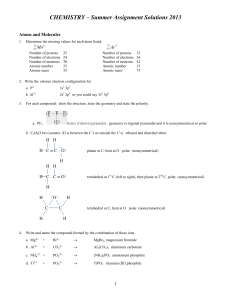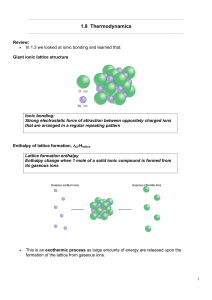
1.8 Thermodynamics
... 3) The resulting enthalpy change is known as the Enthalpy change of solution, DsolH: • If there is energy left over, it is given to the surroundings - exothermic • If there is not enough energy, it is taken in from the surroundings - endothermic • These can all be calculated in another type of Hess' ...
... 3) The resulting enthalpy change is known as the Enthalpy change of solution, DsolH: • If there is energy left over, it is given to the surroundings - exothermic • If there is not enough energy, it is taken in from the surroundings - endothermic • These can all be calculated in another type of Hess' ...
Donnan phenomena in membranes with charge due to ion
... problem, and so we elect to approximate this partition function using the Bragg-Williams model.12,13Thus we assume that the arrangement of particles is random (this would be the case in the absence of interaction). Proceeding in this way may not be quantitatively correct. In fact, there are approxim ...
... problem, and so we elect to approximate this partition function using the Bragg-Williams model.12,13Thus we assume that the arrangement of particles is random (this would be the case in the absence of interaction). Proceeding in this way may not be quantitatively correct. In fact, there are approxim ...
Chapter 7 – Chemical Formulas and Chemical
... are in H2O2 where is carries a -1 and compounds with F and it is +2. 5. H has an oxidation number of +1 with elements with higher electronegativities than it and -1 with all metals. 6. The algebraic sum of the oxidation numbers of all atoms in a neutral compound is equal to zero. 7. The algebraic su ...
... are in H2O2 where is carries a -1 and compounds with F and it is +2. 5. H has an oxidation number of +1 with elements with higher electronegativities than it and -1 with all metals. 6. The algebraic sum of the oxidation numbers of all atoms in a neutral compound is equal to zero. 7. The algebraic su ...
Identification of Aspartic and Isoaspartic Acid Residues in Amyloid β
... Asp isomerization;32,33 however, this can only be applied to detection of modification sites in the protein, but not to identify modifications already existing in biological samples prior the analysis. In addition, Alfaro et al. recently introduced a new method for the affinity enrichment of isoaspa ...
... Asp isomerization;32,33 however, this can only be applied to detection of modification sites in the protein, but not to identify modifications already existing in biological samples prior the analysis. In addition, Alfaro et al. recently introduced a new method for the affinity enrichment of isoaspa ...
AP Chemistry Unit 1 Essential Questions Screencast 1
... 1. What is Avogadro’s number? 2. What is molar mass? 3. Find the molar mass of water H2O? 4. How do you convert between grams and moles and moles and Avogadro’s number? ...
... 1. What is Avogadro’s number? 2. What is molar mass? 3. Find the molar mass of water H2O? 4. How do you convert between grams and moles and moles and Avogadro’s number? ...
Redox Reactions and Electrochemistry
... different concentrations. The driving force (i.e. the EMF) is provided by the difference in concentrations. ...
... different concentrations. The driving force (i.e. the EMF) is provided by the difference in concentrations. ...
Electron Shell Contributions to Gamma-ray Spectra of Positron Annihilation in Noble gases" J. Phys. B.: Atomic, Molecular and Optical Physics , 43 , 165207 (2010). Feng Wang, Lalitha Selvam, and C. M. Surko, Gleb F Gribakin, and C. M. Surko (PDF)
... shapes in close agreement with those measured, indicating (as expected) that the measurements are not due to a simple sum over the momentum densities for all atomic electrons. The robust nature of the present approach makes it possible for us to proceed to more complex molecular systems using the to ...
... shapes in close agreement with those measured, indicating (as expected) that the measurements are not due to a simple sum over the momentum densities for all atomic electrons. The robust nature of the present approach makes it possible for us to proceed to more complex molecular systems using the to ...
FREE Sample Here
... B) electrons are not symmetrically distributed in a molecule. C) molecules held by ionic bonds react with water. D) two polar covalent bonds react. E) a hydrogen atom loses an electron. Answer: B Topic: Concept 2.3 Skill: Knowledge/Comprehension 59) A van der Waals interaction is the weak attraction ...
