Biology, 7e (Campbell) Chapter 9: Cellular Respiration: Harvesting
... B) Electrons are being moved from atoms that have a lower affinity for electrons (such as C) to atoms with a higher affinity for electrons (such as O). C) The oxidation of organic compounds can be used to make ATP. D) The electrons have a higher potential energy when associated with water and CO2 th ...
... B) Electrons are being moved from atoms that have a lower affinity for electrons (such as C) to atoms with a higher affinity for electrons (such as O). C) The oxidation of organic compounds can be used to make ATP. D) The electrons have a higher potential energy when associated with water and CO2 th ...
Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Complex and Tricarboxylic Acid
... • Converts acetyl-CoA to two CO2 while conserving the free energy for ATP production. – The energy is stored as: three NADHs, one FADH2, and one GTP. • Intermediates from the TCA-cycle can be used to synthesize molecules such as amino acids and fatty acids. ...
... • Converts acetyl-CoA to two CO2 while conserving the free energy for ATP production. – The energy is stored as: three NADHs, one FADH2, and one GTP. • Intermediates from the TCA-cycle can be used to synthesize molecules such as amino acids and fatty acids. ...
on the potential efficiency of converting solar radiation to phytoenergy
... Because photosynthesis is a quantum process, the distinction between solar energy flux (irradiance) and photon flux density is important; photon energy is inversely related to wavelength, so that the potential efficiency of energy use is greater with longer wavelength photons. The maximal spectral s ...
... Because photosynthesis is a quantum process, the distinction between solar energy flux (irradiance) and photon flux density is important; photon energy is inversely related to wavelength, so that the potential efficiency of energy use is greater with longer wavelength photons. The maximal spectral s ...
BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY Problem Unit Four
... that are initiated by epinephrine and glucagon and lead to the activation of phosphorylase and the inhibition of glycogen synthase. Include the following details: a) the binding sites for epinephrine and glucagon, b) the effect of epinephrine and glucagon on adenylate cyclase, c) the substrates and ...
... that are initiated by epinephrine and glucagon and lead to the activation of phosphorylase and the inhibition of glycogen synthase. Include the following details: a) the binding sites for epinephrine and glucagon, b) the effect of epinephrine and glucagon on adenylate cyclase, c) the substrates and ...
Lecture 26
... Fea atom coordinates with the OH group of citrate The iron-sulfur cluster does not perform a redox reaction but instead is able to stabilize the ligand-substrate complex. Second stage of the reaction rehydrates cis-aconitate’s double bond in a stereospecific trans addition to form only the 2R,3S iso ...
... Fea atom coordinates with the OH group of citrate The iron-sulfur cluster does not perform a redox reaction but instead is able to stabilize the ligand-substrate complex. Second stage of the reaction rehydrates cis-aconitate’s double bond in a stereospecific trans addition to form only the 2R,3S iso ...
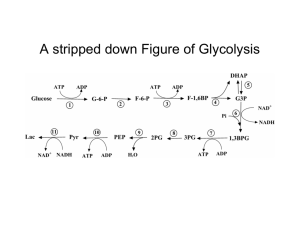
Figure 17-3 Degradation of glucose via the glycolytic pathway.
... •reduced at expense of electrons originally donated by 3-phosphoglyceraldehyde, carried by NADH. Thus, no net oxidation occurs in glycolysis = fermentation; another organic serving as electron acceptor. •lactate, end-product under anaerobic conditions, diffuses thru cell membrane as waste into blood ...
... •reduced at expense of electrons originally donated by 3-phosphoglyceraldehyde, carried by NADH. Thus, no net oxidation occurs in glycolysis = fermentation; another organic serving as electron acceptor. •lactate, end-product under anaerobic conditions, diffuses thru cell membrane as waste into blood ...
Tubeworms and Chemosynthesis Resembling giant lipsticks
... Tubeworms have no mouth, eyes, or stomach ("gut"). Their survival depends on a symbiotic relationship with the billions of bacteria that live inside of them. These bacteria convert the chemicals that shoot out of the hydrothermal vents into food for the worm. This chemical- based food-making process ...
... Tubeworms have no mouth, eyes, or stomach ("gut"). Their survival depends on a symbiotic relationship with the billions of bacteria that live inside of them. These bacteria convert the chemicals that shoot out of the hydrothermal vents into food for the worm. This chemical- based food-making process ...
A Study of Phylogenetic Relationships and Homology of
... in most species. Over time, random mutations in the DNA sequence occur. As a result, its amino acid sequence also changes. Cells without usable cyt c are unlikely to survive. [Margoliash E, 1963]. Hence, the relationship between organisms can be compared by examining the amino acid sequence of cyt c ...
