Openstax - Chemistry - Answer Key
... 5. (a) symbolic, microscopic; (b) macroscopic; (c) symbolic, macroscopic; (d) microscopic 7. Macroscopic. The heat required is determined from macroscopic properties. 9. Liquids can change their shape (flow); solids can’t. Gases can undergo large volume changes as pressure changes; liquids do not. G ...
... 5. (a) symbolic, microscopic; (b) macroscopic; (c) symbolic, macroscopic; (d) microscopic 7. Macroscopic. The heat required is determined from macroscopic properties. 9. Liquids can change their shape (flow); solids can’t. Gases can undergo large volume changes as pressure changes; liquids do not. G ...
FREE Sample Here
... A) The element may undergo radioactive decay. B) The element may react with itself and gain or lose subatomic particles. C) The atoms of the element form chemical bonds with each other, and that changes the weight of the element. D) The element may have multiple stable isotopes, and the isotopic com ...
... A) The element may undergo radioactive decay. B) The element may react with itself and gain or lose subatomic particles. C) The atoms of the element form chemical bonds with each other, and that changes the weight of the element. D) The element may have multiple stable isotopes, and the isotopic com ...
Atomic Number and Mass Number
... 22. Circle the letter of each statement that is true about the average atomic mass of an element and the relative abundance of its isotopes. a. In nature, most elements occur as a mixture of two or more isotopes. b. Isotopes of an element do not have a specific natural percent abundance. c. The aver ...
... 22. Circle the letter of each statement that is true about the average atomic mass of an element and the relative abundance of its isotopes. a. In nature, most elements occur as a mixture of two or more isotopes. b. Isotopes of an element do not have a specific natural percent abundance. c. The aver ...
Chapter 10
... These molar ratios are used to 'convert' between any two compounds, whether they are reactants or products. This allows us to calculate moles of reactants needed, or products produced. ...
... These molar ratios are used to 'convert' between any two compounds, whether they are reactants or products. This allows us to calculate moles of reactants needed, or products produced. ...
A-level Paper 1 Practice Paper 8 - A
... Octahedral and tetrahedral complex ions are produced by the reaction of transition metal ions with ligands which form co-ordinate bonds with the transition metal ion. Define the term ligand and explain what is meant by the term co-ordinate bond. ...
... Octahedral and tetrahedral complex ions are produced by the reaction of transition metal ions with ligands which form co-ordinate bonds with the transition metal ion. Define the term ligand and explain what is meant by the term co-ordinate bond. ...
Effect of Electric Field on the Mobility of Carboxyl
... particle (or central ion) and its surrounding ion atmosphere in an electric field.1-3 An important consideration is the asymmetry of the ion atmosphere, which can result from the constant motion of the central particle that displaces it from the center of its ionic atmosphere. This displacement aris ...
... particle (or central ion) and its surrounding ion atmosphere in an electric field.1-3 An important consideration is the asymmetry of the ion atmosphere, which can result from the constant motion of the central particle that displaces it from the center of its ionic atmosphere. This displacement aris ...
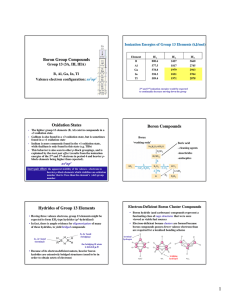
Boron Group Compounds Oxidation States Boron
... • Electron-deficient borane clusters are formed because boron compounds possess fewer valence electrons than are required for a localized bonding scheme terminal hydrogen ...
... • Electron-deficient borane clusters are formed because boron compounds possess fewer valence electrons than are required for a localized bonding scheme terminal hydrogen ...
Solutions, Acids, and Bases
... temperature is said to be saturated. Unsaturated = contains less solute than it can possibly hold Supersaturated = a solution that holds more solute than it should at a given temperature. ...
... temperature is said to be saturated. Unsaturated = contains less solute than it can possibly hold Supersaturated = a solution that holds more solute than it should at a given temperature. ...
Defining the Atom - Central Lyon CSD
... Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or can chemically combine in simple whole-number ratios to form compounds. ...
... Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or can chemically combine in simple whole-number ratios to form compounds. ...
Grade 9 Academic Science
... 3. How do atoms become ions? Do they lose or gain protons, electrons, and/or neutrons? 4. How does an atom become a positively-charged ion? Negatively-charged? 5. Calculate the # of protons, # of electrons, and # of neutrons of 3 metals, 2 non-metals, and 1 metalloid on the PT. 6. Calculate the # of ...
... 3. How do atoms become ions? Do they lose or gain protons, electrons, and/or neutrons? 4. How does an atom become a positively-charged ion? Negatively-charged? 5. Calculate the # of protons, # of electrons, and # of neutrons of 3 metals, 2 non-metals, and 1 metalloid on the PT. 6. Calculate the # of ...
Chemical Solutions - The Chemistry Book
... 2. List at least three substances that are often found dissolved in the aqueous solution called tap water. ...
... 2. List at least three substances that are often found dissolved in the aqueous solution called tap water. ...
chemistry
... questions on this separate answer sheet. Record your answers for the questions in Part B–2 and Part C in your separate answer booklet. Be sure to fill in the heading on the front of your answer booklet. All answers in your answer booklet should be written in pen, except for graphs and drawings, whic ...
... questions on this separate answer sheet. Record your answers for the questions in Part B–2 and Part C in your separate answer booklet. Be sure to fill in the heading on the front of your answer booklet. All answers in your answer booklet should be written in pen, except for graphs and drawings, whic ...
FREE Sample Here
... A) The element may undergo radioactive decay. B) The element may react with itself and gain or lose subatomic particles. C) The atoms of the element form chemical bonds with each other, and that changes the weight of the element. D) The element may have multiple stable isotopes, and the isotopic com ...
... A) The element may undergo radioactive decay. B) The element may react with itself and gain or lose subatomic particles. C) The atoms of the element form chemical bonds with each other, and that changes the weight of the element. D) The element may have multiple stable isotopes, and the isotopic com ...
November 2016 (v1) QP - Paper 4 CIE Chemistry A-level
... (f) Iron(III) ions can oxidise vanadium metal. Construct an equation for the reaction of an excess of iron(III) ions with vanadium metal. Use of the Data Booklet will be helpful. ...
... (f) Iron(III) ions can oxidise vanadium metal. Construct an equation for the reaction of an excess of iron(III) ions with vanadium metal. Use of the Data Booklet will be helpful. ...
November 2016 (v3) QP - Paper 4 CIE Chemistry A-level
... (f) Iron(III) ions can oxidise vanadium metal. Construct an equation for the reaction of an excess of iron(III) ions with vanadium metal. Use of the Data Booklet will be helpful. ...
... (f) Iron(III) ions can oxidise vanadium metal. Construct an equation for the reaction of an excess of iron(III) ions with vanadium metal. Use of the Data Booklet will be helpful. ...
2007 - SolPass
... electronic or mechanical, including photocopying or recording, or by any information storage or retrieval system, without written permission from the copyright owner. Commonwealth of Virginia public school educators may reproduce any portion of these released tests for non-commercial educational pur ...
... electronic or mechanical, including photocopying or recording, or by any information storage or retrieval system, without written permission from the copyright owner. Commonwealth of Virginia public school educators may reproduce any portion of these released tests for non-commercial educational pur ...
Multiple Choice Practice. A) P B) S C) Cl D) Li E) 1 F 1. Has the
... A) The vapor pressure of the solid phase equals the vapor pressure of the liquid phase B) The temperature is 0.01K lower than the normal melting point C) The liquid and gas phases have the same density and are therefore indistinguishable D) The solid phase melts if the pressure increases at constan ...
... A) The vapor pressure of the solid phase equals the vapor pressure of the liquid phase B) The temperature is 0.01K lower than the normal melting point C) The liquid and gas phases have the same density and are therefore indistinguishable D) The solid phase melts if the pressure increases at constan ...
The Oxidation Potential of Oxygen and Chlorine Dioxide
... ie. oxidants (substances that accept electrons, in another words, are reduced) are always on the left side of the ...