... B) electrons are not symmetrically distributed in a molecule. C) molecules held by ionic bonds react with water. D) two polar covalent bonds react. E) a hydrogen atom loses an electron. Answer: B Topic: Concept 2.3 Skill: Knowledge/Comprehension 59) A van der Waals interaction is the weak attraction ...
7 - Wiley
... 39'). The best hybridization is sp2, leaving one p orbital free to form a π bond. The other inner N atom has SN = 2, sp hybridization, and bond angles of 180°. There are two π networks, one delocalized over all three N atoms and the other localized between the outer N atom and its adjacent inner N a ...
... 39'). The best hybridization is sp2, leaving one p orbital free to form a π bond. The other inner N atom has SN = 2, sp hybridization, and bond angles of 180°. There are two π networks, one delocalized over all three N atoms and the other localized between the outer N atom and its adjacent inner N a ...
metal-water interactions and hydrogen bond strength
... νOD vs. H···O and Ow···O bond lengths) are presented in Table 1. Recently linear correlations between the intramolecular bond valences sOH(D) and sOH(D) of water molecules in condensed materials and the wavenumbers of the respective uncoupled OD stretching modes of matrix-isolated HDO molecules hav ...
... νOD vs. H···O and Ow···O bond lengths) are presented in Table 1. Recently linear correlations between the intramolecular bond valences sOH(D) and sOH(D) of water molecules in condensed materials and the wavenumbers of the respective uncoupled OD stretching modes of matrix-isolated HDO molecules hav ...
Synthesis, Crystal-Structure Determination and Magnetic Properties
... ongoing challenge within inorganic solid-state chemistry. One of these ligands is the NCN2- anion, the corresponding base of the cyanamide molecule. Despite the existence of a number of M(NCN) cyanamide or carbodiimide salts of the main-group and nonmagnetic transition metals, the formation of such ...
... ongoing challenge within inorganic solid-state chemistry. One of these ligands is the NCN2- anion, the corresponding base of the cyanamide molecule. Despite the existence of a number of M(NCN) cyanamide or carbodiimide salts of the main-group and nonmagnetic transition metals, the formation of such ...
2014 Exams
... 20. (16 pts) H2S is bubbled through a Cu-As group unknown and a black precipitate forms. (NH4)2S is added and the black precipitate remains. The decantate “A” is set aside for further testing. The black solid is reacted with HNO3 to give a colorless solution, which is then reacted with H2SO4, giving ...
... 20. (16 pts) H2S is bubbled through a Cu-As group unknown and a black precipitate forms. (NH4)2S is added and the black precipitate remains. The decantate “A” is set aside for further testing. The black solid is reacted with HNO3 to give a colorless solution, which is then reacted with H2SO4, giving ...
ATOMIC THEORY
... tube. It is a vacuum tube - all the air has been pumped out. Because these rays originate at the ____________________, they are called cathode rays. Thomson concluded that cathode rays are made up of invisible, _________________________ charged particles referred to as electrons. From Thomson’s expe ...
... tube. It is a vacuum tube - all the air has been pumped out. Because these rays originate at the ____________________, they are called cathode rays. Thomson concluded that cathode rays are made up of invisible, _________________________ charged particles referred to as electrons. From Thomson’s expe ...
FREE Sample Here
... E) 24 amu (atomic mass units). Answer: D Topic: Concept 2.2 Skill: Knowledge/Comprehension 9) The nucleus of a nitrogen atom contains 7 neutrons and 7 protons. Which of the following is a correct statement concerning nitrogen? A) The nitrogen atom has a mass number of approximately 7 daltons and an ...
... E) 24 amu (atomic mass units). Answer: D Topic: Concept 2.2 Skill: Knowledge/Comprehension 9) The nucleus of a nitrogen atom contains 7 neutrons and 7 protons. Which of the following is a correct statement concerning nitrogen? A) The nitrogen atom has a mass number of approximately 7 daltons and an ...
Unit 2 matter - Kowenscience.com
... how many protons an atom of that element has. ▪ For instance, hydrogen has 1 proton, so it’s atomic number is ...
... how many protons an atom of that element has. ▪ For instance, hydrogen has 1 proton, so it’s atomic number is ...
