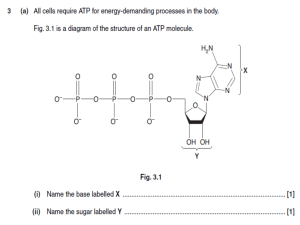
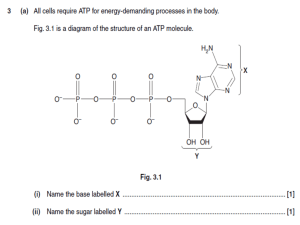
Chapter 5
... – resulting 5-carbon α-ketoglutarate undergoes removal of electrons and H+ and release of CO2 – succinyl-CoA (4-carbon product) converted in four steps to oxaloacetate – electrons and H+ transferred to form FADH2 and NADH – ATP produced ...
... – resulting 5-carbon α-ketoglutarate undergoes removal of electrons and H+ and release of CO2 – succinyl-CoA (4-carbon product) converted in four steps to oxaloacetate – electrons and H+ transferred to form FADH2 and NADH – ATP produced ...
Anaerobic Respiration
... • This is the hydrogen acceptor, not pyruvate. • Pyruvate is produced as a result of glycolysis but is decarboxylated to ethanal • Ethanal is reduced to ethanol. This occurs because of alcohol dehydrogenase enzymes. • To stop a build up of ethanol in human liver cells, alcohol dehydrogenase adds hyd ...
... • This is the hydrogen acceptor, not pyruvate. • Pyruvate is produced as a result of glycolysis but is decarboxylated to ethanal • Ethanal is reduced to ethanol. This occurs because of alcohol dehydrogenase enzymes. • To stop a build up of ethanol in human liver cells, alcohol dehydrogenase adds hyd ...
Answer Key 2 - UC Davis Plant Sciences
... You observe that all the cytochrome c is in the oxidized state, but that all the other diffusible electron carriers are in their reduced states (i.e., CoQH2, NADH, and FADH2). Which complex is inhibited? Write the name of the complex and write the balanced reaction catalyzed by this complex. (3 pts) ...
... You observe that all the cytochrome c is in the oxidized state, but that all the other diffusible electron carriers are in their reduced states (i.e., CoQH2, NADH, and FADH2). Which complex is inhibited? Write the name of the complex and write the balanced reaction catalyzed by this complex. (3 pts) ...
Anaerobic Respiration
... • This is the hydrogen acceptor, not pyruvate. • Pyruvate is produced as a result of glycolysis but is decarboxylated to ethanal • Ethanal is reduced to ethanol. This occurs because of alcohol dehydrogenase enzymes. • To stop a build up of ethanol in human liver cells, alcohol dehydrogenase adds hyd ...
... • This is the hydrogen acceptor, not pyruvate. • Pyruvate is produced as a result of glycolysis but is decarboxylated to ethanal • Ethanal is reduced to ethanol. This occurs because of alcohol dehydrogenase enzymes. • To stop a build up of ethanol in human liver cells, alcohol dehydrogenase adds hyd ...
DO NOW: How are photosynthesis and cellular respiration related?
... replaces the process of aerobic respiration so that the cell can have a continual source of energy, even in the absence of oxygen. •However this shift is only temporary and cells need oxygen for sustained activity. ...
... replaces the process of aerobic respiration so that the cell can have a continual source of energy, even in the absence of oxygen. •However this shift is only temporary and cells need oxygen for sustained activity. ...
chapter8 - Teacherpage
... E Enzymes transfer a phosphate group from each of two intermediates to ADP. Two more ATP have formed by substrate-level phosphorylation. Two molecules of pyruvate form at this last reaction step. F Summing up, glycolysis yields two NADH, two ATP (net), and two pyruvate for each glucose molecule. Fig ...
... E Enzymes transfer a phosphate group from each of two intermediates to ADP. Two more ATP have formed by substrate-level phosphorylation. Two molecules of pyruvate form at this last reaction step. F Summing up, glycolysis yields two NADH, two ATP (net), and two pyruvate for each glucose molecule. Fig ...
