COMPLEX IONS AND AMPHOTERISM
... After you have completed all of the tests on the known solutions, you will be given an unknown solution that contains TWO cations, one of which is colored in aqueous solution and the other of which is colorless. Using the chemical reactions you explored above, you should be able to work out a scheme ...
... After you have completed all of the tests on the known solutions, you will be given an unknown solution that contains TWO cations, one of which is colored in aqueous solution and the other of which is colorless. Using the chemical reactions you explored above, you should be able to work out a scheme ...
File
... 1. Elements are made of tiny particles called atoms. 2. All atoms of a given element are identical. 3. The atoms of a given element are different from those of any other element. 4. Atoms of one element can combine with atoms of other elements to form compounds. A given compound always has the same ...
... 1. Elements are made of tiny particles called atoms. 2. All atoms of a given element are identical. 3. The atoms of a given element are different from those of any other element. 4. Atoms of one element can combine with atoms of other elements to form compounds. A given compound always has the same ...
Practice Test 11 - U of L Class Index
... A chunk of white phosphorus weighing 6.58 grams is put in a 750 mL flask containing dry argon (which is then removed using a vacuum, leaving only the phosphorus in the flask). A separate 750 mL flask contains 3.15 bar of fluorine gas (at 19.65 °C). The two flasks are connected so that the two compou ...
... A chunk of white phosphorus weighing 6.58 grams is put in a 750 mL flask containing dry argon (which is then removed using a vacuum, leaving only the phosphorus in the flask). A separate 750 mL flask contains 3.15 bar of fluorine gas (at 19.65 °C). The two flasks are connected so that the two compou ...
NYS Regents Chemistry
... hh. Metals and non-metals separated by “staircase” beginning at Group 13 i. Metals to the left of the “staircase” (except H) (most elements are metals) ii. Non-metals to the right of the “staircase” (including H) ii. Properties of Metals: i. Are mostly solids (one liquid, Hg) ii. Lose electrons easi ...
... hh. Metals and non-metals separated by “staircase” beginning at Group 13 i. Metals to the left of the “staircase” (except H) (most elements are metals) ii. Non-metals to the right of the “staircase” (including H) ii. Properties of Metals: i. Are mostly solids (one liquid, Hg) ii. Lose electrons easi ...
Chemistry I Review - BarbaraElam-Rice
... 29) Describe the difference between cations and anions. How are they formed? ...
... 29) Describe the difference between cations and anions. How are they formed? ...
2 - TestBankTop
... Millikan performed a series of experiments in which he obtained the charge on the electron by observing how a charged drop of oil falls in the presence and in the absence of an electric field. An atomizer introduces a fine mist of oil drops into the top chamber (Figure 2.6). Several drops happen to ...
... Millikan performed a series of experiments in which he obtained the charge on the electron by observing how a charged drop of oil falls in the presence and in the absence of an electric field. An atomizer introduces a fine mist of oil drops into the top chamber (Figure 2.6). Several drops happen to ...
Atomic Structure Notes
... 1 unit of charge is 1.602 x 10-19 coulombs. A proton is given a charge of +1 and an electron a charge of -1. All charges are measured in these units. 1 unit of mass is 1.661 x 10-27 kg. This is also not a convenient number, so we use “atomic mass units”. Since the mass of protons and neutrons varies ...
... 1 unit of charge is 1.602 x 10-19 coulombs. A proton is given a charge of +1 and an electron a charge of -1. All charges are measured in these units. 1 unit of mass is 1.661 x 10-27 kg. This is also not a convenient number, so we use “atomic mass units”. Since the mass of protons and neutrons varies ...
The d-block elements are commonly known as transition
... CT complex. (2) A few seconds after excess PPh3 was added—CT complex is forming. (3) One minute later after excess PPh3 was added—the CT complex [Ph3PI]+Ihas been formed. (4) Immediately after excess I2 was added, which contains [Ph3PI]+[I3]. ...