... in most species. Over time, random mutations in the DNA sequence occur. As a result, its amino acid sequence also changes. Cells without usable cyt c are unlikely to survive. [Margoliash E, 1963]. Hence, the relationship between organisms can be compared by examining the amino acid sequence of cyt c ...
Citric Acid Cycle: Central Role in Catabolism Entry of Pyruvate into
... TCA cycle reactions (continued) 4. This is the second oxidative decarboxylaion and 3rd irreversible step catalyzed by a-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase. The enzyme is a complex similar to PDH and the coenzymes TPP, lipoamide and FAD are required. CO2 is removed, NADH is formed from NAD+ and a thioester ...
... TCA cycle reactions (continued) 4. This is the second oxidative decarboxylaion and 3rd irreversible step catalyzed by a-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase. The enzyme is a complex similar to PDH and the coenzymes TPP, lipoamide and FAD are required. CO2 is removed, NADH is formed from NAD+ and a thioester ...
Electrone transport chain and oxidative phosphorylation
... B. Electron transport chain Energy-rich molecules, such as glucose, are metab olized by a series of oxidation reactions ultimately yielding CO2 and water (Figure 6.6). The metabolic intermediates of these reactions donate electrons to specific coenzymes—nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD +) and ...
... B. Electron transport chain Energy-rich molecules, such as glucose, are metab olized by a series of oxidation reactions ultimately yielding CO2 and water (Figure 6.6). The metabolic intermediates of these reactions donate electrons to specific coenzymes—nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD +) and ...
Transcript
... there’s been cases of bodies sitting up inside coffins, and pushing tops off coffins. 1. With this lack of energy, this person can’t create any more energy, and the muscles will tend to tighten up, so they are left in this rigor-like state. vi. In order to detach this (stop this), and get back to a ...
... there’s been cases of bodies sitting up inside coffins, and pushing tops off coffins. 1. With this lack of energy, this person can’t create any more energy, and the muscles will tend to tighten up, so they are left in this rigor-like state. vi. In order to detach this (stop this), and get back to a ...
5-2 Necleotide Metabolism (pyrimidine) - Home
... phosphate with aspartate with the release of Pi •ATCase is the major site of regulation in bacteria; it is activated by ATP and inhibited by CTP •carbamoyl phosphate is an “activated” compound, so no energy input is needed at this step ...
... phosphate with aspartate with the release of Pi •ATCase is the major site of regulation in bacteria; it is activated by ATP and inhibited by CTP •carbamoyl phosphate is an “activated” compound, so no energy input is needed at this step ...
Unit 4 Notes
... • Acetylcoenzyme A is effectively a two carbon molecule that combines with a four carbon molecule to produce a six carbon molecule which enters the Krebs cycle. In a series of oxidationreduction reactions the Krebs cycle generates reduced coenzymes and ATP by substrate-level phosphorylation, and car ...
... • Acetylcoenzyme A is effectively a two carbon molecule that combines with a four carbon molecule to produce a six carbon molecule which enters the Krebs cycle. In a series of oxidationreduction reactions the Krebs cycle generates reduced coenzymes and ATP by substrate-level phosphorylation, and car ...
A generalized stoichiometric model of C3, C2, C2
... for integrating knowledge at the systems level (Morandini, 2013; Singh et al., 2014). Classical photosynthetic models have allowed the simulation of leaf-level assimilation in C3, C2, C2+C4, and C4 plants using a mechanistic description based on Rubisco PEPC kinetics (von Caemmerer, 1989, 2000, 201 ...
... for integrating knowledge at the systems level (Morandini, 2013; Singh et al., 2014). Classical photosynthetic models have allowed the simulation of leaf-level assimilation in C3, C2, C2+C4, and C4 plants using a mechanistic description based on Rubisco PEPC kinetics (von Caemmerer, 1989, 2000, 201 ...
Redox cycling”
... thereby only be transferred to electron acceptors Compounds that easily donate electrons have a tendency to reduce other compounds and are therefore often called reductants Compounds that easily take up electrons can often oxidize other compounds and can therefore be called oxidants The oxidiz ...
... thereby only be transferred to electron acceptors Compounds that easily donate electrons have a tendency to reduce other compounds and are therefore often called reductants Compounds that easily take up electrons can often oxidize other compounds and can therefore be called oxidants The oxidiz ...
Biochemistry Lecture 16
... • Through CH3 of acetyl • Transient intermediate: citroyl CoA – Energy rel’d from cleavage acetylCoA • Why? What grps impt to exergonic rxn ...
