Dissociation energy of the Ar-HN complex
... optoacoustic absorptions of N20, CzH 2, HDO, OCS, NH 3 and H 2 0 [18,19]. In total, more than 25 bands with widely different intensities have been observed in the scanned frequency range, 14 of them being at least partly rotationally resolved. Except for one transition of H ~type, all bands had stru ...
... optoacoustic absorptions of N20, CzH 2, HDO, OCS, NH 3 and H 2 0 [18,19]. In total, more than 25 bands with widely different intensities have been observed in the scanned frequency range, 14 of them being at least partly rotationally resolved. Except for one transition of H ~type, all bands had stru ...
AP Chemistry Summer Assignment
... 1. If a compound ends in –ide, what does it tell you about the compound? 2. If a compound ends in –ate what does it tell you about the compound? 3. If a compound ends in –ite what does it tell you about the compound? 4. How does a cation form? What charge does it form? What type of element forms the ...
... 1. If a compound ends in –ide, what does it tell you about the compound? 2. If a compound ends in –ate what does it tell you about the compound? 3. If a compound ends in –ite what does it tell you about the compound? 4. How does a cation form? What charge does it form? What type of element forms the ...
II. Masses of Atoms
... • WHEN TWO PROTONS ARE EXTREMELY CLOSE TO EACH OTHER, THERE IS A STRONG ATTRACTION BETWEEN THEM. • A SIMILAR ATTRACTION EXISTS WHEN NEUTRONS ARE VERY CLOSE TO EACH OTHER OR WHEN PROTONS AND NEUTRONS ARE VERY CLOSE TOGETHER. • THE SHORT-RANGE PROTON-NEUTRON, PROTON-PROTON, AND NEUTRON-NEUTRON FORCES ...
... • WHEN TWO PROTONS ARE EXTREMELY CLOSE TO EACH OTHER, THERE IS A STRONG ATTRACTION BETWEEN THEM. • A SIMILAR ATTRACTION EXISTS WHEN NEUTRONS ARE VERY CLOSE TO EACH OTHER OR WHEN PROTONS AND NEUTRONS ARE VERY CLOSE TOGETHER. • THE SHORT-RANGE PROTON-NEUTRON, PROTON-PROTON, AND NEUTRON-NEUTRON FORCES ...
Chemical Reactions and Stoichiometry
... a. Evolution of heat and light (simultaneously) b. Production of a gas (bubbles, odor change) c. Formation of a precipitate (solid, cloudy) d. Color change (not introduced by an outside source such as dye or ink) Characteristics of a Chemical Reaction – the atoms in one or more reactant rearrange wh ...
... a. Evolution of heat and light (simultaneously) b. Production of a gas (bubbles, odor change) c. Formation of a precipitate (solid, cloudy) d. Color change (not introduced by an outside source such as dye or ink) Characteristics of a Chemical Reaction – the atoms in one or more reactant rearrange wh ...
20-2 Chemistry of Acyl Halides and Anhydrides(PPT)
... Ketone formation is best achieved by using diorganocuprates rather than RLi or RMgX. The latter are unselective and tend to attack more than once leading to alcohol formation. ...
... Ketone formation is best achieved by using diorganocuprates rather than RLi or RMgX. The latter are unselective and tend to attack more than once leading to alcohol formation. ...
File
... Award [3] for correct final answer. Award [2] for (+)540. If old Data Booklet is used accept answer: –535 (kJ mol–1) or award [2] for (+)535. ...
... Award [3] for correct final answer. Award [2] for (+)540. If old Data Booklet is used accept answer: –535 (kJ mol–1) or award [2] for (+)535. ...
What Are Compounds? - Parma School District
... • The charges on the ions in an ionic compound reflect the electron distribution of the compound. • In order to indicate the general distribution of electrons among the bonded atoms in a molecular compound or a polyatomic ion, oxidation numbers are assigned to the atoms composing the compound or ion ...
... • The charges on the ions in an ionic compound reflect the electron distribution of the compound. • In order to indicate the general distribution of electrons among the bonded atoms in a molecular compound or a polyatomic ion, oxidation numbers are assigned to the atoms composing the compound or ion ...
DCY1B - Manonmaniam Sundaranar University
... They have high melting and boiling points except Zn, Cd and Hg. The low melting point of Zn, Cd and Hg may be attributed to the completely filled d-level. (iv) Atomic (covalent) radii: Atomic radii decrease along each transition series due to the increase in nuclear charge. But the decrease in atomi ...
