1.9 M - Thierry Karsenti
... 2. Atom: the smallest particle of an element that retains the identify and properties of the element and can take part in a chemical change. 3. Atomic number (symbol Z): the number of protons in the nucleus of each atom. 4. Compound: a substance that is formed when two or more elements combine chemi ...
... 2. Atom: the smallest particle of an element that retains the identify and properties of the element and can take part in a chemical change. 3. Atomic number (symbol Z): the number of protons in the nucleus of each atom. 4. Compound: a substance that is formed when two or more elements combine chemi ...
A molecular orbital method for inorganic molecules: application to
... atom a with an electronic configuration given by the fpa in (6). If Fa were rigorously the atomic SCF operator appropriate to atom a (for some specific electronic configuration) and pa the appropriate SCF orbital function, then W,, would be exactly the negative of the orbital energy of atomic orbita ...
... atom a with an electronic configuration given by the fpa in (6). If Fa were rigorously the atomic SCF operator appropriate to atom a (for some specific electronic configuration) and pa the appropriate SCF orbital function, then W,, would be exactly the negative of the orbital energy of atomic orbita ...
Chemical bonding and structure
... as protons and electrons. This is because the number of protons (+) is equal to the number of electrons (−), and so their charges cancel each other out. The positively charged protons, located within the nucleus of the atom, are not transferred during chemical reactions. Electrons, however, position ...
... as protons and electrons. This is because the number of protons (+) is equal to the number of electrons (−), and so their charges cancel each other out. The positively charged protons, located within the nucleus of the atom, are not transferred during chemical reactions. Electrons, however, position ...
The Intensity of Ligand Absorption - TopSCHOLAR
... The objective of this work was to determine what factors such as d-electron configuration, back donation, oxidation state on the metal ion, covalency, etc. influence the intensity of the TT* *• TT transition in triphenylphosphine complexes. The region of wavelength covered by this research did not s ...
... The objective of this work was to determine what factors such as d-electron configuration, back donation, oxidation state on the metal ion, covalency, etc. influence the intensity of the TT* *• TT transition in triphenylphosphine complexes. The region of wavelength covered by this research did not s ...
Chemistry 1A Final Exam December 12, 2001 Page 1 of 16 (Closed
... 24) When a system has reached equilibrium, which of the following is true for the rates of the forward and reverse reactions? A) B) C) D) E) ...
... 24) When a system has reached equilibrium, which of the following is true for the rates of the forward and reverse reactions? A) B) C) D) E) ...
Unit5C - OCCC.edu
... Rules for Oxidation Numbers • Oxidation numbers are always reported for individual atoms or ions not groups of atoms or ions!!!!!!!!!!! • For an atom in its elemental form, the oxidation number is always zero. – H2: oxidation # = 0 for each H atom – Cu: oxidation number = 0 – Cl2: oxidation # = 0 f ...
... Rules for Oxidation Numbers • Oxidation numbers are always reported for individual atoms or ions not groups of atoms or ions!!!!!!!!!!! • For an atom in its elemental form, the oxidation number is always zero. – H2: oxidation # = 0 for each H atom – Cu: oxidation number = 0 – Cl2: oxidation # = 0 f ...
Worksheet 1 - Oxidation/Reduction Reactions Oxidation number
... In each of the following reactions, assign oxidation numbers to all of the elements and identify the oxidizing and reducing agents and the change in oxidation number. a. ...
... In each of the following reactions, assign oxidation numbers to all of the elements and identify the oxidizing and reducing agents and the change in oxidation number. a. ...
Week 8 - Day 3 (End of Chapter 6)
... Orbital Diagram for the Formation of H2S .......................................................................................... 13 Valence Bond Theory and NH3 ................................................................................................................ 13 Hybridization – mixin ...
... Orbital Diagram for the Formation of H2S .......................................................................................... 13 Valence Bond Theory and NH3 ................................................................................................................ 13 Hybridization – mixin ...
Saturated Solutions (Solubility Curves and More)
... Like Dissolving Like Ionic compounds, with both positive and negative ‘ends’ to them (Water H- O+) can dissolve many more forms of solutes, due to this law of science. ...
