Chapter 3 Molecules, Compounds, and Chemical Equations
... Formulas Describe Compounds - a compound is a distinct substance that is composed of atoms of two or more elements. - describe the compound by describing the number and type of each atom in the simplest unit of the compound. molecules or ions - each element is represented by its letter symbol. - t ...
... Formulas Describe Compounds - a compound is a distinct substance that is composed of atoms of two or more elements. - describe the compound by describing the number and type of each atom in the simplest unit of the compound. molecules or ions - each element is represented by its letter symbol. - t ...
Understanding physical rock properties and their relation to fluid
... Especially, for Si a continuous increase of ion concentration in the fluid samples is revealed for increasing temperatures, indicating a beginning mineral dissolution above 150◦ C. At near-critical conditions also Al and Pb as well as the rare earth elements (REE) are more intensively dissolved. Fro ...
... Especially, for Si a continuous increase of ion concentration in the fluid samples is revealed for increasing temperatures, indicating a beginning mineral dissolution above 150◦ C. At near-critical conditions also Al and Pb as well as the rare earth elements (REE) are more intensively dissolved. Fro ...
Non-isothermal decomposition of Al, Cr and Fe cross
... The infrared spectra of the present complexes have been measured and the vibration assignments of the bands are cited in Table 2. It is well known[17] that the bands correspond to the symmetry stretching vibrations of the –OCO- (υs) in sodium alginate lie at 1400 cm-1 and that of the asymmetric stre ...
... The infrared spectra of the present complexes have been measured and the vibration assignments of the bands are cited in Table 2. It is well known[17] that the bands correspond to the symmetry stretching vibrations of the –OCO- (υs) in sodium alginate lie at 1400 cm-1 and that of the asymmetric stre ...
General Chemistry I - University of Toledo
... 5.15 Explain how electron shielding gives the order of subshells from lowest to highest in energy. 5.16 Predict the order of filling of subshells based upon energy. 5.17 Assign electron configurations to atoms in their ground state. 5.18 Draw orbital filling diagrams for the ground state of an atom ...
... 5.15 Explain how electron shielding gives the order of subshells from lowest to highest in energy. 5.16 Predict the order of filling of subshells based upon energy. 5.17 Assign electron configurations to atoms in their ground state. 5.18 Draw orbital filling diagrams for the ground state of an atom ...
4-아미노피리딘 – HCl, –HBr 복합체에 대한 양자화학적 연구 : 즈비터
... lower basicity than the 1-N or 3-N. Due to the high relative energy this conformer is of less importance. Since all the basic sites in 4AP are much less basic than ammonia, for which it is known that a solvating water molecule is needed to stabilize the zwitterionic form, it may be expected that the ...
... lower basicity than the 1-N or 3-N. Due to the high relative energy this conformer is of less importance. Since all the basic sites in 4AP are much less basic than ammonia, for which it is known that a solvating water molecule is needed to stabilize the zwitterionic form, it may be expected that the ...
In chemistry, a salt is an ionic compound that
... In chemistry, a salt is an ionic compound that results from the neutralization reaction of an acid and a base.[1] Salts are composed of related numbers of cations (positively charged ions) and anions (negative ions) so that the product is electrically neutral (without a net charge). These component ...
... In chemistry, a salt is an ionic compound that results from the neutralization reaction of an acid and a base.[1] Salts are composed of related numbers of cations (positively charged ions) and anions (negative ions) so that the product is electrically neutral (without a net charge). These component ...
Topic 1: Quantitative chemistry (12
... Be able to identify the ultraviolet, visible and infrared regions, and to describe the variation in wavelength, frequency and energy across the spectrum. TOK: Infrared and ultraviolet spectroscopy are dependent on technology for their existence. What are the knowledge implications of this? Distingui ...
... Be able to identify the ultraviolet, visible and infrared regions, and to describe the variation in wavelength, frequency and energy across the spectrum. TOK: Infrared and ultraviolet spectroscopy are dependent on technology for their existence. What are the knowledge implications of this? Distingui ...
Sample % Sulfate Absolute Deviation A 44.02 B 44.11 C 43.98 D
... sample has cooled, you notice a few globs of liquid mercury are mixed together with unreacted red powder. If the mass of the resulting mixture is 82.5 g, how much oxygen was produced during the heating? Which law are you making use of for this answer? ...