... They have high melting and boiling points except Zn, Cd and Hg. The low melting point of Zn, Cd and Hg may be attributed to the completely filled d-level. (iv) Atomic (covalent) radii: Atomic radii decrease along each transition series due to the increase in nuclear charge. But the decrease in atomi ...
Electronic structure and reactivity analysis of some TTF
... properties of the TTF moiety includes its ability to form molecular metals and superconductors at low temperatures. It has also been incorporated in a number of macrocyclic systems for use as molecular sensors, enzyme biosensors, switches, wires and shuttles, exploiting the inherent electron donor p ...
... properties of the TTF moiety includes its ability to form molecular metals and superconductors at low temperatures. It has also been incorporated in a number of macrocyclic systems for use as molecular sensors, enzyme biosensors, switches, wires and shuttles, exploiting the inherent electron donor p ...
IGCSE SoW 2013
... Describe experiments to demonstrate that a more reactive halogen will displace a less reactive halogen from a solution of one of its salts ...
... Describe experiments to demonstrate that a more reactive halogen will displace a less reactive halogen from a solution of one of its salts ...
Chapter 5 notes
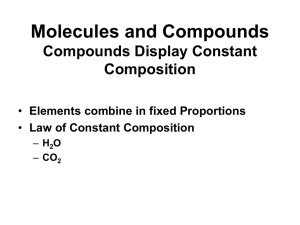
... A compound is a substance composed of two or more elements combined in a specific ratio and held together by chemical bonds. A molecule is formed when two or more atoms join together chemically. A compound is a molecule that contains at least two different elements. All compounds are molecules but n ...
... A compound is a substance composed of two or more elements combined in a specific ratio and held together by chemical bonds. A molecule is formed when two or more atoms join together chemically. A compound is a molecule that contains at least two different elements. All compounds are molecules but n ...
Chemical Reactions and The Mole
... The process of dissolving a solid in a liquid is very common, sugar in water, salt in soup are two obvious examples, but what is the dissolving process? First, let’s define a few terms. A solvent is the substance in a solution that is present in the greater amount. It is the major part of a solution ...
... The process of dissolving a solid in a liquid is very common, sugar in water, salt in soup are two obvious examples, but what is the dissolving process? First, let’s define a few terms. A solvent is the substance in a solution that is present in the greater amount. It is the major part of a solution ...
Miami-Dade College
... j. Relating the strength of acids and bases to their equilibrium constants. k. Describing the effect of adding a “common ion” on the equilibrium. l. Recognizing a buffer solution and giving illustrations of its operation. m. Predicting the effect upon the pH when adding a strong acid or a strong bas ...
... j. Relating the strength of acids and bases to their equilibrium constants. k. Describing the effect of adding a “common ion” on the equilibrium. l. Recognizing a buffer solution and giving illustrations of its operation. m. Predicting the effect upon the pH when adding a strong acid or a strong bas ...
Unit 1 review
... Cations (has a less electrons) Has a positive charge Most common 1+ : H, Li, Na, K, Cs, Ag 2+ : Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, Zn, Cd 3+ : Al ...
... Cations (has a less electrons) Has a positive charge Most common 1+ : H, Li, Na, K, Cs, Ag 2+ : Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, Zn, Cd 3+ : Al ...
AP Chemistry Summer Assignment
... a. Kg b. Liter c. m3 d. mm e. kg/m3 f. Joule g. atm h. cal i. Torr j. g/ml 4. Most laboratory experiments are performed at room temperature at 65˚C. Express this temperature in: a. ˚F b. K 5. A cylinder rod formed from silicon is 46.0 cm long and has a mass of 3.00 kg. The density of silicon is 2.33 ...
... a. Kg b. Liter c. m3 d. mm e. kg/m3 f. Joule g. atm h. cal i. Torr j. g/ml 4. Most laboratory experiments are performed at room temperature at 65˚C. Express this temperature in: a. ˚F b. K 5. A cylinder rod formed from silicon is 46.0 cm long and has a mass of 3.00 kg. The density of silicon is 2.33 ...
Specific adsorption of carbonate ions at the zinc oxide/electrolyte
... been a subject of many studies. ZnO is one of important ceramic materials and has been found to have diversified applications in electronic devices such as gas sensors, varistors and transducers. The adsorption process of ions at the metal oxide/water solution interface and its influence on the elec ...
