CH 4 Notes
... Example: For a 1.0 M solution of NaCl: The solution is 1.0 M in Na1+ ions and 1.0 M in Cl1- ions. Example: For a 1.0 M solution of Na2SO4: The solution is 2.0 M in Na1+ ions and 1.0 M in SO42- ions. ...
... Example: For a 1.0 M solution of NaCl: The solution is 1.0 M in Na1+ ions and 1.0 M in Cl1- ions. Example: For a 1.0 M solution of Na2SO4: The solution is 2.0 M in Na1+ ions and 1.0 M in SO42- ions. ...
Hydrocarbon ions in fuel-rich, CH4-C2H2-0, flames
... Most commonly, the product of this reaction is a mentioned in the previous section, namely, chemistable (i.e. non-radical) hydrocarbon molecule. ionization and thermal ionization. If the pair of Associative detachment reactions are also ex- curves with Tad= 2401 and 2488 K for $ = 2.22 f pected to b ...
... Most commonly, the product of this reaction is a mentioned in the previous section, namely, chemistable (i.e. non-radical) hydrocarbon molecule. ionization and thermal ionization. If the pair of Associative detachment reactions are also ex- curves with Tad= 2401 and 2488 K for $ = 2.22 f pected to b ...
Year 10 Chemistry Exam June 2011 Multiple Choice Section A
... A different atoms of the same element with a different number of protons B different atoms of the same element with a different number of electrons C different atoms of the same element with different mass numbers. D different atoms of the same element with different atomic numbers. 7 The maximum nu ...
... A different atoms of the same element with a different number of protons B different atoms of the same element with a different number of electrons C different atoms of the same element with different mass numbers. D different atoms of the same element with different atomic numbers. 7 The maximum nu ...
Chapter 3
... Anions Prefixes are used when there is a series of four oxyanions. (usually the halogens) Per- is used to indicate one more O than the –ate ending and hypo- is used for one less O than the ...
... Anions Prefixes are used when there is a series of four oxyanions. (usually the halogens) Per- is used to indicate one more O than the –ate ending and hypo- is used for one less O than the ...
Electron - HCC Learning Web
... • A molecule consists of two or more atoms held together by covalent bonds • A single covalent bond, or single bond, is the sharing of one pair of valence electrons • A double covalent bond, or double bond, is the sharing of two pairs of valence electrons • Covalent bonds can form between atoms of ...
... • A molecule consists of two or more atoms held together by covalent bonds • A single covalent bond, or single bond, is the sharing of one pair of valence electrons • A double covalent bond, or double bond, is the sharing of two pairs of valence electrons • Covalent bonds can form between atoms of ...
mark scheme - A-Level Chemistry
... * lose this mark if the line deviates towards the point at 1.17g / 86 cm3 * candidates does not have to extrapolate the line to the origin to score this mark * when checking for best fit, candidate’s line must go through the origin ± one square. Extend candidate’s line if necessary ...
... * lose this mark if the line deviates towards the point at 1.17g / 86 cm3 * candidates does not have to extrapolate the line to the origin to score this mark * when checking for best fit, candidate’s line must go through the origin ± one square. Extend candidate’s line if necessary ...
Carbon-12 Stable
... Elements- pure substance made up of only one type of atom -cannot be broken down into simpler substances by physical or chemical means Compounds- pure substance made up of multiple types of atoms, chemically bound to form particles called molecules ...
... Elements- pure substance made up of only one type of atom -cannot be broken down into simpler substances by physical or chemical means Compounds- pure substance made up of multiple types of atoms, chemically bound to form particles called molecules ...
Coordination Chemistry
... that ammonia could not be completely removed. He then proposed that the ammonia must be bound more tightly to the central cobalt ion. However, when aqueous silver nitrate was added, one of the products formed was solid silver chloride. The amount of silver chloride formed was related to the number o ...