... sample has cooled, you notice a few globs of liquid mercury are mixed together with unreacted red powder. If the mass of the resulting mixture is 82.5 g, how much oxygen was produced during the heating? Which law are you making use of for this answer? ...
Battery Materials
... Potential window of water: 1.23 V To achieve the higher voltages, the non-aqueous electrolytes have to be used ...
... Potential window of water: 1.23 V To achieve the higher voltages, the non-aqueous electrolytes have to be used ...
Chemistry 115 Lecture Number Seventeen Test Two Review April 2
... -oxidation numbers are a value assigned either to every element in an ion or molecule involved in reaction, number can either have a negative or positive value, or could be zero (can be fractions as well as whole numbers) -reactions occur according to the theoretical model of oxidation numbers -in i ...
... -oxidation numbers are a value assigned either to every element in an ion or molecule involved in reaction, number can either have a negative or positive value, or could be zero (can be fractions as well as whole numbers) -reactions occur according to the theoretical model of oxidation numbers -in i ...
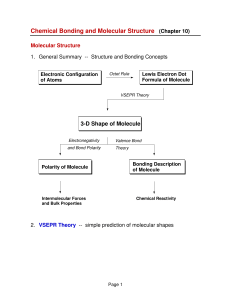
3-D Shape of Molecule
... 2. Molecular Orbitals for simple diatomic molecules (H2 and He2) in H2 the 1s atomic orbitals on the two H atoms are combined into: a bonding MO -- σ1s and an antibonding MO -- σ*1s MO energy level diagram for H2 (only the bonding MO is filled): ...
... 2. Molecular Orbitals for simple diatomic molecules (H2 and He2) in H2 the 1s atomic orbitals on the two H atoms are combined into: a bonding MO -- σ1s and an antibonding MO -- σ*1s MO energy level diagram for H2 (only the bonding MO is filled): ...
Section 4.8: Acid-Base Reactions
... Two compounds react to form two new compounds. All double replacement reactions must have a "driving force" that removes a pair of ions from solution. Ions in a precipitation reaction will keep their same charges as reactants and products. Formation of a precipitate: A precipitate is an insoluble su ...
... Two compounds react to form two new compounds. All double replacement reactions must have a "driving force" that removes a pair of ions from solution. Ions in a precipitation reaction will keep their same charges as reactants and products. Formation of a precipitate: A precipitate is an insoluble su ...
Document
... ionic solids are soluble in water and which are insoluble • all compounds containing Na+, K+, and NH4+ are soluble in water • all nitrates (NO3-) and acetates (CH3COO-) are soluble in water • most chlorides (Cl-) and sulfates (SO42-) are soluble; exceptions are AgCl, BaSO4, and PbSO4 ...
... ionic solids are soluble in water and which are insoluble • all compounds containing Na+, K+, and NH4+ are soluble in water • all nitrates (NO3-) and acetates (CH3COO-) are soluble in water • most chlorides (Cl-) and sulfates (SO42-) are soluble; exceptions are AgCl, BaSO4, and PbSO4 ...
Chapter 3 Molecules, Compounds, and Chemical Equations q
... - hold atoms together to form compounds - are forces of attraction between atoms. - the bonding g attraction comes from attractions between protons and electrons. i.) Ionic bonds - result when electrons have been transferred between atoms, resulting in oppositely charged ions that attract each other ...
... - hold atoms together to form compounds - are forces of attraction between atoms. - the bonding g attraction comes from attractions between protons and electrons. i.) Ionic bonds - result when electrons have been transferred between atoms, resulting in oppositely charged ions that attract each other ...
Structures and Properties of Ceramics
... structural components at high temperatures. TiN has a cubic structure which is perhaps the simplest and best known of structure types. Cations and anions both lie at the nodes of separate fcc lattices. The structure is unchanged if the Ti and N atoms (lattices) are interchanged. ...
... structural components at high temperatures. TiN has a cubic structure which is perhaps the simplest and best known of structure types. Cations and anions both lie at the nodes of separate fcc lattices. The structure is unchanged if the Ti and N atoms (lattices) are interchanged. ...
Worksheet
... (E) 14 15. How many grams of calcium nitrate, Ca(NO3)2, contains 24 grams of oxygen atoms? (A) 164 grams (B) 96 grams (C) 62 grams (D) 50. grams (E) 41 grams 16. The simplest formula for an oxide of nitrogen that is 36.8 percent nitrogen by weight is (A) N2O (B) NO (C) NO2 (D) N2O3 (E) N2O5 17. How ...
