Chemistry Standards Checklist
... b. Compare and contrast trends in the chemical and physical properties of elements and their placement on the Periodic Table. SC5. Students will understand that the rate at which a chemical reaction occurs can be affected by changing concentration, temperature, or pressure and the addition of a ...
... b. Compare and contrast trends in the chemical and physical properties of elements and their placement on the Periodic Table. SC5. Students will understand that the rate at which a chemical reaction occurs can be affected by changing concentration, temperature, or pressure and the addition of a ...
The Wizard Test Maker
... 2. Which of the following is NOT the same for isotopes of the same element? (A) Mass number (B) Atomic number (C) Number of protons (D) Number of valence electrons (E) Number of occupied electron shells in the ground state 3. Two isotopes of uranium are U-237 and U-238. Both would be expected to hav ...
... 2. Which of the following is NOT the same for isotopes of the same element? (A) Mass number (B) Atomic number (C) Number of protons (D) Number of valence electrons (E) Number of occupied electron shells in the ground state 3. Two isotopes of uranium are U-237 and U-238. Both would be expected to hav ...
Metric conversion chart - Welcome to Chemistry At Central High
... Matter & Energy equivalence: E = m c2 ; (“large” units: use Joules, kg and m/sec) 1 amu = 931.494 MeV of energy (For atomic scale units) Radioactive decay: ln N0 – ln Nt = 0.693 t half-life; Electrons: Planck’s constant, h= 6.63 x 10–34 J sec ...
... Matter & Energy equivalence: E = m c2 ; (“large” units: use Joules, kg and m/sec) 1 amu = 931.494 MeV of energy (For atomic scale units) Radioactive decay: ln N0 – ln Nt = 0.693 t half-life; Electrons: Planck’s constant, h= 6.63 x 10–34 J sec ...
Key
... a) How many types of orbitals are there in the shell with n=3 in an atom? b) What is the maximum number of electrons in a set of 5d orbitals? a) Write the electron configuration for the silicon atom. b) Write the noble gas configuration for nickel, (Ni)? c) The element with an electron configuration ...
... a) How many types of orbitals are there in the shell with n=3 in an atom? b) What is the maximum number of electrons in a set of 5d orbitals? a) Write the electron configuration for the silicon atom. b) Write the noble gas configuration for nickel, (Ni)? c) The element with an electron configuration ...
O usually has oxidation number of -2, except in peroxides where it is
... The sum of the oxidation numbers of the elements in a polyatomic ion must equal the ion charge. Consider these examples. If there are two poly atomic ions in a compound deal with them first. e.g. Carbonate ion, . O has oxidation number of -2. There are 3O’s in the formula so the total negative charg ...
... The sum of the oxidation numbers of the elements in a polyatomic ion must equal the ion charge. Consider these examples. If there are two poly atomic ions in a compound deal with them first. e.g. Carbonate ion, . O has oxidation number of -2. There are 3O’s in the formula so the total negative charg ...
Slide 1
... The compounds of transition metals are usually brightly colored and are often used to color paints. Transition elements have 1 or 2 valence electrons, which they lose when they form bonds with other atoms. Some transition elements can lose electrons in their next-to-outermost level. ...
... The compounds of transition metals are usually brightly colored and are often used to color paints. Transition elements have 1 or 2 valence electrons, which they lose when they form bonds with other atoms. Some transition elements can lose electrons in their next-to-outermost level. ...
Charge
... Electrostatics is the study of the effects of stationary charges on each other in their surroundings. Charges are created by the transfer of electrons to or from one body to another. (Protons are NEVER transferred.) Objects with equal numbers of protons and electrons are neutral. They have no net c ...
... Electrostatics is the study of the effects of stationary charges on each other in their surroundings. Charges are created by the transfer of electrons to or from one body to another. (Protons are NEVER transferred.) Objects with equal numbers of protons and electrons are neutral. They have no net c ...
SPS1: Students will investigate our current understanding of the
... Conductivity-ABILITY TO CONDUCT ELECTRICITY (IONIC COMPOUNDS The conductivity gives important clues as to the type of solute dissolved. In aqueous (waterbased) solutions, dissolved ionic compounds yield solutions with high conductivity. Cations and anions readily carry electrical charges through t ...
... Conductivity-ABILITY TO CONDUCT ELECTRICITY (IONIC COMPOUNDS The conductivity gives important clues as to the type of solute dissolved. In aqueous (waterbased) solutions, dissolved ionic compounds yield solutions with high conductivity. Cations and anions readily carry electrical charges through t ...