... that ammonia could not be completely removed. He then proposed that the ammonia must be bound more tightly to the central cobalt ion. However, when aqueous silver nitrate was added, one of the products formed was solid silver chloride. The amount of silver chloride formed was related to the number o ...
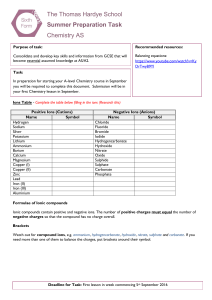
The Thomas Hardye School Summer Preparation Task Chemistry AS
... Oxide Sulphide Sulphate Carbonate Phosphate ...
... Oxide Sulphide Sulphate Carbonate Phosphate ...
Process Monitoring
... The electrons in the covalent bond are held in place by this bond and hence they are localised to region surrounding the atom. Since they cannot move or change their energy, electrons in a bond are not considered "free" and cannot participate in current flow, absorption or other physical processes ...
... The electrons in the covalent bond are held in place by this bond and hence they are localised to region surrounding the atom. Since they cannot move or change their energy, electrons in a bond are not considered "free" and cannot participate in current flow, absorption or other physical processes ...
Earth Science - Green Local Schools
... Atomic mass unit Parts of the atom – nucleus, proton, neutron, electron, Average atomic mass energy levels Metal Valence electron Nonmetal Period Semiconductor Group Alkali metal Ion Alkaline-earth metal Atomic number Transition metal Mass number Noble gases Electron Cloud Model / Bohr Model Be ab ...
... Atomic mass unit Parts of the atom – nucleus, proton, neutron, electron, Average atomic mass energy levels Metal Valence electron Nonmetal Period Semiconductor Group Alkali metal Ion Alkaline-earth metal Atomic number Transition metal Mass number Noble gases Electron Cloud Model / Bohr Model Be ab ...
What`s in a Name? - Department of Chemistry | Washington
... naming acids. An acid is a proton donor. Therefore, for the purpose of nomenclature, an acid can be viewed as a molecule with one or more protons (H+) bonded to an anion. Note that the molecule must not carry a charge. For example, HSO3− is not an acid molecule; it is an anion because it carries a − ...
... naming acids. An acid is a proton donor. Therefore, for the purpose of nomenclature, an acid can be viewed as a molecule with one or more protons (H+) bonded to an anion. Note that the molecule must not carry a charge. For example, HSO3− is not an acid molecule; it is an anion because it carries a − ...
ppt Lewis Dot Diagram Rules
... Drawing Lewis Diagrams for Molecules Step 1 Draw each element separately, showing the valence electrons. (Use different symbols for different atoms) Step 2 Choose the least occurring atom as the central atom (or the least electronegative). Except hydrogens or Oxygens. Step 3 Add next frequently occ ...
... Drawing Lewis Diagrams for Molecules Step 1 Draw each element separately, showing the valence electrons. (Use different symbols for different atoms) Step 2 Choose the least occurring atom as the central atom (or the least electronegative). Except hydrogens or Oxygens. Step 3 Add next frequently occ ...
Document
... which is described by an additional quantum number, mp, and therefore also a magnetic moment. However, it is several orders of magnitude smaller than that of the electron. ...
... which is described by an additional quantum number, mp, and therefore also a magnetic moment. However, it is several orders of magnitude smaller than that of the electron. ...
16. Quantitative volumetric analysis with conductometric detection of
... Conductometry is an electroanalytical method involving the measurement of electrolytic conductivity which value changes with the change of the concentration of ions in solution. Electrolytic conductivity of the solution is due to an electric charge transfer by cations (positive ions) and anions (neg ...
... Conductometry is an electroanalytical method involving the measurement of electrolytic conductivity which value changes with the change of the concentration of ions in solution. Electrolytic conductivity of the solution is due to an electric charge transfer by cations (positive ions) and anions (neg ...
Chemistry - Delhi Public School, Faridabad
... Q. 40 Out of H 2 and H 2 which is more stable? Why? Q. 41 He H- ion can not exist. Why? Q. 42 O2 molecule is paramagnetic, whereas N2 molecule is diamagnetic. Why? Q. 43 Arrange the following in the increasing order of stability : ...