Biology, 8e (Campbell) Chapter 2 The Chemical Context of Life
... B) electrons are not symmetrically distributed in a molecule. C) molecules held by ionic bonds react with water. D) two polar covalent bonds react. E) a hydrogen atom loses an electron. Answer: B Topic: Concept 2.3 Skill: Knowledge/Comprehension 59) A van der Waals interaction is the weak attraction ...
... B) electrons are not symmetrically distributed in a molecule. C) molecules held by ionic bonds react with water. D) two polar covalent bonds react. E) a hydrogen atom loses an electron. Answer: B Topic: Concept 2.3 Skill: Knowledge/Comprehension 59) A van der Waals interaction is the weak attraction ...
FREE Sample Here
... B) electrons are not symmetrically distributed in a molecule. C) molecules held by ionic bonds react with water. D) two polar covalent bonds react. E) a hydrogen atom loses an electron. Answer: B Topic: Concept 2.3 Skill: Knowledge/Comprehension 59) A van der Waals interaction is the weak attraction ...
... B) electrons are not symmetrically distributed in a molecule. C) molecules held by ionic bonds react with water. D) two polar covalent bonds react. E) a hydrogen atom loses an electron. Answer: B Topic: Concept 2.3 Skill: Knowledge/Comprehension 59) A van der Waals interaction is the weak attraction ...
FREE Sample Here
... B) electrons are not symmetrically distributed in a molecule. C) molecules held by ionic bonds react with water. D) two polar covalent bonds react. E) a hydrogen atom loses an electron. Answer: B Topic: Concept 2.3 Skill: Knowledge/Comprehension 59) A van der Waals interaction is the weak attraction ...
... B) electrons are not symmetrically distributed in a molecule. C) molecules held by ionic bonds react with water. D) two polar covalent bonds react. E) a hydrogen atom loses an electron. Answer: B Topic: Concept 2.3 Skill: Knowledge/Comprehension 59) A van der Waals interaction is the weak attraction ...
Unit 12: Electrochemistry
... ionization energy; they (and what it means for the can easily lose electrons element) - Table S when energy is added ...
... ionization energy; they (and what it means for the can easily lose electrons element) - Table S when energy is added ...
Chemistry - School District of Springfield Township
... and physical changes. • Describe the kinetic-molecular theory and explain how it accounts for observed solid, liquid, gas, and plasma behavior. • Describe the mathematical relationship between atomic behavior and the properties of matter and predict the behavior of matter through the application of ...
... and physical changes. • Describe the kinetic-molecular theory and explain how it accounts for observed solid, liquid, gas, and plasma behavior. • Describe the mathematical relationship between atomic behavior and the properties of matter and predict the behavior of matter through the application of ...
CHEMISTRY – Summer Assignment Solutions 2013
... Naming – always name the ions not the formulas (cation then anion). Name tells the type of ions involved not how many of each ion cations: name the element; if more than one oxidation state is possible (d-block) follow with the charge in Roman numerals in parentheses anions: if monatomic then use ...
... Naming – always name the ions not the formulas (cation then anion). Name tells the type of ions involved not how many of each ion cations: name the element; if more than one oxidation state is possible (d-block) follow with the charge in Roman numerals in parentheses anions: if monatomic then use ...
C - mvhs-fuhsd.org
... 63. Which of the following best represents the products of the net ionic equation for the reaction that occurs when solid barium phosphate and solid magnesium sulfide are added to water? A. Mg2+ + PO43- + BaS B. Mg3(PO4)2 + Ba2+ + S2C. Mg3(PO4)2 + BaS D. Mg2+ + PO43- + Ba2+ + S2E. BaMg + SPO4 64. W ...
... 63. Which of the following best represents the products of the net ionic equation for the reaction that occurs when solid barium phosphate and solid magnesium sulfide are added to water? A. Mg2+ + PO43- + BaS B. Mg3(PO4)2 + Ba2+ + S2C. Mg3(PO4)2 + BaS D. Mg2+ + PO43- + Ba2+ + S2E. BaMg + SPO4 64. W ...
Preface from the Textbook - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... stoichiometry and reaction classes, show how gas behavior is modeled, and highlight the relation between heat and chemical change. • Chapters 7 through 15 take an “atoms-first” approach, as they move from atomic structure and electron configuration to how atoms bond and what the resulting molecules ...
... stoichiometry and reaction classes, show how gas behavior is modeled, and highlight the relation between heat and chemical change. • Chapters 7 through 15 take an “atoms-first” approach, as they move from atomic structure and electron configuration to how atoms bond and what the resulting molecules ...