insoluble compounds of heavy metal complexes
... Heavy metals such as Zn, Cu, Ni, Cr, Mo are essential nutrients for plants and animals. However, they become toxic at high concentrations. The toxicity of heavy metals depends mostly on a free ion, i.e. on a soluble metal compound concentration rather than on the total metal concentration. The insol ...
... Heavy metals such as Zn, Cu, Ni, Cr, Mo are essential nutrients for plants and animals. However, they become toxic at high concentrations. The toxicity of heavy metals depends mostly on a free ion, i.e. on a soluble metal compound concentration rather than on the total metal concentration. The insol ...
Student Notes
... • A salt bridge is used to complete the electrical circuit. • Cations move from anode to cathode. • Anions move from cathode to anode. • The two solid metals are the electrodes (cathode and anode). • As oxidation occurs, Zn is converted to Zn2+ and 2e–. • The electrons flow toward the cathode where ...
... • A salt bridge is used to complete the electrical circuit. • Cations move from anode to cathode. • Anions move from cathode to anode. • The two solid metals are the electrodes (cathode and anode). • As oxidation occurs, Zn is converted to Zn2+ and 2e–. • The electrons flow toward the cathode where ...
Document
... 12.When 20 gm of an acid (C11H8O2) is dissolved in 50 gm benzene (K f=1.72K kg mol‐1) a freezing point depression of 2K is observed.Thevant Hoff’s factor is ...
... 12.When 20 gm of an acid (C11H8O2) is dissolved in 50 gm benzene (K f=1.72K kg mol‐1) a freezing point depression of 2K is observed.Thevant Hoff’s factor is ...
Chemistry 40S – Exam Review
... 15. The [OH-] in a solution is 1.0 x 10-4 mol/L. What is the pH of the solution? 16. What is the [H3O+] in a 0.20 mol/L NaOH solution? 17. A solution has a [H+] of 0.0010 M. What is the [OH-]? 18. What is the [H3O+] in a 0.020 M Ba(OH)2(aq) solution? 19. A base added to a neutral solution will: a) ...
... 15. The [OH-] in a solution is 1.0 x 10-4 mol/L. What is the pH of the solution? 16. What is the [H3O+] in a 0.20 mol/L NaOH solution? 17. A solution has a [H+] of 0.0010 M. What is the [OH-]? 18. What is the [H3O+] in a 0.020 M Ba(OH)2(aq) solution? 19. A base added to a neutral solution will: a) ...
2 The Nature of Matter
... evaporation (also known as vapourization): liquid to gas condensation: gas to liquid sublimation: solid to gas deposition: gas to solid ...
... evaporation (also known as vapourization): liquid to gas condensation: gas to liquid sublimation: solid to gas deposition: gas to solid ...
Book-Abstracts - The Fritz Haber Center for Molecular dynamics
... wide range of phenomena such as in upper atmosphere and outer space chemistry where it may be an important factor affecting heterogeneous chemical processes. In biological systems the interaction of slow electrons is also a most important aspect of radiation medicine as many very low energy secondar ...
... wide range of phenomena such as in upper atmosphere and outer space chemistry where it may be an important factor affecting heterogeneous chemical processes. In biological systems the interaction of slow electrons is also a most important aspect of radiation medicine as many very low energy secondar ...
File
... 1. Atoms are made of _________________ (+), _________________ (neutral), and ___________________ (-). 2. ______________________ and ____________________ are in the nucleus of the atom and when added together they give you the ___________________________ of the atom. 3. _________________ move quickly ...
... 1. Atoms are made of _________________ (+), _________________ (neutral), and ___________________ (-). 2. ______________________ and ____________________ are in the nucleus of the atom and when added together they give you the ___________________________ of the atom. 3. _________________ move quickly ...