... Like Dissolving Like Ionic compounds, with both positive and negative ‘ends’ to them (Water H- O+) can dissolve many more forms of solutes, due to this law of science. ...
AP Chemistry Summer Assignment
... For those students who have already taken a high school chemistry course, much of the material in the summer packet will be familiar to you. For those students who will be taking AP Chemistry as your first high school chemistry course, the problems will help you build a foundation in chemistry and i ...
... For those students who have already taken a high school chemistry course, much of the material in the summer packet will be familiar to you. For those students who will be taking AP Chemistry as your first high school chemistry course, the problems will help you build a foundation in chemistry and i ...
CBSE-12th/2011/CHEMISTRY
... larger in size. so lp repulsion is less significant. Also, S-S bond is stronger than O-O bond & S=S is less strong(less than 2 S-S bonds). This is also affected by the fact that O forms strong bonds with mostly other elements than itself. Ans.13 (i)In aqueous solution, Cu+ ion undergoes oxidation to ...
... larger in size. so lp repulsion is less significant. Also, S-S bond is stronger than O-O bond & S=S is less strong(less than 2 S-S bonds). This is also affected by the fact that O forms strong bonds with mostly other elements than itself. Ans.13 (i)In aqueous solution, Cu+ ion undergoes oxidation to ...
Unit 8: Reactions - Mark Rosengarten
... oxygen! Or if the salt on your plate decomposed suddenly into sodium (explosive metal) and chlorine (poisonous, corrosive gas)! Compounds exist because it requires less energy to exist in compound form. This is why the diatomic molecules exist>hydrogen has less energy as H2 than as just H>so wheneve ...
... oxygen! Or if the salt on your plate decomposed suddenly into sodium (explosive metal) and chlorine (poisonous, corrosive gas)! Compounds exist because it requires less energy to exist in compound form. This is why the diatomic molecules exist>hydrogen has less energy as H2 than as just H>so wheneve ...
Appendix - Cengage
... Electrons tend to move around the nucleus in a specific pattern. The orbitals, or pathways traveled by electrons around the nucleus, are arranged in an orderly series of concentric layers known as electron shells, which consecutively surround the nucleus. Each electron shell can hold a specific numb ...
... Electrons tend to move around the nucleus in a specific pattern. The orbitals, or pathways traveled by electrons around the nucleus, are arranged in an orderly series of concentric layers known as electron shells, which consecutively surround the nucleus. Each electron shell can hold a specific numb ...
Differentiated Chemistry Worksheet and Laboratory
... What main feature of Dalton’s atomic model was abandoned after Thomson’s discoveries? ...
... What main feature of Dalton’s atomic model was abandoned after Thomson’s discoveries? ...
ANew Copper(II)ComplexwiththeN,N`-Bis(antipyryl-4
... molecules are distorted in a different manner. In one of them, the copper(II) center and the nitrogen (N1 and N2) atoms lie slightly below (0.017, 0.245, and 0.1933 Å, respectively) whereas the oxygen atoms are located above the mean plane of CuN2 O2 (O1 0.1, O2 0.2 Å). The second chromophore is m ...
... molecules are distorted in a different manner. In one of them, the copper(II) center and the nitrogen (N1 and N2) atoms lie slightly below (0.017, 0.245, and 0.1933 Å, respectively) whereas the oxygen atoms are located above the mean plane of CuN2 O2 (O1 0.1, O2 0.2 Å). The second chromophore is m ...
Chemical Thermodynamics -
... (Look at oxidation numbers in the "skeleton equation") 2. Balance atoms other than H and O. 3. Balance O with H2O. 4. Balance H with H+. 5. Balance charge with appropriate number of electrons. 6. If in acidic solution, then skip to step 7. If in basic solution, then add equal number of OH- to both s ...
... (Look at oxidation numbers in the "skeleton equation") 2. Balance atoms other than H and O. 3. Balance O with H2O. 4. Balance H with H+. 5. Balance charge with appropriate number of electrons. 6. If in acidic solution, then skip to step 7. If in basic solution, then add equal number of OH- to both s ...
