PPT
... • Find the longest chain that contains C=O. • Using the root alkane name, drop the –e ending and change to –one. • Number the longest carbon chain so the C=O group has the lowest number. • Name and number other substituents as before. Examples: ...
... • Find the longest chain that contains C=O. • Using the root alkane name, drop the –e ending and change to –one. • Number the longest carbon chain so the C=O group has the lowest number. • Name and number other substituents as before. Examples: ...
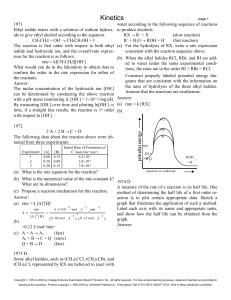
Kinetics
... What would you do in the laboratory to obtain data to confirm the order in the rate expression for either of the reactants. Answer: The molar concentration of the hydroxide ion [OH-] can be determined by conducting the above reaction with a pH meter monitoring it. [OH-] = 110-14/-log pH. By measuri ...
... What would you do in the laboratory to obtain data to confirm the order in the rate expression for either of the reactants. Answer: The molar concentration of the hydroxide ion [OH-] can be determined by conducting the above reaction with a pH meter monitoring it. [OH-] = 110-14/-log pH. By measuri ...
Chapter 14
... The naming of epoxides can either be from the starting alkene used to synthesize the OXIDE ...
... The naming of epoxides can either be from the starting alkene used to synthesize the OXIDE ...
Step 2
... number to each element wherever it appears in the equation. If the reaction is a redox reaction, identify the element that undergoes an increase in oxidation number and the elements the undergoes a decrease. Find the numerical values of the increase and decrease. Determine the smallest whole-number ...
... number to each element wherever it appears in the equation. If the reaction is a redox reaction, identify the element that undergoes an increase in oxidation number and the elements the undergoes a decrease. Find the numerical values of the increase and decrease. Determine the smallest whole-number ...
Chapter 4 Aqueous Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry
... Net Ionic Equation • To form the net ionic equation, cross out anything that does not change from the left side of the equation to the right. • The only things left in the equation are those things that change (i.e., react) during the course of the reaction. • Those things that didn’t change (and w ...
... Net Ionic Equation • To form the net ionic equation, cross out anything that does not change from the left side of the equation to the right. • The only things left in the equation are those things that change (i.e., react) during the course of the reaction. • Those things that didn’t change (and w ...
Rapid and Efficient Functionalized Ionic Liquid-Catalyzed
... as solvent/catalyst; a possible reason for this is the high viscosity of the IL, which slows down the mass transfer in the catalytic system. Hence, we began our investigation by the evaluation of solvents that would decrease the viscosity of the reaction system. We attempted to add an additional 50 ...
... as solvent/catalyst; a possible reason for this is the high viscosity of the IL, which slows down the mass transfer in the catalytic system. Hence, we began our investigation by the evaluation of solvents that would decrease the viscosity of the reaction system. We attempted to add an additional 50 ...
CHEM120 - ORGANIC CHEMISTRY WORKSHEET 1
... 3. Write (i) structural formulae and (ii) draw the bond line notation for the following compounds: (a) 2,2,4-trimethylhexane (b) 3-ethyl-2,4,5-trimethyloctane (c) 2-bromo-2,4,6-trimethyloctane ...
... 3. Write (i) structural formulae and (ii) draw the bond line notation for the following compounds: (a) 2,2,4-trimethylhexane (b) 3-ethyl-2,4,5-trimethyloctane (c) 2-bromo-2,4,6-trimethyloctane ...
M.Sc. II - Punjabi University
... (b) Ligand replacement reaction. Labile and inert complexes, crystal field stabilization, general aspects, dissociation or displacement, classification of mechanism, water exchange rates, formation of complexes from aqueous ions, equation and base hydrolysis, attack on ligands. (c) Reactions of Squa ...
... (b) Ligand replacement reaction. Labile and inert complexes, crystal field stabilization, general aspects, dissociation or displacement, classification of mechanism, water exchange rates, formation of complexes from aqueous ions, equation and base hydrolysis, attack on ligands. (c) Reactions of Squa ...
Chemistry Review 2 answer key
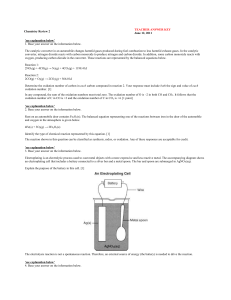
... Rust on an automobile door contains Fe2O3(s). The balanced equation representing one of the reactions between iron in the door of the automobile and oxygen in the atmosphere is given below. 4Fe(s) + 3O2(g) → 2Fe2O3(s) Identify the type of chemical reaction represented by this equation. [1] The react ...
... Rust on an automobile door contains Fe2O3(s). The balanced equation representing one of the reactions between iron in the door of the automobile and oxygen in the atmosphere is given below. 4Fe(s) + 3O2(g) → 2Fe2O3(s) Identify the type of chemical reaction represented by this equation. [1] The react ...
4. The dioxygen molecule, O2: Uptake, Transport and Storage of an
... photochemistry; Units and dimensions; Electronic energy states of atoms; Interaction of spin and orbital angular momenta; Term symbols and the ground state of atoms; Selection rules; Primary processes of excited mercury atoms; Grotrain energy-level diagram for mercury; Physical and chemical quenchin ...
... photochemistry; Units and dimensions; Electronic energy states of atoms; Interaction of spin and orbital angular momenta; Term symbols and the ground state of atoms; Selection rules; Primary processes of excited mercury atoms; Grotrain energy-level diagram for mercury; Physical and chemical quenchin ...
$doc.title
... http: www.chem.wisc.edu/areas /clc (Resource page) Reactions of Alcohols #5: Oxidation of Primary Alcohols to Aldehydes ...
... http: www.chem.wisc.edu/areas /clc (Resource page) Reactions of Alcohols #5: Oxidation of Primary Alcohols to Aldehydes ...