biologic chemistry
... NATURE OF MATTER: ATOMS: “Basic unit of matter” An atom is the smallest portion of a substance that still retains the unique properties of that substance. ...
... NATURE OF MATTER: ATOMS: “Basic unit of matter” An atom is the smallest portion of a substance that still retains the unique properties of that substance. ...
Chapters 1-3 Packet
... Nonmetals - elements found on the right side of the staircase, gases, liquid, & solid; usually poor conductors and are brittle Metalloids - elements that lie along staircase which have properties of both metals and nonmetals (except Al, which is usually considered a metal) -------------------------- ...
... Nonmetals - elements found on the right side of the staircase, gases, liquid, & solid; usually poor conductors and are brittle Metalloids - elements that lie along staircase which have properties of both metals and nonmetals (except Al, which is usually considered a metal) -------------------------- ...
Carefully detach the last page. It is the Data Sheet.
... The vapour pressure of water is 3.17 kPa at 298 K. ...
... The vapour pressure of water is 3.17 kPa at 298 K. ...
Semiconductor Crystals_Nov 6 2008
... In terms of carrier mobility, this conductivity can be written as: =(e + h) =(nee + peh) where n and p are the electron and hole concentrations, respectively. Hence, the conductivity can be thought of as the sum of the contribution due to electrons and the contribution due to holes. By compari ...
... In terms of carrier mobility, this conductivity can be written as: =(e + h) =(nee + peh) where n and p are the electron and hole concentrations, respectively. Hence, the conductivity can be thought of as the sum of the contribution due to electrons and the contribution due to holes. By compari ...
X012/13/02
... 2. Burning magnesium continues to burn when placed in a gas jar of carbon dioxide according to the ...
... 2. Burning magnesium continues to burn when placed in a gas jar of carbon dioxide according to the ...
Chapter 4 2013
... 3. Break the compounds into their ions and write the ionic equation for the reaction. 3. Refer to the table of solubility rules and decide whether any of the ion combinations is insoluble. 4. If a candidate is insoluble, that reaction will occur. 5. Remove the spectator ions and write the net ionic ...
... 3. Break the compounds into their ions and write the ionic equation for the reaction. 3. Refer to the table of solubility rules and decide whether any of the ion combinations is insoluble. 4. If a candidate is insoluble, that reaction will occur. 5. Remove the spectator ions and write the net ionic ...
Chemistry Midterm Review 2006
... of each. Objectives 2.2 1. What kind of elements form ionic compounds? What kind of elements form covalent(molecular) compounds? 2. Which of the following compounds are ionic? H2O, Na2O, CO2, CaS2, SO2, CaCO3. 3. Know the difference between a formula unit and a molecule. 4. Define ion. What is the d ...
... of each. Objectives 2.2 1. What kind of elements form ionic compounds? What kind of elements form covalent(molecular) compounds? 2. Which of the following compounds are ionic? H2O, Na2O, CO2, CaS2, SO2, CaCO3. 3. Know the difference between a formula unit and a molecule. 4. Define ion. What is the d ...
Chapter1011
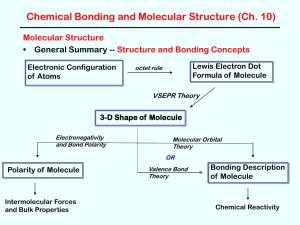
... • Use valence bond theory to describe the bonding in the following (use clear 3-D pictures showing orbital overlap, etc) H2O NH3 CH4 PF3 --simple s bonds and lone pairs H2CNH --double bond like H2CCH2 ethene and H2CO formaldehyde) HCN --triple bond like HCCH ethyne and N2 nitrogen) ...
... • Use valence bond theory to describe the bonding in the following (use clear 3-D pictures showing orbital overlap, etc) H2O NH3 CH4 PF3 --simple s bonds and lone pairs H2CNH --double bond like H2CCH2 ethene and H2CO formaldehyde) HCN --triple bond like HCCH ethyne and N2 nitrogen) ...
