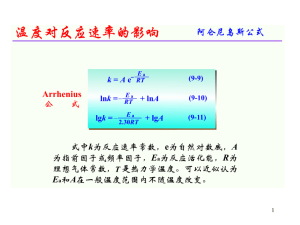
Electrophilic Additions to Double Bonds
... Certainly no subject or field is making more progress on so many fronts at the present moment than biology, and if we were to name the most powerful assumption of all, which leads one on and on in an attempt to understand life, it is that all things are made of atoms, and that everything that living ...
... Certainly no subject or field is making more progress on so many fronts at the present moment than biology, and if we were to name the most powerful assumption of all, which leads one on and on in an attempt to understand life, it is that all things are made of atoms, and that everything that living ...
AQA_GCSE_Chemistry_Higher_Unit_2_Notes
... 1. Covalent bonds are formed between 2 non-metallic elements. 2. The atoms share electrons in order to complete their outer shells. 3. The atoms all attain noble gas structure (complete outer shells). 4. The new particles formed are neutral molecules. Structures of Substances There are 4 main struct ...
... 1. Covalent bonds are formed between 2 non-metallic elements. 2. The atoms share electrons in order to complete their outer shells. 3. The atoms all attain noble gas structure (complete outer shells). 4. The new particles formed are neutral molecules. Structures of Substances There are 4 main struct ...
Chemistry EOC Review 2015 Name Per ___ This review is part of
... Describe trends in properties (e.g., ionization energy or reactivity as a function of location on the periodic table, boiling point of organic liquids as a function of molecular weight). Atomic radius is one-half of the distance between the center of identical atoms that are not bonded together. Ion ...
... Describe trends in properties (e.g., ionization energy or reactivity as a function of location on the periodic table, boiling point of organic liquids as a function of molecular weight). Atomic radius is one-half of the distance between the center of identical atoms that are not bonded together. Ion ...
Ideas to Implementation by Jonathan Chan
... These holes act as a positive flow of current moving in the opposite direction to the electron current flow. Conduction in the conduction band is a flow of electrons and in the valence band is a flow of positive holes. The hole current flows towards the negative potential while the electron current ...
... These holes act as a positive flow of current moving in the opposite direction to the electron current flow. Conduction in the conduction band is a flow of electrons and in the valence band is a flow of positive holes. The hole current flows towards the negative potential while the electron current ...
File
... “Electromagnetic Spectrum” from Reference Tables to relate color, frequency and wavelength of the light emitted to the energy of the photon); s, p, d and f blocks on the periodic table, electron configurations ...
... “Electromagnetic Spectrum” from Reference Tables to relate color, frequency and wavelength of the light emitted to the energy of the photon); s, p, d and f blocks on the periodic table, electron configurations ...
Test Objectives: Unit 1 – Measurement
... List the elements that are liquids & gases at STP List the 7 diatomic elements List the properties of metals, non-metals & metalloids Identify an element as a metal, non-metal or metalloid based upon its properties Memorize: “Metals are Losers, Are you sure? Yes, I’m Positive” and be able to explain ...
... List the elements that are liquids & gases at STP List the 7 diatomic elements List the properties of metals, non-metals & metalloids Identify an element as a metal, non-metal or metalloid based upon its properties Memorize: “Metals are Losers, Are you sure? Yes, I’m Positive” and be able to explain ...
elements in a family have the same number of
... Atoms of this family have 6 valence electrons. Most elements in this family share electrons when forming compounds. Oxygen is the most abundant element in the earth’s crust. It is extremely active and combines with almost all elements. ...
... Atoms of this family have 6 valence electrons. Most elements in this family share electrons when forming compounds. Oxygen is the most abundant element in the earth’s crust. It is extremely active and combines with almost all elements. ...
Chapter 8: Ionic Compounds
... a single positive charge. The 11 protons that establish the character of sodium still remain within its nucleus. Reactivity of metals is based on the ease with which they lose valence electrons to achieve a stable octet, or noble gas configuration. Group 1A elements, [noble gas]ns1, lose their one v ...
... a single positive charge. The 11 protons that establish the character of sodium still remain within its nucleus. Reactivity of metals is based on the ease with which they lose valence electrons to achieve a stable octet, or noble gas configuration. Group 1A elements, [noble gas]ns1, lose their one v ...
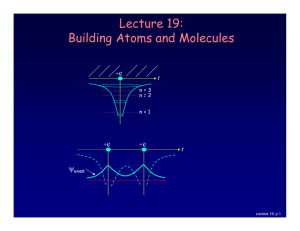
Lecture 19: Building Atoms and Molecules
... which is described by an additional quantum number, mp, and therefore also a magnetic moment. However, it is several orders of magnitude smaller than that of the electron. ...
... which is described by an additional quantum number, mp, and therefore also a magnetic moment. However, it is several orders of magnitude smaller than that of the electron. ...
Monte Carlo studies of a novel X-ray tube anode design
... 1. Introduction The intense multiple scattering experienced by electrons due to the numerous electron–electron and electron–nucleus collisions as they slow down in matter gives rise to the phenomenon of electron back scattering from absorbers. For electrons with energies up to several hundred keV th ...
... 1. Introduction The intense multiple scattering experienced by electrons due to the numerous electron–electron and electron–nucleus collisions as they slow down in matter gives rise to the phenomenon of electron back scattering from absorbers. For electrons with energies up to several hundred keV th ...
Compounds & Moles
... One mole of pennies stacked on top of each other would reach from the Earth to the moon 7 times If you started counting when you were born and never stopped until the day you died, you would never come close to reaching 6.022×1023 ...
... One mole of pennies stacked on top of each other would reach from the Earth to the moon 7 times If you started counting when you were born and never stopped until the day you died, you would never come close to reaching 6.022×1023 ...