... ie. oxidants (substances that accept electrons, in another words, are reduced) are always on the left side of the ...
Atoms, Ions and Molecules
... Essentials of his theory. . . 1. An element is composed of tiny particles called atoms. All atoms of a given element show the same chemical properties. 2. Atoms of different elements have different properties. In an ordinary chemical reaction, no atom of any element disappears or is changed into an ...
... Essentials of his theory. . . 1. An element is composed of tiny particles called atoms. All atoms of a given element show the same chemical properties. 2. Atoms of different elements have different properties. In an ordinary chemical reaction, no atom of any element disappears or is changed into an ...
Original powerpoint (~1.9 MB)
... If Qsp > Ksp, the solution is supersaturated, so the system is not at equilibrium. The concentration of the ions is greater than it would be at equilibrium, and so the reaction wants to shift from ions towards the solid. We expect precipitation to occur! If Qsp = Ksp, the solution is saturated, and ...
... If Qsp > Ksp, the solution is supersaturated, so the system is not at equilibrium. The concentration of the ions is greater than it would be at equilibrium, and so the reaction wants to shift from ions towards the solid. We expect precipitation to occur! If Qsp = Ksp, the solution is saturated, and ...
Name: Chemistry Honors Date: Period: ____ Reduction/Oxidation
... This is a question that could have a multitude of answers! As the name may suggest, electrochemistry deals with the chemistry of electrons: here electrons are and how they can move. Electrochemistry is the study of electron movement as it relates to chemical reactions. From photosynthesis to a rusti ...
... This is a question that could have a multitude of answers! As the name may suggest, electrochemistry deals with the chemistry of electrons: here electrons are and how they can move. Electrochemistry is the study of electron movement as it relates to chemical reactions. From photosynthesis to a rusti ...
FREE Sample Here
... A) The element may undergo radioactive decay. B) The element may react with itself and gain or lose subatomic particles. C) The atoms of the element form chemical bonds with each other, and that changes the weight of the element. D) The element may have multiple stable isotopes, and the isotopic com ...
... A) The element may undergo radioactive decay. B) The element may react with itself and gain or lose subatomic particles. C) The atoms of the element form chemical bonds with each other, and that changes the weight of the element. D) The element may have multiple stable isotopes, and the isotopic com ...
MOS (metal-oxide- semiconductor)
... Oxide-trapped charge Qot Oxide-trapped charge are associated with defect in the silicon dioxide. These charges can be created, for example, by X-ray radiation or high – energy electron bombardment the trap are distributed inside the oxide layer. Most of process-related oxidetrapped charge can be re ...
... Oxide-trapped charge Qot Oxide-trapped charge are associated with defect in the silicon dioxide. These charges can be created, for example, by X-ray radiation or high – energy electron bombardment the trap are distributed inside the oxide layer. Most of process-related oxidetrapped charge can be re ...
(1–1.5 kV) nitrogen-ion bombardment on sharply pointed tips
... the insertion of the specimen into the main chamber; this procedure is employed to maintain UHV conditions. Typically the ambient pressure in the main chamber is ,2310210 Torr. Then the tip is cooled to 60 K, which is the temperature of analysis ~T a !, and a positive voltage is applied to it to obt ...
... the insertion of the specimen into the main chamber; this procedure is employed to maintain UHV conditions. Typically the ambient pressure in the main chamber is ,2310210 Torr. Then the tip is cooled to 60 K, which is the temperature of analysis ~T a !, and a positive voltage is applied to it to obt ...
View accepted manuscript: Metastable triply charged diatomic
... In the tunneling limit [1] of multiphoton atomic ionization, the laser field oscillates so slowly that electrons adiabatically adjust to the field. Only the most weakly bound electron can tunnel through the oscillating barrier created by the laser field and the binding potential. Together with the h ...
... In the tunneling limit [1] of multiphoton atomic ionization, the laser field oscillates so slowly that electrons adiabatically adjust to the field. Only the most weakly bound electron can tunnel through the oscillating barrier created by the laser field and the binding potential. Together with the h ...