1. The compound which could act both as oxidising as well as
... (d) Fe3+ (c) Cr (atomic numbers: Cr = 24, Fe = 26, Co = 27, Ni = 28) The correct sequence of the increasing order of the number of unpaired electrons in these ions is (a) 1, 2, 3, 4 (b) 4, 2, 3, 1 (c) 1, 3, 2, 4 (d) 3, 4, 2, 1 If Auf - bau rule is not followed, 19th electron in Fe (Z = 21) will have ...
... (d) Fe3+ (c) Cr (atomic numbers: Cr = 24, Fe = 26, Co = 27, Ni = 28) The correct sequence of the increasing order of the number of unpaired electrons in these ions is (a) 1, 2, 3, 4 (b) 4, 2, 3, 1 (c) 1, 3, 2, 4 (d) 3, 4, 2, 1 If Auf - bau rule is not followed, 19th electron in Fe (Z = 21) will have ...
AS Paper 1 Practice Paper 16 - A
... Sodium azide has a high melting point. Predict the type of bonding in a crystal of sodium azide. Suggest why its melting point is high. Type of bonding ............................................................................................. Reason for high melting point ........................ ...
... Sodium azide has a high melting point. Predict the type of bonding in a crystal of sodium azide. Suggest why its melting point is high. Type of bonding ............................................................................................. Reason for high melting point ........................ ...
Reduction and Oxidation
... bond. It can be considered as the charge that an atom would have if the more electronegative atom in a bond obtains the two electrons of the bond completely. When an element is ascribed a particular oxidation number, it is called the element is in a specific oxidation sta ...
... bond. It can be considered as the charge that an atom would have if the more electronegative atom in a bond obtains the two electrons of the bond completely. When an element is ascribed a particular oxidation number, it is called the element is in a specific oxidation sta ...
the Language of Chemistry
... He was the first person to make the distinction between organic and inorganic compounds. He introduced the classical system of chemical symbols in 1811, in which elements are abbreviated by one or two letters to make a distinct abbreviation from their Latin names. He developed the radical theory of ...
... He was the first person to make the distinction between organic and inorganic compounds. He introduced the classical system of chemical symbols in 1811, in which elements are abbreviated by one or two letters to make a distinct abbreviation from their Latin names. He developed the radical theory of ...
Lecture 2 - Chemistry at Winthrop University
... Complete and Net Ionic Equations • A Complete Ionic Equation shows all chemical species present in the reaction • A Net Ionic Equation shows the net change taking place in the reaction – The Net Ionic Equation is made by taking the Spectator Ions out of the complete ionic equation ...
... Complete and Net Ionic Equations • A Complete Ionic Equation shows all chemical species present in the reaction • A Net Ionic Equation shows the net change taking place in the reaction – The Net Ionic Equation is made by taking the Spectator Ions out of the complete ionic equation ...
1 - WordPress.com
... 40. An ionic bond forms between what types of elements? A metal and a nonmetal An ionic bond is the attraction between positively charged metal cations and negatively charged anions. In an ionic bond, electrons are transferred from the metal (cation) to the nonmetal (anion). What is the structure of ...
... 40. An ionic bond forms between what types of elements? A metal and a nonmetal An ionic bond is the attraction between positively charged metal cations and negatively charged anions. In an ionic bond, electrons are transferred from the metal (cation) to the nonmetal (anion). What is the structure of ...
The ocean is a mixture.
... Transition elements have properties similar to one another and to other metals, but their properties do not fit in with those of any other family. Many transition metals combine chemically with oxygen to form compounds called oxides. They have one or two electrons in the outer level Reactivity: less ...
... Transition elements have properties similar to one another and to other metals, but their properties do not fit in with those of any other family. Many transition metals combine chemically with oxygen to form compounds called oxides. They have one or two electrons in the outer level Reactivity: less ...
Lectures 1-6 - TCD Chemistry
... of mixing; real solutions, effect of intermolecular forces on ΔH of solution. ...
... of mixing; real solutions, effect of intermolecular forces on ΔH of solution. ...
chapter 4 review: types of chemical reactions and
... Write molecular, complete ionic, and net ionic equations. 6. Aqueous nickel (II) chloride reacts with aqueous sodium hydroxide molecular: ...
... Write molecular, complete ionic, and net ionic equations. 6. Aqueous nickel (II) chloride reacts with aqueous sodium hydroxide molecular: ...
Chem. 121, Sec 11 Name: Student I.D. Please Show Your Work
... 8. Determine the relative rates of diffusion of hydrogen gas and oxygen gas at 25◦C? (3 marks) ...