CHEMISTRY 112 LECTURE
... Since an electrode potential, E°, depends upon the concentration of the solutions used in the electrode, a cell may be constructed from two half-cells composed of the same materials but differing in concentration of ions. The spontaneous reaction occurs in the direction that tends to make the two io ...
... Since an electrode potential, E°, depends upon the concentration of the solutions used in the electrode, a cell may be constructed from two half-cells composed of the same materials but differing in concentration of ions. The spontaneous reaction occurs in the direction that tends to make the two io ...
4.1 Writing and Balancing Chemical Equations
... The physical states of reactants and products in chemical equations very often are indicated with a parenthetical abbreviation following the formulas. Common abbreviations include s for solids, l for liquids, g for gases, and aq for substances dissolved in water (aqueous solutions, as introduced in ...
... The physical states of reactants and products in chemical equations very often are indicated with a parenthetical abbreviation following the formulas. Common abbreviations include s for solids, l for liquids, g for gases, and aq for substances dissolved in water (aqueous solutions, as introduced in ...
Chapter 4 Aqueous Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry
... • To form the net ionic equation, cross out anything that does not change from the left side of the equation to the right. • The only things left in the equation are those things that change phase (i.e., chemically react (precipitate) during the course of the reaction. • Those things that didn’t cha ...
... • To form the net ionic equation, cross out anything that does not change from the left side of the equation to the right. • The only things left in the equation are those things that change phase (i.e., chemically react (precipitate) during the course of the reaction. • Those things that didn’t cha ...
University of Crete, Materials Science, English 3 special Module 1
... separated or decomposed into simpler substances. On the other hand, a chemical combination of an element is a compound. Mixtures are divided into two kinds: heterogeneous and homogeneous. The former consists of discernible parts or phases whereas the latter is made up of components that cannot be in ...
... separated or decomposed into simpler substances. On the other hand, a chemical combination of an element is a compound. Mixtures are divided into two kinds: heterogeneous and homogeneous. The former consists of discernible parts or phases whereas the latter is made up of components that cannot be in ...
Mr. B`s Chemistry
... A piece of nickel metal is immersed in a solution of copper(II) sulfate. Ni + Cu2+ ...
... A piece of nickel metal is immersed in a solution of copper(II) sulfate. Ni + Cu2+ ...
Chemistry Final Exam Test Yourself I
... electrons. Composed of non-metals (Covalent) A compound is this when the atoms in it give or take electrons. Composed of at least one non-metal and one metal (Ionic) ...
... electrons. Composed of non-metals (Covalent) A compound is this when the atoms in it give or take electrons. Composed of at least one non-metal and one metal (Ionic) ...
Tutorial 5 - Electrochemistry
... The electrical energy generated by the spontaneous reaction is proportional to the cell potential. The standard cell potential (the cell potential measured when all the species are in their standard states) is given by: E°cell = E°cathode - E°anode ...
... The electrical energy generated by the spontaneous reaction is proportional to the cell potential. The standard cell potential (the cell potential measured when all the species are in their standard states) is given by: E°cell = E°cathode - E°anode ...
Chemistry - Beachwood City Schools
... between the levels. The greater the energy difference, the shorter the wavelength of light, the more violet the color. 3. The electron configurations of all Group 1 metals end with a single s electron. When these metals lose this s electron, they acquire noble gas electron configurations which end i ...
... between the levels. The greater the energy difference, the shorter the wavelength of light, the more violet the color. 3. The electron configurations of all Group 1 metals end with a single s electron. When these metals lose this s electron, they acquire noble gas electron configurations which end i ...
1. This is a question about trends in chemistry In
... CH3CH2*CH(OH)CH2CH2CH3 and can exist as two different optical isomers (enantiomers), which are nonsuperimposable mirror images. A molecule which contains just one chiral centre will always exist in two enantiomeric forms. However, some molecules with two or more chiral centres can be achiral, i.e. t ...