... Q. 40 Out of H 2 and H 2 which is more stable? Why? Q. 41 He H- ion can not exist. Why? Q. 42 O2 molecule is paramagnetic, whereas N2 molecule is diamagnetic. Why? Q. 43 Arrange the following in the increasing order of stability : ...
Matter Key
... substance which can be separated physically or chemically. (sand, salt, iron) Know how to calculate density and determine which objects float or sink Object is .89 grams and 2.3 mL What is density? Will it float in water? Why? 0.89g/2.3 mL = 0.39 g/mL 1.0g/mL ...
... substance which can be separated physically or chemically. (sand, salt, iron) Know how to calculate density and determine which objects float or sink Object is .89 grams and 2.3 mL What is density? Will it float in water? Why? 0.89g/2.3 mL = 0.39 g/mL 1.0g/mL ...
Name__________________________________________ Answers to Sample Exam Questions #1 Chemistry 112
... b) Atoms of the same element can be different. c) Compounds form when atoms combine in whole number ratios. d) A chemical reaction involves rearrangement of atoms. 3. Which of the following pairs of compounds illustrates the law of multiple proportions? a) Fe, FeO3 b) Cl, Cl2 c) H2SO4, NaOH d) H2O, ...
... b) Atoms of the same element can be different. c) Compounds form when atoms combine in whole number ratios. d) A chemical reaction involves rearrangement of atoms. 3. Which of the following pairs of compounds illustrates the law of multiple proportions? a) Fe, FeO3 b) Cl, Cl2 c) H2SO4, NaOH d) H2O, ...
Year 9 Chemical Sciences Program Term 3 Course 2 2017
... Define mass number and periodic table Describe how the elements are ordered on the periodic table Calculate mass number from the number of protons and neutrons Determine the number of electrons in an atom from the number of protons Explain the difference between atomic number and mass numb ...
... Define mass number and periodic table Describe how the elements are ordered on the periodic table Calculate mass number from the number of protons and neutrons Determine the number of electrons in an atom from the number of protons Explain the difference between atomic number and mass numb ...
First Midterm Answer Key
... π-electrons are more polarizable than σ-electrons, even though N is less electronegative than O, the C-N triple bond has more π-electrons (2 π-bonds compared to 1), and thus the electrons are more polarized, the dipole moment is thus larger Question 7 (22 pts.) For the indicated localized molecular ...
... π-electrons are more polarizable than σ-electrons, even though N is less electronegative than O, the C-N triple bond has more π-electrons (2 π-bonds compared to 1), and thus the electrons are more polarized, the dipole moment is thus larger Question 7 (22 pts.) For the indicated localized molecular ...
KEY_Reaction Types WS
... task is deciding what type of reaction is taking place. In this chapter we study three types: ...
... task is deciding what type of reaction is taking place. In this chapter we study three types: ...
I, I, I, 4- Measurement Unit Conversions- Kilo
... Describe trends in properties (e.g., ionization energy or reactivity as a function of location on the periodic table, boiling point of organic liquids as a function of molecular weight). Atomic radius is one-half of the distance between the center of identical atoms that are not bonded together. Ion ...
... Describe trends in properties (e.g., ionization energy or reactivity as a function of location on the periodic table, boiling point of organic liquids as a function of molecular weight). Atomic radius is one-half of the distance between the center of identical atoms that are not bonded together. Ion ...
Chapter 2
... compound, the total charges from the cations and anions must cancel-out (or sum to zero). • Therefore, Mg needs to lose 6 electrons (3 2+) and N gain those 6 electrons (2 3-). • The resulting formula is: Mg3N2. ...
... compound, the total charges from the cations and anions must cancel-out (or sum to zero). • Therefore, Mg needs to lose 6 electrons (3 2+) and N gain those 6 electrons (2 3-). • The resulting formula is: Mg3N2. ...