... CT complex. (2) A few seconds after excess PPh3 was added—CT complex is forming. (3) One minute later after excess PPh3 was added—the CT complex [Ph3PI]+Ihas been formed. (4) Immediately after excess I2 was added, which contains [Ph3PI]+[I3]. ...
Formulae and equations
... The smallest particle of a compound (a combination of two or more elements). It is also the name given to the smallest part of those elements which do not exist as atoms in the free state i.e. hydrogen H2, oxygen O2, nitrogen N2, fluorine F2, chlorine Cl2, bromine Br2 and iodine I2. N.B. ionic compo ...
... The smallest particle of a compound (a combination of two or more elements). It is also the name given to the smallest part of those elements which do not exist as atoms in the free state i.e. hydrogen H2, oxygen O2, nitrogen N2, fluorine F2, chlorine Cl2, bromine Br2 and iodine I2. N.B. ionic compo ...
Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
... Millikan performed a series of experiments in which he obtained the charge on the electron by observing how a charged drop of oil falls in the presence and in the absence of an electric field. An atomizer introduces a fine mist of oil drops into the top chamber (Figure 2.6). Several drops happen to ...
... Millikan performed a series of experiments in which he obtained the charge on the electron by observing how a charged drop of oil falls in the presence and in the absence of an electric field. An atomizer introduces a fine mist of oil drops into the top chamber (Figure 2.6). Several drops happen to ...
Scientific Notation - Warren County Public Schools
... • Atomic number increases by one. (proton formed in nucleus; stable daughter isotope). ...
... • Atomic number increases by one. (proton formed in nucleus; stable daughter isotope). ...
CHEM 1211K Test IV MULTIPLE CHOICE. (3 points each) 1) The
... 10) Which of the following statements about gases is false? A) All gases are colorless and odorless at room temperature. B) Distances between molecules of gas are very large compared to bond distances within molecules. C) Non-reacting gas mixtures are homogeneous. D) Gases expand spontaneously to f ...
... 10) Which of the following statements about gases is false? A) All gases are colorless and odorless at room temperature. B) Distances between molecules of gas are very large compared to bond distances within molecules. C) Non-reacting gas mixtures are homogeneous. D) Gases expand spontaneously to f ...
Unit 01 Qual Chem
... Physical Change = a change that does not alter the identity of a substance (shape, size, state) Chemical Change = a change in which one or more substances are converted into substances with different chemical properties ...
... Physical Change = a change that does not alter the identity of a substance (shape, size, state) Chemical Change = a change in which one or more substances are converted into substances with different chemical properties ...
Unit 3 Revision Notes 213.00KB 2017-03-01 18
... The periodic tables patterns are now known to be based on the structure of the atom. Elements in the periodic table are arranged in order of atomic number (number of protons in the nucleus) The group number of an element shows the number of electrons in the outer shell. The period number shows the n ...
... The periodic tables patterns are now known to be based on the structure of the atom. Elements in the periodic table are arranged in order of atomic number (number of protons in the nucleus) The group number of an element shows the number of electrons in the outer shell. The period number shows the n ...
INTRO TO NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY
... (atomic number) B. Mass and Energy Relationships 1. mass defect- difference between the mass of an atom and the sum of the masses of the subatomic particles composing that atom 2. Example: helium-4: 2 protons (2 x 1.007276 amu) = 2.014552 amu 2 neutrons (2 x 1.008665 amu) = 2.017330 amu 2 electrons ...
... (atomic number) B. Mass and Energy Relationships 1. mass defect- difference between the mass of an atom and the sum of the masses of the subatomic particles composing that atom 2. Example: helium-4: 2 protons (2 x 1.007276 amu) = 2.014552 amu 2 neutrons (2 x 1.008665 amu) = 2.017330 amu 2 electrons ...
lectures on subjects in physics, chemistry and biology
... of equal atoms and that a charged hydrogen atom carries one such atomic unit of electricity, an oxygen atom two, and an iron atom three. J. J. Thomson adopted this idea and supposed that his electrons were the atoms of negative electricity. Since he found the charge per unit weight of the electrons ...
