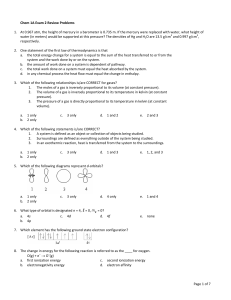
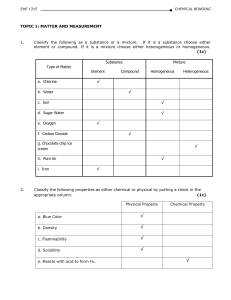
Physical Chemistry 20130410 week 2 Wednesday April 10 2013
... since dividing the formula for [C] by the formula for [D] for rate of reaction simplifies to k1/k2. If k1/k2 >>1 then [C]>>[D] so C is favored kinetically. If K1/K2<<1 then [D]>>[D] so D is favored thermodynamically. See handout for 1,3 butadiene. HBr is a very strong acid. The intermediate of a rea ...
... since dividing the formula for [C] by the formula for [D] for rate of reaction simplifies to k1/k2. If k1/k2 >>1 then [C]>>[D] so C is favored kinetically. If K1/K2<<1 then [D]>>[D] so D is favored thermodynamically. See handout for 1,3 butadiene. HBr is a very strong acid. The intermediate of a rea ...
Chapter 9 Stoichiometry
... When baking cookies, a recipe is usually used, telling the exact amount of each ingredient ...
... When baking cookies, a recipe is usually used, telling the exact amount of each ingredient ...
SOFCs. Electrolytes
... SOFCs. Polarization phenomena G=-nFE Equilibrium conditions. Only describes the maximum available energy/voltage (OCV) In practice, when the current flows through the circuit, there is a voltage drop due the polarization of the electrodes : = EOCV – ET = 0.3-0.4 V ET = 0.6 – 0.7 V Polarizatio ...
... SOFCs. Polarization phenomena G=-nFE Equilibrium conditions. Only describes the maximum available energy/voltage (OCV) In practice, when the current flows through the circuit, there is a voltage drop due the polarization of the electrodes : = EOCV – ET = 0.3-0.4 V ET = 0.6 – 0.7 V Polarizatio ...
functional group
... a dipole moment, it has the highest boiling point. Induced dipole-induced dipole forces are greatest in CCl4 because it has the greatest number of Cl atoms. Cl is more polarizable than H. Minto - Lectures 7-8 ...
... a dipole moment, it has the highest boiling point. Induced dipole-induced dipole forces are greatest in CCl4 because it has the greatest number of Cl atoms. Cl is more polarizable than H. Minto - Lectures 7-8 ...
Document
... Exchange of Heat between System and Surroundings When heat is released by the system to the surroundings, the process is exothermic. ...
... Exchange of Heat between System and Surroundings When heat is released by the system to the surroundings, the process is exothermic. ...
2. Electrodics
... The process of adding electrons to either an ion or a neutral species is called reduction, while the reverse process (i.e., removal of electrons) is called oxidation. ...
... The process of adding electrons to either an ion or a neutral species is called reduction, while the reverse process (i.e., removal of electrons) is called oxidation. ...
DEPARTMENT OF CHEMISTRY, CFS, IIUM
... the amount of matter is called an intensive property. A characteristic that can be observed without producing new kinds of matter is called a physical property. A characteristic that depends on how a kind of matter changes suring interactions with other kinds of matter is called chemical property. M ...
... the amount of matter is called an intensive property. A characteristic that can be observed without producing new kinds of matter is called a physical property. A characteristic that depends on how a kind of matter changes suring interactions with other kinds of matter is called chemical property. M ...
Methodology for the olefination of aldehydes and ketones via the Meyer-Schuster reaction
... Phosphorus ylides are prepared before the reaction or in-situ and precautions must be taken due to their sensitivity to moisture and air. The carbanion of the ylide is the characteristic component that allows for nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl carbon. The ylides have been found to demonstrate ...
... Phosphorus ylides are prepared before the reaction or in-situ and precautions must be taken due to their sensitivity to moisture and air. The carbanion of the ylide is the characteristic component that allows for nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl carbon. The ylides have been found to demonstrate ...
Chem 1202 - LSU Department of Chemistry
... Now consider an irreversible (spontaneous) reaction (e.g., a mixture of water and ice at room temperature). It has been found experimentally that for all spontaneous (non-equilibrium) reactions: ...
... Now consider an irreversible (spontaneous) reaction (e.g., a mixture of water and ice at room temperature). It has been found experimentally that for all spontaneous (non-equilibrium) reactions: ...