Chapter 6
... 4. Aerobic cellular respiration occurs in three stages. Name these and briefly describe what happens in each stage. Glycolysis results in a glucose molecule being broken down to two pyruvic acid molecules. Initially 2 ATPs are used, but ultimately 4 ATPs are produced. NAD+ is also oxidized to NADH ...
... 4. Aerobic cellular respiration occurs in three stages. Name these and briefly describe what happens in each stage. Glycolysis results in a glucose molecule being broken down to two pyruvic acid molecules. Initially 2 ATPs are used, but ultimately 4 ATPs are produced. NAD+ is also oxidized to NADH ...
Sugar
... • 10/4 = 2.5 for electrons entering as NADH • For electrons entering as succinate (FADH2), about 6 H+ pumped per electron pair to oxygen ...
... • 10/4 = 2.5 for electrons entering as NADH • For electrons entering as succinate (FADH2), about 6 H+ pumped per electron pair to oxygen ...
Energy For Muscular Activity - South Carleton HS Physical
... 1. What are the differences between the 3 energy systems? 2. List one advantage and one disadvantage of each of the 3 energy systems. 3. Give an example of three activities or sports that use each of (a) the high energy phosphate system, (b) the anaerobic glycolytic system, and (c) the aerobic oxida ...
... 1. What are the differences between the 3 energy systems? 2. List one advantage and one disadvantage of each of the 3 energy systems. 3. Give an example of three activities or sports that use each of (a) the high energy phosphate system, (b) the anaerobic glycolytic system, and (c) the aerobic oxida ...
Green: - WordPress.com
... linked by single bonds. Every carotene has 40 carbon atoms but a slightly different number of hydrogen atoms. http://www.chemspider.com/ImageView.aspx?id=4444129&mode=3d ...
... linked by single bonds. Every carotene has 40 carbon atoms but a slightly different number of hydrogen atoms. http://www.chemspider.com/ImageView.aspx?id=4444129&mode=3d ...
ppt
... electron is NOT recycled back to PSI. For the process to continue, an electron must be stripped from another molecule and transferred to the PS to be excited by sunlight… ...
... electron is NOT recycled back to PSI. For the process to continue, an electron must be stripped from another molecule and transferred to the PS to be excited by sunlight… ...
C4 Photosynthesis
... (Figure 3-2). Suspended within the stroma are stacks of pancakelike membranes. Individual membrane layers (the “pancakes”) are thylakoids; an entire stack of thylakoids is a granum (plural, grana). Within the thylakoids are the light-absorbing pigments and enzymes for the light-dependent reactions. ...
... (Figure 3-2). Suspended within the stroma are stacks of pancakelike membranes. Individual membrane layers (the “pancakes”) are thylakoids; an entire stack of thylakoids is a granum (plural, grana). Within the thylakoids are the light-absorbing pigments and enzymes for the light-dependent reactions. ...
Cell Size and Shape
... NADH and FADH2 releases the hydrogen atoms trapped during glycolysis & the citric acid cycle Thus, NADH/FADH2 becomes NAD/FAD again ...
... NADH and FADH2 releases the hydrogen atoms trapped during glycolysis & the citric acid cycle Thus, NADH/FADH2 becomes NAD/FAD again ...
chapter 14
... In the following flow chart, replace the symbols a,b,c and d with appropriate terms. Briefly explain the process and give any two application of it. ...
... In the following flow chart, replace the symbols a,b,c and d with appropriate terms. Briefly explain the process and give any two application of it. ...
PPT CH 22
... • Is the oxygen-requiring breakdown of food and production of ATP • Process is also called oxidative phosphorylation as energy from oxidative reactions is used to phosphorylate ADP making ATP • Performed by enzymes in the mitochondrial matrix • Three oxidations transfer hydride to NAD+ or FAD • Elec ...
