3 chemical foundations: elements, atoms and ions
... 3.4 Natural States of the Elements Matter almost always is found as mixtures of different chemical compounds. Elements are rarely found in their pure forms. However, some elements are relatively unreactive and, on occasion, may be found in pure form. Examples include: the noble metals such as gold ( ...
... 3.4 Natural States of the Elements Matter almost always is found as mixtures of different chemical compounds. Elements are rarely found in their pure forms. However, some elements are relatively unreactive and, on occasion, may be found in pure form. Examples include: the noble metals such as gold ( ...
Chapter1 - WilsonChemWiki
... Examples: write the ionic forms for Na (Group 1A), Mg (Group 2A), Cl (Group 7A). Answer: Na+, Mg+2, Cl-. Ionic Compounds Ionic compounds: are formed between Metals and Non-metals when the valence electrons are transferred. (Metal) cations and (nonmetal) anions are held together by an electrostatic a ...
... Examples: write the ionic forms for Na (Group 1A), Mg (Group 2A), Cl (Group 7A). Answer: Na+, Mg+2, Cl-. Ionic Compounds Ionic compounds: are formed between Metals and Non-metals when the valence electrons are transferred. (Metal) cations and (nonmetal) anions are held together by an electrostatic a ...
Chapter 2 Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
... • When atoms lose or gain electrons, they become ions. Often they lose or gain electrons to have the same number of electrons as the nearest noble gas. Cations are positive and are formed by elements on the left side of the periodic chart. Anions are negative and are formed by elements on the ri ...
... • When atoms lose or gain electrons, they become ions. Often they lose or gain electrons to have the same number of electrons as the nearest noble gas. Cations are positive and are formed by elements on the left side of the periodic chart. Anions are negative and are formed by elements on the ri ...
PVS103 - unit 6 notes
... We have already seen how electronegativity increases on moving across the periodic table. Can you remember why? As a result electronegativity is a periodic property, so for example, the halogens (Group 7a elements) are all highly electronegative. ...
... We have already seen how electronegativity increases on moving across the periodic table. Can you remember why? As a result electronegativity is a periodic property, so for example, the halogens (Group 7a elements) are all highly electronegative. ...
IB Definitions
... The mass number is the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom The atomic number is equivalent to the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom Isotopes are atoms which have the same atomic number but different mass numbers (due to the presence of different numbers of neutro ...
... The mass number is the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom The atomic number is equivalent to the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom Isotopes are atoms which have the same atomic number but different mass numbers (due to the presence of different numbers of neutro ...
Click here for the Reaction NOTES Handout
... diatomic, ex. Nitrogen gas or just nitrogen is N2, especially in equations. Diatomic means there are 2 atoms that are covalently bonded (sharing electrons equally). Seven elements exist in nature as diatomic molecules: ...
... diatomic, ex. Nitrogen gas or just nitrogen is N2, especially in equations. Diatomic means there are 2 atoms that are covalently bonded (sharing electrons equally). Seven elements exist in nature as diatomic molecules: ...
Chemistry I Final Exam Review Problems 2016
... ____ 61. In a pyramidal molecule, how many unshared pairs of valence electrons does the central atom have? a. none c. two b. one d. three ____ 62. Which of the following contains the largest number of oxygen atoms? a. 4H2 O c. H2 SO4 b. 3CO2 d. 2Al(NO3 ) 3 ____ 63. An element’s most stable ion forms ...
... ____ 61. In a pyramidal molecule, how many unshared pairs of valence electrons does the central atom have? a. none c. two b. one d. three ____ 62. Which of the following contains the largest number of oxygen atoms? a. 4H2 O c. H2 SO4 b. 3CO2 d. 2Al(NO3 ) 3 ____ 63. An element’s most stable ion forms ...
Equilibrium
... ● More particles = harder for particles to evaporate = higher boiling point ● The boiling point of a liquid is determined by the strength of the IMF’s in the liquid ● Alcohols have the highest boiling point, then ketones, and alkanes have the lowest boiling point ● Polarity affects boiling point. No ...
... ● More particles = harder for particles to evaporate = higher boiling point ● The boiling point of a liquid is determined by the strength of the IMF’s in the liquid ● Alcohols have the highest boiling point, then ketones, and alkanes have the lowest boiling point ● Polarity affects boiling point. No ...
3.10 Neutralization
... 2Na(s) + Cl2(g) → 2NaCl(s) NaCl(s) consists of ions: 2Na(s) + Cl2(g) → 2Na+(s) + 2Cl-(s) Na(s) → Na+(s) ⇒ loss of 1e- by Na Cl2(g) → 2Cl-(s) ⇒ gain of 2e- by Cl2 Result: transfer of electrons from Na to Cl2 ...