... of equal atoms and that a charged hydrogen atom carries one such atomic unit of electricity, an oxygen atom two, and an iron atom three. J. J. Thomson adopted this idea and supposed that his electrons were the atoms of negative electricity. Since he found the charge per unit weight of the electrons ...
2 - TEST BANK 360
... Millikan performed a series of experiments in which he obtained the charge on the electron by observing how a charged drop of oil falls in the presence and in the absence of an electric field. An atomizer introduces a fine mist of oil drops into the top chamber (Figure 2.6). Several drops happen to ...
... Millikan performed a series of experiments in which he obtained the charge on the electron by observing how a charged drop of oil falls in the presence and in the absence of an electric field. An atomizer introduces a fine mist of oil drops into the top chamber (Figure 2.6). Several drops happen to ...
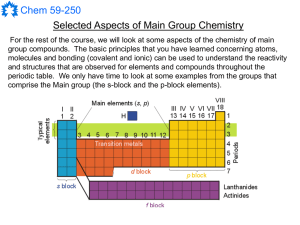
Main Group Notes 1
... Such compounds were among the first that were recognized to contain bonds between metals and carbon. These were thus some of the initial examples of organometallic chemistry (one of the most studied branches of inorganic chemistry today). ...
... Such compounds were among the first that were recognized to contain bonds between metals and carbon. These were thus some of the initial examples of organometallic chemistry (one of the most studied branches of inorganic chemistry today). ...
AP Chemistry MC Review Questions
... (D) Shielding effect (E) Wave nature of matter 18. _____Can be used to predict that a gaseous carbon atom in its ground state is paramagnetic 19. _____Explains the experimental phenomenon of electron diffraction 20. _____Indicates that an atomic orbital can hold no more than two electrons 21. _____P ...
... (D) Shielding effect (E) Wave nature of matter 18. _____Can be used to predict that a gaseous carbon atom in its ground state is paramagnetic 19. _____Explains the experimental phenomenon of electron diffraction 20. _____Indicates that an atomic orbital can hold no more than two electrons 21. _____P ...
Ch 2 ppt - Houston ISD
... • A cation is a positively charged ion • An anion is a negatively charged ion • An ionic bond is an attraction between an anion and a cation ...
... • A cation is a positively charged ion • An anion is a negatively charged ion • An ionic bond is an attraction between an anion and a cation ...
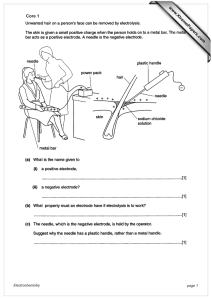
Core 1 www.XtremePapers.com Electrochemistry page 1
... does not conduct electricity (to operator) / plastic is an insulator / so operator does not get an electric shock ...
... does not conduct electricity (to operator) / plastic is an insulator / so operator does not get an electric shock ...
Document
... Bond formation involves the electrons (e-) in the outermost (valence) shell. A complete outer shell consists of 8 valence electrons (except H and He which have 2) Destruction of a bond corresponds to a release of energy. Generally double or triple bond energies are higher than for single bonds. Ioni ...
... Bond formation involves the electrons (e-) in the outermost (valence) shell. A complete outer shell consists of 8 valence electrons (except H and He which have 2) Destruction of a bond corresponds to a release of energy. Generally double or triple bond energies are higher than for single bonds. Ioni ...
Inorganic Pharmaceutical Chemistry Hybrid Orbitals Hybridization
... make the ion out of a lump of plasticene (or a bit of clay or dough) and three bits of cardboard cut to shape A substance with no plane of symmetry is going to have optical isomers - one of which is the mirror image of the other. One of the isomers will rotate the plane of polarisation of plane pola ...
... make the ion out of a lump of plasticene (or a bit of clay or dough) and three bits of cardboard cut to shape A substance with no plane of symmetry is going to have optical isomers - one of which is the mirror image of the other. One of the isomers will rotate the plane of polarisation of plane pola ...