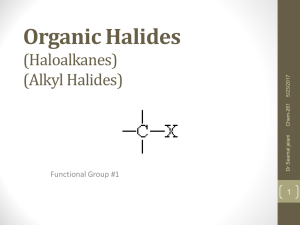Document
... (c) Carbon dioxide is fed into the phosphine generator to keep the phosphine concentration less than 2·6%. Above this level phosphine can ignite due to the presence of diphosphane, P2H4(g), as an impurity. Draw a structural formula for diphosphane. ...
... (c) Carbon dioxide is fed into the phosphine generator to keep the phosphine concentration less than 2·6%. Above this level phosphine can ignite due to the presence of diphosphane, P2H4(g), as an impurity. Draw a structural formula for diphosphane. ...
Basic Physical Chemistry (12.4 MB ppt)
... - the study of the conversion of heat energy into different forms of energy (in particular, mechanical, chemical, and electrical energy); different energy conversions into heat energy; and its relation to macroscopic variables such as temperature, pressure, and volume. Its underpinnings, based upon ...
... - the study of the conversion of heat energy into different forms of energy (in particular, mechanical, chemical, and electrical energy); different energy conversions into heat energy; and its relation to macroscopic variables such as temperature, pressure, and volume. Its underpinnings, based upon ...
The Process of Chemical Reactions
... on a particle—in a gas, for example—you would be constantly colliding with other particles, speeding up or slowing down, and increasing or decreasing your kinetic energy. Sometimes you collide with a slow moving particle while moving slowly yourself. This collision is not too jarring. It has a low n ...
... on a particle—in a gas, for example—you would be constantly colliding with other particles, speeding up or slowing down, and increasing or decreasing your kinetic energy. Sometimes you collide with a slow moving particle while moving slowly yourself. This collision is not too jarring. It has a low n ...
Practice problems
... which occurs at the anode. The I– ions are the source of electrons, and the Cr2O72– ions accept the electrons. Hence, the electrons flow through the external circuit from the electrode immersed in the KI solution (the anode) to the electrode immersed in the K2Cr2O7 – H2SO4 solution (the cathode). Th ...
... which occurs at the anode. The I– ions are the source of electrons, and the Cr2O72– ions accept the electrons. Hence, the electrons flow through the external circuit from the electrode immersed in the KI solution (the anode) to the electrode immersed in the K2Cr2O7 – H2SO4 solution (the cathode). Th ...
Press here to hemy 102 lab manual
... moments of polyatomic molecules are the vector sums of the individual bond dipoles. Therefore, H2O has a dipole moment (a polar molecule) and CCl4 does not (a nonpolar molecule). ...
... moments of polyatomic molecules are the vector sums of the individual bond dipoles. Therefore, H2O has a dipole moment (a polar molecule) and CCl4 does not (a nonpolar molecule). ...
Organic Halides (Haloalkanes) (Alkyl Halides)
... • The presence of a halide makes the molecule more polar. • Since water is also polar and “like dissolves like”, alkyl halides are soluble in water. The more halides connected to the parent chain, the more polar the molecule. • The polar nature of the molecule means that boiling and melting points o ...
... • The presence of a halide makes the molecule more polar. • Since water is also polar and “like dissolves like”, alkyl halides are soluble in water. The more halides connected to the parent chain, the more polar the molecule. • The polar nature of the molecule means that boiling and melting points o ...
This article was published in an Elsevier journal. The attached copy
... an easy phase separation. In the subsequent step, Section 3 including reactions (9) and (10), the separation of HI from L − 2, the heavier iodine/iodide–water phase, is the most critical scenario of the cycle [4] and believed to be the most expensive and energy-consuming step [5]. After establishing ...
... an easy phase separation. In the subsequent step, Section 3 including reactions (9) and (10), the separation of HI from L − 2, the heavier iodine/iodide–water phase, is the most critical scenario of the cycle [4] and believed to be the most expensive and energy-consuming step [5]. After establishing ...










![Synthesis of [RuCl2(NO)2(THF)] and its Double CN BondForming](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001773792_1-763ad0089529123821e01ed17077bbf2-300x300.png)