... • Is the oxygen-requiring breakdown of food and production of ATP • Process is also called oxidative phosphorylation as energy from oxidative reactions is used to phosphorylate ADP making ATP • Performed by enzymes in the mitochondrial matrix • Three oxidations transfer hydride to NAD+ or FAD • Elec ...
Anaerobic Fermentation
... Your body doesn't always get enough oxygen during excercise... *Body compensates for the lack of oxygen by a process called Anaerobic fermentation that carries out a series of chemical reactions that produce ATP from glucose in the absence of O 2 *Fermentation allows glycolysis to continue maki ...
... Your body doesn't always get enough oxygen during excercise... *Body compensates for the lack of oxygen by a process called Anaerobic fermentation that carries out a series of chemical reactions that produce ATP from glucose in the absence of O 2 *Fermentation allows glycolysis to continue maki ...
Document
... oxygen as final electron acceptor. • ATP formation uses proton motive force - voltage across membrane (ion gradient) that results from high [H+] in intermembrane space. ...
... oxygen as final electron acceptor. • ATP formation uses proton motive force - voltage across membrane (ion gradient) that results from high [H+] in intermembrane space. ...
03_Membrane rest potential. Generation and radiation action
... This allows valinomycin to enter the lipid core of the bilayer, to solubilize K+ within this hydrophobic milieu. Crystal structure (at Virtual Museum of Minerals & Molecules). ...
... This allows valinomycin to enter the lipid core of the bilayer, to solubilize K+ within this hydrophobic milieu. Crystal structure (at Virtual Museum of Minerals & Molecules). ...
Cellular respiration
... Membrane Reactions Membrane reactions have two purposes: to further oxidize NADH and FADH2 and transfer their energy to ATP to regenerate NAD+ and FAD and make them available again to earlier reaction steps ...
... Membrane Reactions Membrane reactions have two purposes: to further oxidize NADH and FADH2 and transfer their energy to ATP to regenerate NAD+ and FAD and make them available again to earlier reaction steps ...
document
... 6.6 Redox reactions release energy when electrons “fall” from a hydrogen carrier to oxygen • NADH delivers electrons to a series of electron carriers in an electron transport chain – As electrons move from carrier to carrier, their energy is released in small quantities ...
... 6.6 Redox reactions release energy when electrons “fall” from a hydrogen carrier to oxygen • NADH delivers electrons to a series of electron carriers in an electron transport chain – As electrons move from carrier to carrier, their energy is released in small quantities ...
Worked Example 20.1
... Acetyl-CoA is the substrate for the cycle. Along with GDP and CoA, the oxidized coenzymes NAD + and FAD might also be considered substrates, despite their status as coenzymes, because these substances cycle between the reduced and oxidized states. The products of the cycle are CO2 and the energy-ric ...
... Acetyl-CoA is the substrate for the cycle. Along with GDP and CoA, the oxidized coenzymes NAD + and FAD might also be considered substrates, despite their status as coenzymes, because these substances cycle between the reduced and oxidized states. The products of the cycle are CO2 and the energy-ric ...
Chemistry of Life
... b. The number of _________________ in an atom represent its __________________. c. If an atom has 4 protons, it will have __________electrons. 4. Atoms of the same element that differ in the number of neutrons they contain are known as __________________________. a. They are identified by their ____ ...
... b. The number of _________________ in an atom represent its __________________. c. If an atom has 4 protons, it will have __________electrons. 4. Atoms of the same element that differ in the number of neutrons they contain are known as __________________________. a. They are identified by their ____ ...
... summarised below (see also Refs 7,8). Natta and co-workers prepared polyacetylene in 1958 by polymerising acetylene in hexane using Et3Al/Ti(OPr)4 (Et= ethyl, Pr=propyl) as a catalyst. Though the resulting material was highly crystalline and of regular structure, it was a black, air-sensitive, infus ...
Cellular Respiration - Esperanza High School
... (Carrying electrons from, food) Mitochondrial matrix ...
... (Carrying electrons from, food) Mitochondrial matrix ...