Metabolism Stages Figure
... The Three Stages of Catabolism Stage I: Hydrolysis of Macromolecules into Building Blocks ...
... The Three Stages of Catabolism Stage I: Hydrolysis of Macromolecules into Building Blocks ...
Lecture-Intro to metabolism - Creighton Chemistry Webserver
... 2. Metabolic reactions occur in many small steps - “pathways” Why so many steps? Many enzymes in series result in complex transformation Energy released at a small step can be captured efficiently Cells mainly use one type of energy packet (ATP) to fuel any small step Different metabolic processes c ...
... 2. Metabolic reactions occur in many small steps - “pathways” Why so many steps? Many enzymes in series result in complex transformation Energy released at a small step can be captured efficiently Cells mainly use one type of energy packet (ATP) to fuel any small step Different metabolic processes c ...
NADH - Cloudfront.net
... Electron Transport Chain • A chemical reaction that uses high energy electrons made in the Krebs cycle to convert ADP into ATP. • Aerobic – means with oxygen • Anaerobic – means without oxygen ...
... Electron Transport Chain • A chemical reaction that uses high energy electrons made in the Krebs cycle to convert ADP into ATP. • Aerobic – means with oxygen • Anaerobic – means without oxygen ...
Option B Rev A
... Fate of Lactate: Not the bad guy it was always made out to be! Lactate accumulates in blood as rate of muscle production exceeds rate of clearance/utilization Lactate formation is NOT the cause of the lowering of muscle pH that occurs during exercise – Lactate accumulation occurs simultaneously ...
... Fate of Lactate: Not the bad guy it was always made out to be! Lactate accumulates in blood as rate of muscle production exceeds rate of clearance/utilization Lactate formation is NOT the cause of the lowering of muscle pH that occurs during exercise – Lactate accumulation occurs simultaneously ...
Fermentation - cloudfront.net
... Steps? Kreb’s cycle and electron transport chain Glycolysis: -- In the cytoplasm -- Glucose is split into 2 pyruvate -- 2 ATP created ...
... Steps? Kreb’s cycle and electron transport chain Glycolysis: -- In the cytoplasm -- Glucose is split into 2 pyruvate -- 2 ATP created ...
Cellular Respiration
... Extracts energy from NADH & FADH2 Passes electrons from higher to lower energy states Produces 32 or 34 molecules of ATP ...
... Extracts energy from NADH & FADH2 Passes electrons from higher to lower energy states Produces 32 or 34 molecules of ATP ...
espiration - WordPress.com
... muscle tissue in the presence of oxygen. The muscle preparation was able to respire some of the lactate and this provided the energy needed to convert the remaining lactate into glycogen. The diagram summarises the biochemical steps involved. ...
... muscle tissue in the presence of oxygen. The muscle preparation was able to respire some of the lactate and this provided the energy needed to convert the remaining lactate into glycogen. The diagram summarises the biochemical steps involved. ...
lecture9
... Our approach is to discover the enzymes for the synthesis and utilization of poly P in bacteria, yeast and animal cells. These enzymes will reveal novel mechanisms and insights and when purified will open the route of reverse genetics: the peptide sequence leads to the gene and thereby the means to ...
... Our approach is to discover the enzymes for the synthesis and utilization of poly P in bacteria, yeast and animal cells. These enzymes will reveal novel mechanisms and insights and when purified will open the route of reverse genetics: the peptide sequence leads to the gene and thereby the means to ...
Dynamics of the energy flow through photosystem II under changing
... the exciton may be directed to different pathways. In a dark-acclimated and non-photoinhibited leaf, the exciton can be transferred to another pigment molecule or to the primary acceptor pheophytin and subsequently used in photochemistry. Alternatively, the exciton may also be emitted as fluorescence ...
... the exciton may be directed to different pathways. In a dark-acclimated and non-photoinhibited leaf, the exciton can be transferred to another pigment molecule or to the primary acceptor pheophytin and subsequently used in photochemistry. Alternatively, the exciton may also be emitted as fluorescence ...
3 – Efficiency of Cellular Respiration
... Use the following questions to generate a summary note of the key points of chapter 4.3 of your textbook. You do not need to answer them stepwise, but rather use them to guide the content of your summary note. You are encouraged to write in point form and use subheadings. Your note should be detaile ...
... Use the following questions to generate a summary note of the key points of chapter 4.3 of your textbook. You do not need to answer them stepwise, but rather use them to guide the content of your summary note. You are encouraged to write in point form and use subheadings. Your note should be detaile ...
Nerve activates contraction
... • Lactic acid fermentation by some fungi and bacteria is used to make cheese and yogurt. • Muscle cells switch from aerobic respiration to lactic acid fermentation to generate ATP when O2 is scarce. • The waste product, lactate, may cause muscle fatigue, but ultimately it is converted back to pyruva ...
... • Lactic acid fermentation by some fungi and bacteria is used to make cheese and yogurt. • Muscle cells switch from aerobic respiration to lactic acid fermentation to generate ATP when O2 is scarce. • The waste product, lactate, may cause muscle fatigue, but ultimately it is converted back to pyruva ...
overview, inorgs, trace nutrients
... present in starch that caused the diseases. Later it was learned that the symptoms were due to something missing. • The B-complex vitamins are missing in refined foods (white bread, white rice), which have had the metabolically active portions of the whole grain removed. • These vitamins are cofacto ...
... present in starch that caused the diseases. Later it was learned that the symptoms were due to something missing. • The B-complex vitamins are missing in refined foods (white bread, white rice), which have had the metabolically active portions of the whole grain removed. • These vitamins are cofacto ...