... • Through CH3 of acetyl • Transient intermediate: citroyl CoA – Energy rel’d from cleavage acetylCoA • Why? What grps impt to exergonic rxn ...
Chapter 17 - FIU Faculty Websites
... formation of the acetyl CoA binding site. The formation of the reaction intermediate citryl CoA causes a structural change that completes active site formation, enabling cleavage of the thioester linkage. Citryl CoA is cleaved to form citrate and coenzyme A. ...
... formation of the acetyl CoA binding site. The formation of the reaction intermediate citryl CoA causes a structural change that completes active site formation, enabling cleavage of the thioester linkage. Citryl CoA is cleaved to form citrate and coenzyme A. ...
L14_Adv06PDHwebCT
... • then DG ~0 (no net change in free energy) • easily reversed by changing ratio of [products]/[substrate] as don’t need to overcome high DG For A+B ↔C+D product A+B C+D substrate A+B C+D • enzymes that catalyse such reactions act to restore equilibrium • rate regulated by [products]/[reacta ...
... • then DG ~0 (no net change in free energy) • easily reversed by changing ratio of [products]/[substrate] as don’t need to overcome high DG For A+B ↔C+D product A+B C+D substrate A+B C+D • enzymes that catalyse such reactions act to restore equilibrium • rate regulated by [products]/[reacta ...
the molecular mechanism of photosynthetic glyceraldehyde
... Photosynthetic GAPDH subunits (GapA and GapB) give rise in chloroplasts of higher plants to two different isoforms with either A4 or AnBn stochiometry, the latter being more abundant and displaying sophisticated regulatory properties. Photosynthetic GAPDH can use both NADPH and NADH as electron dono ...
... Photosynthetic GAPDH subunits (GapA and GapB) give rise in chloroplasts of higher plants to two different isoforms with either A4 or AnBn stochiometry, the latter being more abundant and displaying sophisticated regulatory properties. Photosynthetic GAPDH can use both NADPH and NADH as electron dono ...
Cellular Respiration
... Lactic acid fermentation can supply enough ATP to last about 90 seconds. However, extra oxygen is required to get rid of the lactic acid produced. Following intense exercise, a person will huff and puff for several minutes in order to pay back the built-up “oxygen debt” and clear the lactic acid fro ...
... Lactic acid fermentation can supply enough ATP to last about 90 seconds. However, extra oxygen is required to get rid of the lactic acid produced. Following intense exercise, a person will huff and puff for several minutes in order to pay back the built-up “oxygen debt” and clear the lactic acid fro ...
CONTRIBUTIONS OF ANAEROBIC METABOLISM TO pH
... The proton balance of these pathways cannot simply be explained by proton release via ATP hydrolysis, since proton-relevant reactions, which do not directly include ATP synthesis, are involved. Other reactions deliver energy for ATP synthesis but do not affect the acid-base status. Fig. 2 shows the ...
... The proton balance of these pathways cannot simply be explained by proton release via ATP hydrolysis, since proton-relevant reactions, which do not directly include ATP synthesis, are involved. Other reactions deliver energy for ATP synthesis but do not affect the acid-base status. Fig. 2 shows the ...
tRNA aminoacylation by arginyltRNA synthetase: induced
... interact with the sugar±phosphate backbone; and (iii) polar side chains that are involved in direct or water-mediated interactions with the nucleic acid. Cyt35, which has been shown to be the strongest identity determinant for tRNAArg (Giege et al., 1998), is recognized mainly by main chain atoms o ...
... interact with the sugar±phosphate backbone; and (iii) polar side chains that are involved in direct or water-mediated interactions with the nucleic acid. Cyt35, which has been shown to be the strongest identity determinant for tRNAArg (Giege et al., 1998), is recognized mainly by main chain atoms o ...
Chem 465 Biochemistry II
... dehydrogenase complex and á-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex. Pyruvate dehydrogenase catalyzes the reaction Pyruvate + CoASH 6AcetylCoA + NADH + H+ á-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase catalyzes the reaction á-ketoglutarate + CoASH 6SuccinylCoA + NADH + H+. Pyruvate dehydrogenase and á-ketoglutarate deh ...
... dehydrogenase complex and á-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex. Pyruvate dehydrogenase catalyzes the reaction Pyruvate + CoASH 6AcetylCoA + NADH + H+ á-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase catalyzes the reaction á-ketoglutarate + CoASH 6SuccinylCoA + NADH + H+. Pyruvate dehydrogenase and á-ketoglutarate deh ...