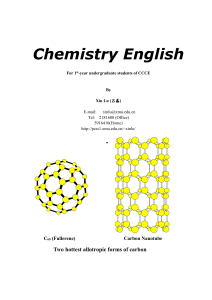
Chemistry English
... How to illustrate the 2p orbitals that contain 6 electrons? 3.12 Writing Electronic Configurations for Atoms The electronic configurations for an atom is written by listing the orbitals occupied by electrons in the atom along with the number of electrons in each orbitals. Three Rules which must be f ...
... How to illustrate the 2p orbitals that contain 6 electrons? 3.12 Writing Electronic Configurations for Atoms The electronic configurations for an atom is written by listing the orbitals occupied by electrons in the atom along with the number of electrons in each orbitals. Three Rules which must be f ...
CHEM 1405 Practice Exam #2
... A) Solid sodium carbonate is heated to give solid sodium oxide and carbon dioxide gas. B) Sodium carbonate decomposes to sodium oxide and carbon dioxide. C) Sodium carbonate decomposes to sodium oxide and carbon dioxide gas. D) Sodium carbonate is heated to give sodium oxide and carbon dioxide. 20) ...
... A) Solid sodium carbonate is heated to give solid sodium oxide and carbon dioxide gas. B) Sodium carbonate decomposes to sodium oxide and carbon dioxide. C) Sodium carbonate decomposes to sodium oxide and carbon dioxide gas. D) Sodium carbonate is heated to give sodium oxide and carbon dioxide. 20) ...
Chapter 3 Chemical Reactions
... from the left side to the right side of the equation (spectator ions). Write the net ionic equation with the species that remain. Be sure to include charges on ions and states of your ions (aq) and precipitate (s). © 2009, Prentice-Hall, Inc. ...
... from the left side to the right side of the equation (spectator ions). Write the net ionic equation with the species that remain. Be sure to include charges on ions and states of your ions (aq) and precipitate (s). © 2009, Prentice-Hall, Inc. ...
Topic 5 Reacting masses and chemical equations notes
... Because of the incredibly small size of atoms, it is not possible to weigh them directly. Instead the masses of atoms are related to an arbitrary standard; for this purpose the mass of one atom of 12C is taken to be 12.0000. The mass of any other atom compared to that of the carbon atom is called it ...
... Because of the incredibly small size of atoms, it is not possible to weigh them directly. Instead the masses of atoms are related to an arbitrary standard; for this purpose the mass of one atom of 12C is taken to be 12.0000. The mass of any other atom compared to that of the carbon atom is called it ...
Answer Key
... E) 42 g 9. The mass of 1.63 1021 silicon atoms is A) 1.04 104 g. B) 28.08 g. C) 2.71 10–23 g. D) 7.60 10–2 g. E) 4.58 1022 g. ...
... E) 42 g 9. The mass of 1.63 1021 silicon atoms is A) 1.04 104 g. B) 28.08 g. C) 2.71 10–23 g. D) 7.60 10–2 g. E) 4.58 1022 g. ...
Final Exam Review Packet
... barometric pressure is 758 mm Hg. What is the volume of this gas at STP? a. 23.6 mL b. 25.1 mL c. 30.3 mL d. 32.2 mL ...
... barometric pressure is 758 mm Hg. What is the volume of this gas at STP? a. 23.6 mL b. 25.1 mL c. 30.3 mL d. 32.2 mL ...
Semester 1 exam review
... 11. Why are the transition metals called the transition metals 12. Give three elements in the alkaline earth metals family and a specific use of each. 13. What are the general properties of the halogen family? 14. What are three elements and their uses that are found in the nitrogen family? 15. What ...
... 11. Why are the transition metals called the transition metals 12. Give three elements in the alkaline earth metals family and a specific use of each. 13. What are the general properties of the halogen family? 14. What are three elements and their uses that are found in the nitrogen family? 15. What ...
File
... The reactivity of alkali metals decreases going down the group. What is the reason for this? The atoms of each element get F larger going down the group. This means that the outer shell gets further away from the nucleus and is shielded by more electron shells. Cl The further the outer shell ...