ALL ABOUT PHOTOSYNTHESIS AND CELLULAR RESPIRATION
... A Leaves provide support for growth and a place to store food B Leaves provide a place for photosynthesis to occur C Leaves absorb water and minerals and transport nutrients to the stem. D Leaves create a barrier that prevents water in the plant’s tissues from evaporating. 4. Which is the most likel ...
... A Leaves provide support for growth and a place to store food B Leaves provide a place for photosynthesis to occur C Leaves absorb water and minerals and transport nutrients to the stem. D Leaves create a barrier that prevents water in the plant’s tissues from evaporating. 4. Which is the most likel ...
What do you know about Cellular Respiration?
... come directly from food, from glycolysis, or from the citric acid cycle ...
... come directly from food, from glycolysis, or from the citric acid cycle ...
lecture_22 - WordPress.com
... Fatty acids are oxidized in matrix of mitochondria Activation and transport fatty acids to mitochondria Three enzymatic reactions: Acyl CoA synthetase Carnitine acyl transferase I Carnitine acyl transferase II ...
... Fatty acids are oxidized in matrix of mitochondria Activation and transport fatty acids to mitochondria Three enzymatic reactions: Acyl CoA synthetase Carnitine acyl transferase I Carnitine acyl transferase II ...
`Metabolic flux` describes the rate of flow of intermediates through a
... energy & yields more ATP than fermentation ...
... energy & yields more ATP than fermentation ...
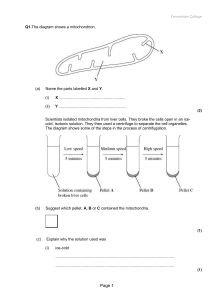
RespirationQuestions.doc - KS3, GCSE and A
... Write the letter A on the diagram to show one step where ATP is used. Write the letter B on the diagram at two steps where ATP is produced. ...
... Write the letter A on the diagram to show one step where ATP is used. Write the letter B on the diagram at two steps where ATP is produced. ...
Chapter 13 Carbohydrate Metabolism
... to the site of the electron transport chain. • Brain and muscle cells employ a transport mechanism that passes electrons from cytoplasmic NADH through the membrane to FAD molecules inside the mitochondria, forming FADH2. This cytoplasmic NADH generates 1.5 molecules of ATP. • Liver, heart, and kidne ...
... to the site of the electron transport chain. • Brain and muscle cells employ a transport mechanism that passes electrons from cytoplasmic NADH through the membrane to FAD molecules inside the mitochondria, forming FADH2. This cytoplasmic NADH generates 1.5 molecules of ATP. • Liver, heart, and kidne ...
cellular respiration study guide
... 3. Why is being “reduced” equivalent to having a greater potential energy? ...
... 3. Why is being “reduced” equivalent to having a greater potential energy? ...
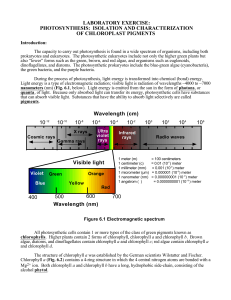
laboratory exercise: photosynthesis: isolation and characterization of
... Chlorophyll a in pure form dissolved in acetone has an absorption maximum at 663 nm. In the intact cell, however, chlorophyll a may show 2 or more different absorption maxima-- for example, 672 nm and 683 nm. The exact position of the absorption peak of chlorophyll a differs from one species of plan ...
... Chlorophyll a in pure form dissolved in acetone has an absorption maximum at 663 nm. In the intact cell, however, chlorophyll a may show 2 or more different absorption maxima-- for example, 672 nm and 683 nm. The exact position of the absorption peak of chlorophyll a differs from one species of plan ...
Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry 5/e
... three stage - Organic fuel molecules are oxidized to yield twocarbon fragemnts in the form of acetyla –coA - The acetyl group is oxidized into carbon dioxide in the citric acid cycle; energy released is conserved in the NADH and FADH2 - This reduced coenzyme transferred electron to oxygen through ET ...
... three stage - Organic fuel molecules are oxidized to yield twocarbon fragemnts in the form of acetyla –coA - The acetyl group is oxidized into carbon dioxide in the citric acid cycle; energy released is conserved in the NADH and FADH2 - This reduced coenzyme transferred electron to oxygen through ET ...
Glycolysis 1
... dehydrogenase generates 2 NADH molecules that can be shuttled into the mitochondria to produce more ATP by oxidative phosphorylation. 3. reaction 10 is an irreversible reaction that must be bypassed in gluconeogenesis by two separate enzymatic reactions catalyzed by pyruvate carboxylase and phosphoe ...
... dehydrogenase generates 2 NADH molecules that can be shuttled into the mitochondria to produce more ATP by oxidative phosphorylation. 3. reaction 10 is an irreversible reaction that must be bypassed in gluconeogenesis by two separate enzymatic reactions catalyzed by pyruvate carboxylase and phosphoe ...
Learning objectives
... Learning objectives Elements and compounds 1. Distinguish between an element and a compound. 2. Identify the four elements that make up 96% of living matter. 3. Define the term trace element and give an example. Atoms and molecules 4. Draw and label a simplified model of an atom. Explain how this mo ...
... Learning objectives Elements and compounds 1. Distinguish between an element and a compound. 2. Identify the four elements that make up 96% of living matter. 3. Define the term trace element and give an example. Atoms and molecules 4. Draw and label a simplified model of an atom. Explain how this mo ...