex II) generated during citric acid cycle gets transferred to ubiquinone. The electrons from ubiquinone are received by cytochrome bc1 (complex III) and further get transferred to cytochrome c. The cytochrome c acts as a mobile carrier between complex III and cy ...
ch 9ppt
... cytosol into the mitochondria and introduces it into the citric acid cycle. How the process of chemiosmosis utilizes the electrons from NADH and FADH2 to produce ATP. ...
... cytosol into the mitochondria and introduces it into the citric acid cycle. How the process of chemiosmosis utilizes the electrons from NADH and FADH2 to produce ATP. ...
Lecture1
... The energy stored in the chlorophyll goes to break up water molecule (Proteolysis/photolysis of water) to give energized electron and oxygen. The energy of the electron is used to synthesis ATP. The energized electrons are accepted by electron acceptor and are eventually used to reduce NADP to NADP ...
... The energy stored in the chlorophyll goes to break up water molecule (Proteolysis/photolysis of water) to give energized electron and oxygen. The energy of the electron is used to synthesis ATP. The energized electrons are accepted by electron acceptor and are eventually used to reduce NADP to NADP ...
ATP
... After: (1) Kritsky MS; Lyudnikova TA; Mironov EA; Moskaleva IV. The UV radiation-driven reduction of pterins in aqueous solution. J Photochem Photobiol B-Biol 1997 39(1) 43-48 (2) Lyudnikova TA; Dashina OA; Telegina TA; Kritsky MS. Investigation of the photochemical properties of biopterin and its r ...
... After: (1) Kritsky MS; Lyudnikova TA; Mironov EA; Moskaleva IV. The UV radiation-driven reduction of pterins in aqueous solution. J Photochem Photobiol B-Biol 1997 39(1) 43-48 (2) Lyudnikova TA; Dashina OA; Telegina TA; Kritsky MS. Investigation of the photochemical properties of biopterin and its r ...