... (E) 14 15. How many grams of calcium nitrate, Ca(NO3)2, contains 24 grams of oxygen atoms? (A) 164 grams (B) 96 grams (C) 62 grams (D) 50. grams (E) 41 grams 16. The simplest formula for an oxide of nitrogen that is 36.8 percent nitrogen by weight is (A) N2O (B) NO (C) NO2 (D) N2O3 (E) N2O5 17. How ...
2013 Avogadro Exam
... • Mark only one answer for each question. • Questions are all of the same value. • There is a penalty (1/4 off) for each incorrect answer, but no penalty if you do not answer. 7. Take care that you make firm, black pencil marks, just filling the oval. Be careful that any erasures are complete—make t ...
... • Mark only one answer for each question. • Questions are all of the same value. • There is a penalty (1/4 off) for each incorrect answer, but no penalty if you do not answer. 7. Take care that you make firm, black pencil marks, just filling the oval. Be careful that any erasures are complete—make t ...
CST REVIEW Percent Error 1. 2. What is the formula for density?
... 26. Name them. 27. What type of bonds are formed when two or more non-metal atoms combine? 28. Chemical bonds between atoms in molecules such as H2, CH4, NH3, H2CCH2, NH2CH2COOH, N2, Cl2, and many large biological molecules are bonds. 29. Identify the following as a monatomic gas or a diatomic molec ...
... 26. Name them. 27. What type of bonds are formed when two or more non-metal atoms combine? 28. Chemical bonds between atoms in molecules such as H2, CH4, NH3, H2CCH2, NH2CH2COOH, N2, Cl2, and many large biological molecules are bonds. 29. Identify the following as a monatomic gas or a diatomic molec ...
Chapter 4_Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
... A chemical bond is defined as an attractive force that holds the constituents (atoms, ions etc.) together in a chemical species. Various theories have been suggested for the formation of chemical bonds such as the electronic theory, valence shell electron pair repulsion theory, valence bond theory, ...
... A chemical bond is defined as an attractive force that holds the constituents (atoms, ions etc.) together in a chemical species. Various theories have been suggested for the formation of chemical bonds such as the electronic theory, valence shell electron pair repulsion theory, valence bond theory, ...
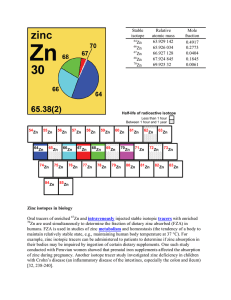
Zinc isotopes in biology Oral tracers of enriched Zn and
... atomic number (Z) – The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. atomic weight (relative mean atomic mass) – the sum of the products of the relative atomic mass and the mole fraction of each stable and long-lived radioactive isotope of that element in the sample. The symbol of the atomic weight ...
... atomic number (Z) – The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. atomic weight (relative mean atomic mass) – the sum of the products of the relative atomic mass and the mole fraction of each stable and long-lived radioactive isotope of that element in the sample. The symbol of the atomic weight ...
Chapter 4:Chemical Quantities and Aqueous Reactions:
... expected products. Refer to the solubility rules to determine if solid forms. (D-D) double displacement: AB + CD AD + CB A double displacement reaction starts with two ionic compounds in which the ions exchange to produce new balanced ionic compounds. Always write the cation before the anion and v ...
... expected products. Refer to the solubility rules to determine if solid forms. (D-D) double displacement: AB + CD AD + CB A double displacement reaction starts with two ionic compounds in which the ions exchange to produce new balanced ionic compounds. Always write the cation before the anion and v ...
Plasma Physics Definitions
... DC Glow Discharge • Positive ions are accelerated toward the negative electrode (cathode). Collision with the cathode causes the emission of secondary electrons which are emitted from the cathode into the plasma. ...
... DC Glow Discharge • Positive ions are accelerated toward the negative electrode (cathode). Collision with the cathode causes the emission of secondary electrons which are emitted from the cathode into the plasma. ...
Oxidation and Reduction
... Fictive charges which are given to an element by some rules. The oxidation number is described by positive or negative roman numbers and they are written above or in brackets after the element they are assigned to. Rules of the assignment of the oxidation number: *the sum of the ON’s of all the atom ...
... Fictive charges which are given to an element by some rules. The oxidation number is described by positive or negative roman numbers and they are written above or in brackets after the element they are assigned to. Rules of the assignment of the oxidation number: *the sum of the ON’s of all the atom ...