... been a subject of many studies. ZnO is one of important ceramic materials and has been found to have diversified applications in electronic devices such as gas sensors, varistors and transducers. The adsorption process of ions at the metal oxide/water solution interface and its influence on the elec ...
State Standard - SchoolNotes.com
... ionization energy, electron affinity, atomic size, ionic size, and reactivity). C-2.4 Compare the nuclear reactions of fission and fusion to chemical reactions (including the parts of the atom involved and the relative amounts of energy released). C-2.5 Compare alpha, beta, and gamma radiation in te ...
... ionization energy, electron affinity, atomic size, ionic size, and reactivity). C-2.4 Compare the nuclear reactions of fission and fusion to chemical reactions (including the parts of the atom involved and the relative amounts of energy released). C-2.5 Compare alpha, beta, and gamma radiation in te ...
REACTION PREDICTION
... Double Replacement (metathesis) Two compounds react to form two new compounds. All double replacement reactions must have a "driving force" that removes a pair of ions from solution. Ions keep their same charges as reactants and products. Formation of a precipitate: A precipitate is an insoluble su ...
... Double Replacement (metathesis) Two compounds react to form two new compounds. All double replacement reactions must have a "driving force" that removes a pair of ions from solution. Ions keep their same charges as reactants and products. Formation of a precipitate: A precipitate is an insoluble su ...
pblock - Chemistry Courses
... 2nd period: Only s and p orbitals are possible with n = 2 Therefore, the maximum number of bonds is 4 (single and/or double bonds) Examples: CH4, NF4+, BH43rd (and higher periods): can use d-orbitals to make bonds E.g. ...
... 2nd period: Only s and p orbitals are possible with n = 2 Therefore, the maximum number of bonds is 4 (single and/or double bonds) Examples: CH4, NF4+, BH43rd (and higher periods): can use d-orbitals to make bonds E.g. ...
The Big book of C1 chemistry
... C1.3.3 Properties and uses of metals The elements in the central block of the periodic table are known as transition metals. Like other metals they are good conductors of heat and electricity and can be bent or hammered into shape. They are useful as structural materials and for making things that m ...
... C1.3.3 Properties and uses of metals The elements in the central block of the periodic table are known as transition metals. Like other metals they are good conductors of heat and electricity and can be bent or hammered into shape. They are useful as structural materials and for making things that m ...
The Buffer Equation
... solvent through the membrane by a distillation process or by dissolving in the material of the membrane in which the solute is insoluble. In other cases, the membrane may act as a sieve, having a pore size sufficiently large to allow passage of solvent but not of solute molecules, in either case, th ...
... solvent through the membrane by a distillation process or by dissolving in the material of the membrane in which the solute is insoluble. In other cases, the membrane may act as a sieve, having a pore size sufficiently large to allow passage of solvent but not of solute molecules, in either case, th ...
AP Chemistry Review Preparing for the AP
... Give examples and solve calculation problems related to each of the three theories. Sketch a cathode ray tube as demonstrated in class and state how J.J. Thomson’s experiments led to the idea that atoms have positive and negative parts, the negative parts are all the same, and the negative parts ...
... Give examples and solve calculation problems related to each of the three theories. Sketch a cathode ray tube as demonstrated in class and state how J.J. Thomson’s experiments led to the idea that atoms have positive and negative parts, the negative parts are all the same, and the negative parts ...
Acids and bases
... Hydrogen bromide and iodide behave similarly but the extent of ionization of the three hydrogen halides varies along the series: HI > HBr > HCl. This contrasts with the fact that all three compounds are classed as strong acids (i.e. fully ionized) in aqueous solution. Thus, acetic acid exerts a diff ...
... Hydrogen bromide and iodide behave similarly but the extent of ionization of the three hydrogen halides varies along the series: HI > HBr > HCl. This contrasts with the fact that all three compounds are classed as strong acids (i.e. fully ionized) in aqueous solution. Thus, acetic acid exerts a diff ...
Eastern Kentucky University
... Describe and define terms and conditions associated with atomic structure and atomic theory Recognize and describe how the periodic table of elements is used and the structure of the table List and describe how the various bonding forces act to hold atoms together Define the various structures of ma ...
... Describe and define terms and conditions associated with atomic structure and atomic theory Recognize and describe how the periodic table of elements is used and the structure of the table List and describe how the various bonding forces act to hold atoms together Define the various structures of ma ...