Photosynthesis has 3 stages
... In the fall the leaves turn many different colors. This is because there is another pigment found in them. This pigment is called (s)________________. Having both kinds of pigments allows plants to (t) ________________ more light energy. Production of oxygen: Disk shaped structures that are embedded ...
... In the fall the leaves turn many different colors. This is because there is another pigment found in them. This pigment is called (s)________________. Having both kinds of pigments allows plants to (t) ________________ more light energy. Production of oxygen: Disk shaped structures that are embedded ...
Chemical Bonding
... Formation of a chemical bond Free atoms of elements are in random motion and possess some energy. Farther the atoms are, greater is their energy and lesser is the stability. Two or more atoms unite to form a molecule because in doing so, the energy of the united atoms is lowered. Thus the ‘molecule’ ...
... Formation of a chemical bond Free atoms of elements are in random motion and possess some energy. Farther the atoms are, greater is their energy and lesser is the stability. Two or more atoms unite to form a molecule because in doing so, the energy of the united atoms is lowered. Thus the ‘molecule’ ...
UNIT NUM="1" ID="UN
... building the atoms of the other elements by adding 1 proton and 1 electron at a time (along with an appropriate number of neutrons). Figure 2.9, an abbreviated version of what is called the periodic table of the elements, shows this distribution of electrons for the first 18 elements, from hydrogen ...
... building the atoms of the other elements by adding 1 proton and 1 electron at a time (along with an appropriate number of neutrons). Figure 2.9, an abbreviated version of what is called the periodic table of the elements, shows this distribution of electrons for the first 18 elements, from hydrogen ...
O - gearju.com
... atoms are bonded to each other. Put least electronegative element in the center. 2. Count total number of valence e−. Add 1 for each negative charge. Subtract 1 for each positive charge. 3. Draw a single covalent bond between the central and each surrounding atom. Complete an octet for all atoms exc ...
... atoms are bonded to each other. Put least electronegative element in the center. 2. Count total number of valence e−. Add 1 for each negative charge. Subtract 1 for each positive charge. 3. Draw a single covalent bond between the central and each surrounding atom. Complete an octet for all atoms exc ...
O - gearju.com
... atoms are bonded to each other. Put least electronegative element in the center. 2. Count total number of valence e−. Add 1 for each negative charge. Subtract 1 for each positive charge. 3. Draw a single covalent bond between the central and each surrounding atom. Complete an octet for all atoms exc ...
... atoms are bonded to each other. Put least electronegative element in the center. 2. Count total number of valence e−. Add 1 for each negative charge. Subtract 1 for each positive charge. 3. Draw a single covalent bond between the central and each surrounding atom. Complete an octet for all atoms exc ...
Chapter 8 – Covalent Bonding
... Double Covalent Bond – a bond that involves two shared pairs of electrons Triple Covalent Bond – a bond that involves three shared pairs of electrons Let’s Practice ...
... Double Covalent Bond – a bond that involves two shared pairs of electrons Triple Covalent Bond – a bond that involves three shared pairs of electrons Let’s Practice ...
File
... Inside the battery itself, a chemical reaction produces the electrons. Electrons flow from the battery into a wire, and must travel from the negative to the positive terminal (anode to cathode) for the chemical reaction to take place. That is why a battery can sit on a shelf for a year and still ha ...
... Inside the battery itself, a chemical reaction produces the electrons. Electrons flow from the battery into a wire, and must travel from the negative to the positive terminal (anode to cathode) for the chemical reaction to take place. That is why a battery can sit on a shelf for a year and still ha ...
3.091 – Introduction to Solid State Chemistry Lecture Notes No
... (Group VIII) are the most stable elements with regard to bond formation, i.e. toward electronic rearrangements. It is therefore useful to examine the reasons for their stability. Inert gases all have electronic structures consisting of filled subshells. For all but helium the outer (or valence) shel ...
... (Group VIII) are the most stable elements with regard to bond formation, i.e. toward electronic rearrangements. It is therefore useful to examine the reasons for their stability. Inert gases all have electronic structures consisting of filled subshells. For all but helium the outer (or valence) shel ...
Ch. 20 study questions
... cathode half-cell had decreased to .50 M a. Calculate the initial cell potential b. Calculate the cell potential at time, t. c. Calculate the total charge provided by the cell. d Calculate (approx.) the energy provided by the cell. ...
... cathode half-cell had decreased to .50 M a. Calculate the initial cell potential b. Calculate the cell potential at time, t. c. Calculate the total charge provided by the cell. d Calculate (approx.) the energy provided by the cell. ...
Final Analysis – Exam Review
... Production of heat b. Colour d. Formation of a new gas Fill in the blanks: 1. Mass is the amount of _____________________________in an object. 2. Volume is the amount of ____________________________ that matter occupies. 3. Tap water is considered to be a(n) ___________________________ not a compoun ...
... Production of heat b. Colour d. Formation of a new gas Fill in the blanks: 1. Mass is the amount of _____________________________in an object. 2. Volume is the amount of ____________________________ that matter occupies. 3. Tap water is considered to be a(n) ___________________________ not a compoun ...
Lecture 7
... Like group 1 compounds, much of the reactivity is due to the reactions of the anions, but unlike group 1, the cations here have twice as much charge and so are more polarizing. This polarizing power is especially noticeable at the top of the group: the beryllium ion is very small and polarizes water ...
... Like group 1 compounds, much of the reactivity is due to the reactions of the anions, but unlike group 1, the cations here have twice as much charge and so are more polarizing. This polarizing power is especially noticeable at the top of the group: the beryllium ion is very small and polarizes water ...