... The reactivity of alkali metals decreases going down the group. What is the reason for this? The atoms of each element get F larger going down the group. This means that the outer shell gets further away from the nucleus and is shielded by more electron shells. Cl The further the outer shell ...
Lecture 3 - TAMU Chemistry
... ligands are derived from anionic precursors: halides, hydroxide, alkoxide alkyls—species that are one-electron neutral ligands, but two electron donors as anionic ligands. EDTA4- is classified as an L2X4 ligand, features four anions and two neutral donor sites. C5H5 is classified an ...
... ligands are derived from anionic precursors: halides, hydroxide, alkoxide alkyls—species that are one-electron neutral ligands, but two electron donors as anionic ligands. EDTA4- is classified as an L2X4 ligand, features four anions and two neutral donor sites. C5H5 is classified an ...
Kinetic study of the oxidation of malonic acid by
... the seventieth years [9] and for this reason, great attention is given to the study of its partial reaction steps, too. Such a step is also the oxidation of malonic acid by the Mn(III) ions which is the topic of this study. The first reaction order with respect to concentration of the Mn(III) ions i ...
... the seventieth years [9] and for this reason, great attention is given to the study of its partial reaction steps, too. Such a step is also the oxidation of malonic acid by the Mn(III) ions which is the topic of this study. The first reaction order with respect to concentration of the Mn(III) ions i ...
AP_chemical reaction and quantities
... • Many reactions take place between compounds or elements that are dissolved in water. Ionic compounds and some polar covalent compounds break apart (dissociate) when they dissolve in water and form ions. ...
... • Many reactions take place between compounds or elements that are dissolved in water. Ionic compounds and some polar covalent compounds break apart (dissociate) when they dissolve in water and form ions. ...
lect2_htm
... This effect is important - avoided crossings are often the reason why chemical reactions have a barrier. The Rule applies to molecular orbitals as well as wavefunctions for whole molecules. For example, consider a situation where a molecule has two molecular orbitals. The energies of these MOs are ...
... This effect is important - avoided crossings are often the reason why chemical reactions have a barrier. The Rule applies to molecular orbitals as well as wavefunctions for whole molecules. For example, consider a situation where a molecule has two molecular orbitals. The energies of these MOs are ...
82KB - NZQA
... This is a combination reaction because two elements, sulfur and chlorine combine to form a new substance / compound, (di)sulfur dichloride. 2Na(s) + Cl2(g) → 2NaCl(s) S(s) + Cl2(g) → SCl2(s) or 2S(s) (or S2 (s)) + Cl2(g) → S2Cl2(g) Sodium is a metal element and when it reacts with chlorine gas, both ...
... This is a combination reaction because two elements, sulfur and chlorine combine to form a new substance / compound, (di)sulfur dichloride. 2Na(s) + Cl2(g) → 2NaCl(s) S(s) + Cl2(g) → SCl2(s) or 2S(s) (or S2 (s)) + Cl2(g) → S2Cl2(g) Sodium is a metal element and when it reacts with chlorine gas, both ...
Chapter 1: Matter and Measurement
... Metals tend to lose electrons (lose negative charge) to form positively charged ions called cations. Non-metals tend to gain electrons (gain negative charge) to form negatively charged ions called anions. Chemistry 140 Fall 2002 Dutton ...
... Metals tend to lose electrons (lose negative charge) to form positively charged ions called cations. Non-metals tend to gain electrons (gain negative charge) to form negatively charged ions called anions. Chemistry 140 Fall 2002 Dutton ...
PDF w
... actually used as a basis. The great effect of water on reaction 14, which is 57 kcal. exothermic in the gas, is shown by returning to reaction 11 in water which is 2 kcal. endothermic. The difference is chiefly due to the heats of hydration of the ions. The negative hydration heats for the halide io ...
... actually used as a basis. The great effect of water on reaction 14, which is 57 kcal. exothermic in the gas, is shown by returning to reaction 11 in water which is 2 kcal. endothermic. The difference is chiefly due to the heats of hydration of the ions. The negative hydration heats for the halide io ...