... 2Na(s) + Cl2(g) → 2NaCl(s) NaCl(s) consists of ions: 2Na(s) + Cl2(g) → 2Na+(s) + 2Cl-(s) Na(s) → Na+(s) ⇒ loss of 1e- by Na Cl2(g) → 2Cl-(s) ⇒ gain of 2e- by Cl2 Result: transfer of electrons from Na to Cl2 ...
Balancing Chemical Reactions
... 1.) In reactions dealing solely with ions, one can leave the polyatomic ions as groups for ease of balancing. 2.) In reactions dealing with only ions and water, water can be considered as a combination of a hydrogen ion and hydroxide ion. 3.) If given a reaction with polyatomic ions that are broken ...
... 1.) In reactions dealing solely with ions, one can leave the polyatomic ions as groups for ease of balancing. 2.) In reactions dealing with only ions and water, water can be considered as a combination of a hydrogen ion and hydroxide ion. 3.) If given a reaction with polyatomic ions that are broken ...
CHAPTER 2 THE CHEMISTRY OF LIFE 2.1 Chemical Elements
... Ions form when atoms lose or gain one or more electrons. An ionic bond is an attraction between oppositely charged ions. It is formed when electrons are transferred from one atom to another atom. For example, sodium loses an electron, forming a positive charge, and chlorine gains an electron to give ...
... Ions form when atoms lose or gain one or more electrons. An ionic bond is an attraction between oppositely charged ions. It is formed when electrons are transferred from one atom to another atom. For example, sodium loses an electron, forming a positive charge, and chlorine gains an electron to give ...
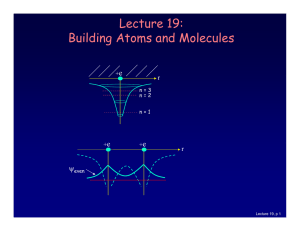
Lecture 19: Building Atoms and Molecules
... which is described by an additional quantum number, mp, and therefore also a magnetic moment. However, it is several orders of magnitude smaller than that of the electron. ...
... which is described by an additional quantum number, mp, and therefore also a magnetic moment. However, it is several orders of magnitude smaller than that of the electron. ...
2.ATOMS, MOLECULES, AND IONS
... 2.28 a. Since the mass of an atom is not only due to the sum of the masses of the protons, neutrons, and electrons, when you change the element in which you are basing the amu, the mass of the amu must change as well. b. Since the amount of material that makes up a hydrogen atom doesn’t change, when ...
... 2.28 a. Since the mass of an atom is not only due to the sum of the masses of the protons, neutrons, and electrons, when you change the element in which you are basing the amu, the mass of the amu must change as well. b. Since the amount of material that makes up a hydrogen atom doesn’t change, when ...
First of all, do you know any methods to check
... First of all, do you know any methods to check chemical ...
... First of all, do you know any methods to check chemical ...
$doc.title
... side of the arrow (and also the number of oxygen atoms on the left side of the arrow), equals the number of hydrogen atoms (and likewise the number of oxygen atoms), on the right side of the arrow. Atoms are the smallest units of matter that retain chemical properties. Atoms are not visible under n ...
... side of the arrow (and also the number of oxygen atoms on the left side of the arrow), equals the number of hydrogen atoms (and likewise the number of oxygen atoms), on the right side of the arrow. Atoms are the smallest units of matter that retain chemical properties. Atoms are not visible under n ...
CHEMISTRY PHYSICAL SETTING Thursday, PS/CHEMISTRY
... (1) atomic mass (3) mass number (2) atomic number (4) oxidation number 2 Which particle has a mass that is approximately the same as the mass of a proton? (1) an alpha particle (3) a neutron (2) a beta particle (4) a positron 3 An atom of an element forms a 2+ ion. In which group on the Periodic Tab ...
... (1) atomic mass (3) mass number (2) atomic number (4) oxidation number 2 Which particle has a mass that is approximately the same as the mass of a proton? (1) an alpha particle (3) a neutron (2) a beta particle (4) a positron 3 An atom of an element forms a 2+ ion. In which group on the Periodic Tab ...
Chapter 10 - Chemical Reactions
... Many times, Balancing equations is a trial & error process Ex: Combustion of Gasoline (Octane) 2C8H18(g) + 25O2(g) 16CO2(g) + 18H2O(g) However, you should be familiar with the rules which describe balanced chemical reactions. 1. Number of Atoms of each element conserved in reactants and products 2. ...