Document
... (Look at oxidation numbers in the "skeleton equation") 2. Balance atoms other than H and O. 3. Balance O with H2O. 4. Balance H with H+. 5. Balance charge with appropriate number of electrons. 6. If in acidic solution, then skip to step 7. If in basic solution, then add equal number of OH- to both s ...
... (Look at oxidation numbers in the "skeleton equation") 2. Balance atoms other than H and O. 3. Balance O with H2O. 4. Balance H with H+. 5. Balance charge with appropriate number of electrons. 6. If in acidic solution, then skip to step 7. If in basic solution, then add equal number of OH- to both s ...
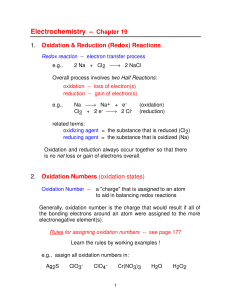
Topic 7b Redox notes
... Simple definitions of oxidation and reduction are based on the loss/gain of oxygen or the loss/gain of hydrogen. Oxidation is the gain of oxygen or the loss of hydrogen; reduction is the loss of oxygen or the gain of hydrogen. These definitions can only be used when a chemical reaction involves hydr ...
... Simple definitions of oxidation and reduction are based on the loss/gain of oxygen or the loss/gain of hydrogen. Oxidation is the gain of oxygen or the loss of hydrogen; reduction is the loss of oxygen or the gain of hydrogen. These definitions can only be used when a chemical reaction involves hydr ...
CHEM 210 Ch06
... • Any ion that has a net positive charge at that pH will migrate toward the negatively charged cathode. • Any ion having a net negative charge will migrate toward the positively charged anode. • If the net charge is zero, the species will not move. • An amino acid’s isoelectric pH, or isoelectric po ...
... • Any ion that has a net positive charge at that pH will migrate toward the negatively charged cathode. • Any ion having a net negative charge will migrate toward the positively charged anode. • If the net charge is zero, the species will not move. • An amino acid’s isoelectric pH, or isoelectric po ...
Stoichiometry - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... describing the composition, bonding, and structural formulas for aliphatic hydrocarbons: alkanes, alkenes, and alkynes (straight, branched, and cyclic, maximum two double or one triple bond) describing the bonding shapes around each of the carbon atoms involved in a single, double, or triple bon ...
... describing the composition, bonding, and structural formulas for aliphatic hydrocarbons: alkanes, alkenes, and alkynes (straight, branched, and cyclic, maximum two double or one triple bond) describing the bonding shapes around each of the carbon atoms involved in a single, double, or triple bon ...
avogadro exam 2012 - University of Waterloo
... 26 Which of the following atoms has the greatest number of unpaired electrons in its ground electronic state? A ...
... 26 Which of the following atoms has the greatest number of unpaired electrons in its ground electronic state? A ...
lecture slides of chap19_FU
... Will the following reaction occur spontaneously at 250C if [Fe2+] = 0.60 M and [Cd2+] = 0.010 M? Fe2+ (aq) + Cd (s) Fe (s) + Cd2+ (aq) Oxidation: Reduction: ...
... Will the following reaction occur spontaneously at 250C if [Fe2+] = 0.60 M and [Cd2+] = 0.010 M? Fe2+ (aq) + Cd (s) Fe (s) + Cd2+ (aq) Oxidation: Reduction: ...
solution is a solution that contains the maximum amount of solute
... ____4____ and the coefficient for the NO is ____6_____. ...
... ____4____ and the coefficient for the NO is ____6_____. ...
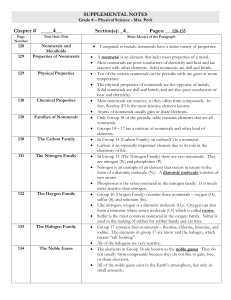
Name - TeacherWeb
... The elements in Group 18 are known as the noble gases. They do not usually form compounds because they do not like to gain, lose, or share electrons. All of the noble gases exist in the Earth’s atmosphere, but only in small amounts. ...
... The elements in Group 18 are known as the noble gases. They do not usually form compounds because they do not like to gain, lose, or share electrons. All of the noble gases exist in the Earth’s atmosphere, but only in small amounts. ...