... CH3CH2*CH(OH)CH2CH2CH3 and can exist as two different optical isomers (enantiomers), which are nonsuperimposable mirror images. A molecule which contains just one chiral centre will always exist in two enantiomeric forms. However, some molecules with two or more chiral centres can be achiral, i.e. t ...
14.1 Redox equations
... Work out the formula of the species before and after the change; balance if required Work out the oxidation state of the element before and after the change Add electrons to one side of the equation so that the oxidation states balance If the charges on all the species (ions and electrons) on either ...
... Work out the formula of the species before and after the change; balance if required Work out the oxidation state of the element before and after the change Add electrons to one side of the equation so that the oxidation states balance If the charges on all the species (ions and electrons) on either ...
NTD_Final_Ch3-1_3-2 DOWNLOAD
... bonds with four adjacent atoms as shown in Fig. 2(a). In the figure, each dot represents a normal valence electron involved in the covalent bond. One of these covalent electrons can be lost by thermal excitation leaving behind an unsaturated bond or hole. In the silicon doped by an element in group ...
... bonds with four adjacent atoms as shown in Fig. 2(a). In the figure, each dot represents a normal valence electron involved in the covalent bond. One of these covalent electrons can be lost by thermal excitation leaving behind an unsaturated bond or hole. In the silicon doped by an element in group ...
L1 – CHEMISTRY FINAL REVIEW
... MP/BP depends on what type of compounds you are comparing them with. With other molecular comps. High, but compared to other types of cmpds. low. Non-Polar Mc’s- Cl2; CH4; nonconductors and low MP/BP. Will dissolve in non-polar Solvents only. Network Covalent- Ex; graphite, diamond and quartz; they ...
... MP/BP depends on what type of compounds you are comparing them with. With other molecular comps. High, but compared to other types of cmpds. low. Non-Polar Mc’s- Cl2; CH4; nonconductors and low MP/BP. Will dissolve in non-polar Solvents only. Network Covalent- Ex; graphite, diamond and quartz; they ...
SOLID-STATE PHYSICS II 2007 O. Entin-Wohlman
... Hence the d−shell is five-fold degenerate, namely, there are five single-electron wave functions (or orbitals) corresponding to the d−shell. Each of these orbitals can accumulate two spin directions, namely it may have sz = ±1/2, and therefore the full degeneracy of the d−shell is 10. In other words ...
... Hence the d−shell is five-fold degenerate, namely, there are five single-electron wave functions (or orbitals) corresponding to the d−shell. Each of these orbitals can accumulate two spin directions, namely it may have sz = ±1/2, and therefore the full degeneracy of the d−shell is 10. In other words ...
Polarity of covalent bonds
... Early concepts in covalent bonding arose from this kind of image of the molecule of methane. Covalent bonding is implied in the Lewis structure that indicates sharing of electrons between atoms. The term "covalence" in regard to bonding was first used in 1919 by Irving Langmuir in a Journal of the A ...
... Early concepts in covalent bonding arose from this kind of image of the molecule of methane. Covalent bonding is implied in the Lewis structure that indicates sharing of electrons between atoms. The term "covalence" in regard to bonding was first used in 1919 by Irving Langmuir in a Journal of the A ...
Welcome to AP Chemistry! AP Chemistry is
... which contains a monatomic anion, drop the start the name with hydro, drop the -ide ending of the anion and add the suffix, -ic acid. For example, HBr is hydrobromic acid. 2. Oxyacids contain polyatomic anions such as nitrite, carbonate, etc. To name an acid with an anion ending with the -ite suffix ...
... which contains a monatomic anion, drop the start the name with hydro, drop the -ide ending of the anion and add the suffix, -ic acid. For example, HBr is hydrobromic acid. 2. Oxyacids contain polyatomic anions such as nitrite, carbonate, etc. To name an acid with an anion ending with the -ite suffix ...