... Many times, Balancing equations is a trial & error process Ex: Combustion of Gasoline (Octane) 2C8H18(g) + 25O2(g) 16CO2(g) + 18H2O(g) However, you should be familiar with the rules which describe balanced chemical reactions. 1. Number of Atoms of each element conserved in reactants and products 2. ...
Campbell Biology in Focus (Urry) Chapter 2 The Chemical Context
... C) CO2 D) H2O E) CH4 31) In comparing covalent bonds and ionic bonds, which of the following would you expect? A) An atom can form covalent bonds with multiple partner atoms, but only a single ionic bond with a single partner atom. B) Covalent bonds and ionic bonds occupy opposite ends of a continuo ...
... C) CO2 D) H2O E) CH4 31) In comparing covalent bonds and ionic bonds, which of the following would you expect? A) An atom can form covalent bonds with multiple partner atoms, but only a single ionic bond with a single partner atom. B) Covalent bonds and ionic bonds occupy opposite ends of a continuo ...
普通化学 (全英文) 教学大纲
... (a).[cation]m × [anion]n < Ksp under saturated solution, No precipitate (b).[cation]m × [anion]n = Ksp saturated solution, Start to precipitate (c).[cation]m × [anion]n > Ksp Over saturated solution, Precipitate is formed 6.9.The common ion effect 6.10.Calculation of ion concentrations in solu ...
... (a).[cation]m × [anion]n < Ksp under saturated solution, No precipitate (b).[cation]m × [anion]n = Ksp saturated solution, Start to precipitate (c).[cation]m × [anion]n > Ksp Over saturated solution, Precipitate is formed 6.9.The common ion effect 6.10.Calculation of ion concentrations in solu ...
1. All the questions are compulsory. 2. Q. N
... Use of calculators is not allowed, use log tables wherever required. 1. Name the non stoichiometric point defect responsible for colour in alkali metal halides. 2. What is shape selective catalysis? 3. Amongst the isomeric alkanes of molecular formula C5H12, identify the one that on photochemical ch ...
... Use of calculators is not allowed, use log tables wherever required. 1. Name the non stoichiometric point defect responsible for colour in alkali metal halides. 2. What is shape selective catalysis? 3. Amongst the isomeric alkanes of molecular formula C5H12, identify the one that on photochemical ch ...
Chemistry - CBSE Academic
... mankind with serious waste disposal problem as these materials do not disintegrate by themselves. In view of this, certain polymers are being developed which are broken down rapidly by microorganisms. Shalini feels relaxed that such kinds of biomaterials are being developed. (a) Name the class of th ...
... mankind with serious waste disposal problem as these materials do not disintegrate by themselves. In view of this, certain polymers are being developed which are broken down rapidly by microorganisms. Shalini feels relaxed that such kinds of biomaterials are being developed. (a) Name the class of th ...
AS Paper 1 Practice Paper 12 - A
... Give the oxidation state of bromine in HBr and in HBrO Deduce what will happen to this equilibrium as the HBrO reacts with micro-organisms in the swimming pool water. Explain your answer. ...
... Give the oxidation state of bromine in HBr and in HBrO Deduce what will happen to this equilibrium as the HBrO reacts with micro-organisms in the swimming pool water. Explain your answer. ...
+ H 2 O(l)
... basically a bookkeeping method for keeping track of electrons You must be able to identify an oxidation-reduction reaction. But first, we must learn the rules for assigning oxidation #’s to different species. ...
... basically a bookkeeping method for keeping track of electrons You must be able to identify an oxidation-reduction reaction. But first, we must learn the rules for assigning oxidation #’s to different species. ...
2 Chemical bonding is a genuinely quantum effect, which cannot be
... • interactions mediated by, and resulting directly from the presence of a covalent bond between the atoms. We usually put springs between the atoms and have to care about bond and dihedral angles. With this treatment, we describe all the quantummechanical phenomena like exchange and correlation usin ...
... • interactions mediated by, and resulting directly from the presence of a covalent bond between the atoms. We usually put springs between the atoms and have to care about bond and dihedral angles. With this treatment, we describe all the quantummechanical phenomena like exchange and correlation usin ...
Atom - U of L Class Index
... discovered canal rays in 1886using a “reverse cathode ray” tube Those that pass through the hole (“canal”) can be analyzed for charge-mass ratio, which are much smaller than electron, but largest for hydrogen ...
... discovered canal rays in 1886using a “reverse cathode ray” tube Those that pass through the hole (“canal”) can be analyzed for charge-mass ratio, which are much smaller than electron, but largest for hydrogen ...