... 8. Determine the relative rates of diffusion of hydrogen gas and oxygen gas at 25◦C? (3 marks) ...
nuclear physics ppt
... A nucleon is a general term to denote a nuclear particle - that is, either a proton or a neutron. The atomic number Z of an element is equal to the number of protons in the nucleus of that element. The mass number A of an element is equal to the total number of nucleons (protons + neutrons). The mas ...
... A nucleon is a general term to denote a nuclear particle - that is, either a proton or a neutron. The atomic number Z of an element is equal to the number of protons in the nucleus of that element. The mass number A of an element is equal to the total number of nucleons (protons + neutrons). The mas ...
Production of Materials by Jimmy Huang
... The alkene further splits into smaller alkenes until either ethylene or propene (or both) is formed e.g. C5H10 C2H4 + C3H6. Therefore, the overall products of catalytic cracking are alkanes of shorter chain lengths and small alkenes. The catalysts used are inorganic compounds known as zeolites, wh ...
... The alkene further splits into smaller alkenes until either ethylene or propene (or both) is formed e.g. C5H10 C2H4 + C3H6. Therefore, the overall products of catalytic cracking are alkanes of shorter chain lengths and small alkenes. The catalysts used are inorganic compounds known as zeolites, wh ...
Document
... 34. Why do metals generally have lower ionizations energies than nonmetals? Metals have loosely held valence electrons. Metals want to lose electrons to have a stable octet. It is easier for a metal to lose 1,2, 3, or 4 electrons than gain that number. Metals have low electronegativities and are not ...
... 34. Why do metals generally have lower ionizations energies than nonmetals? Metals have loosely held valence electrons. Metals want to lose electrons to have a stable octet. It is easier for a metal to lose 1,2, 3, or 4 electrons than gain that number. Metals have low electronegativities and are not ...
Chemistry Final Exam Review 2013
... 1. Which idea of John Dalton is no longer considered part of the modern view of atoms? a. Atoms are extremely small. b. Atoms of the same element have identical masses. c. Atoms combine in simple whole number ratios to form compounds. d. Atoms of different elements can combine in different ratios to ...
... 1. Which idea of John Dalton is no longer considered part of the modern view of atoms? a. Atoms are extremely small. b. Atoms of the same element have identical masses. c. Atoms combine in simple whole number ratios to form compounds. d. Atoms of different elements can combine in different ratios to ...
Chapter 4 - Mr. Fischer.com
... An atom is the smallest particle of an element that retains its identity in a chemical reaction. A. Early philosophers believed that atoms were indivisible and indestructible. B. Dalton’s Atomic theory. Dalton used experimental methods, to transform Democritus’s ideas on atoms into scientific theory ...
... An atom is the smallest particle of an element that retains its identity in a chemical reaction. A. Early philosophers believed that atoms were indivisible and indestructible. B. Dalton’s Atomic theory. Dalton used experimental methods, to transform Democritus’s ideas on atoms into scientific theory ...
File
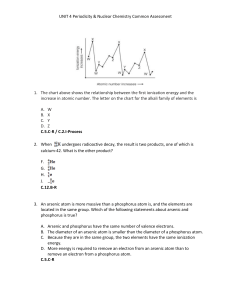
... 4. Iodine-131 is a radioactive isotope with a half-life of 8 days. How many grams of a 64 g sample of iodine-131 will remain at the end of 24 days? F. 56 g G. 48 g H. 32 g J. 8 g C.12.B-R / C.2.G-Process 5. What element in the second period has the largest atomic radius? A. Carbon B. Lithium C. Pota ...
... 4. Iodine-131 is a radioactive isotope with a half-life of 8 days. How many grams of a 64 g sample of iodine-131 will remain at the end of 24 days? F. 56 g G. 48 g H. 32 g J. 8 g C.12.B-R / C.2.G-Process 5. What element in the second period has the largest atomic radius? A. Carbon B. Lithium C. Pota ...
Partial Pressures of Gases
... Steps for Balancing Chemical Equations by Inspection 1. Write the chemical formula for each reactant and product, including the state of matter for each one. 2. Try balancing any atom that is not in a polyatomic ion and is not carbon, oxygen or hydrogen.(ECHO) 3. If possible, balance polyatomic ions ...
... Steps for Balancing Chemical Equations by Inspection 1. Write the chemical formula for each reactant and product, including the state of matter for each one. 2. Try balancing any atom that is not in a polyatomic ion and is not carbon, oxygen or hydrogen.(ECHO) 3. If possible, balance polyatomic ions ...