Answers - Scioly.org
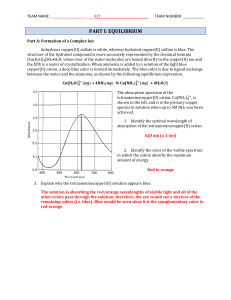
... or Cd(NH3 , are the ammonia ligands attached through stronger coordinate covalent bonds to the center metal cation? Explain your answer. The lower Kf value for tetraamminecadmium(II) indicates that a larger concentration of ammonia molecules is present in the equilibrium mixture. This implies that t ...
... or Cd(NH3 , are the ammonia ligands attached through stronger coordinate covalent bonds to the center metal cation? Explain your answer. The lower Kf value for tetraamminecadmium(II) indicates that a larger concentration of ammonia molecules is present in the equilibrium mixture. This implies that t ...
Proteomics1_2012
... Tandem MS/MS (peptide sequencing): Pulls each peptide from the first MS Breaks up peptide bond Identifies each fragment based on m/z ...
... Tandem MS/MS (peptide sequencing): Pulls each peptide from the first MS Breaks up peptide bond Identifies each fragment based on m/z ...
slides introducing IR/Raman of proteins
... V = V0 + S (dV/dqi)0qi + (½) S (d2V/dqiqj)0qiqj + . . . . . • This results in a molecular energy that is just the sum of the individual vibrational energies of each normal mode: ...
... V = V0 + S (dV/dqi)0qi + (½) S (d2V/dqiqj)0qiqj + . . . . . • This results in a molecular energy that is just the sum of the individual vibrational energies of each normal mode: ...
PRACTICE TEST for EXAM 10
... is monoprotic. So is HC2H3O2: the H at the beginning is acidic, the 3 Hs in the middle are not. c. Polyprotic means the molecule has more than one acidic hydrogen. H2SO4 and H3PO4 are polyprotic. d. Amphoteric means the molecule or ion may act as either an acid (H1+ donor) or a base (H1+ acceptor), ...
... is monoprotic. So is HC2H3O2: the H at the beginning is acidic, the 3 Hs in the middle are not. c. Polyprotic means the molecule has more than one acidic hydrogen. H2SO4 and H3PO4 are polyprotic. d. Amphoteric means the molecule or ion may act as either an acid (H1+ donor) or a base (H1+ acceptor), ...
Chemistry I Syllabus 2011-2012
... relative mass of atoms determined? What does that indicate about the way in which they react? 3. What evidence is there for the existence of electrons and the nucleus? 4. How does the spectrum of hydrogen provide insight into a model of the structure of the atom? 5. How do the ionization energies of ...
... relative mass of atoms determined? What does that indicate about the way in which they react? 3. What evidence is there for the existence of electrons and the nucleus? 4. How does the spectrum of hydrogen provide insight into a model of the structure of the atom? 5. How do the ionization energies of ...
Chapter 11 Chemical Reactions
... Two things replace each other. – Reactants must be two ionic compounds, in aqueous solution ...
... Two things replace each other. – Reactants must be two ionic compounds, in aqueous solution ...
Name: Northwest Vista College Chem 1311
... 7. How many carbon atoms are there in 10 lbs of sugar, C12H22O11? A) 9.6 x 1025 atoms B) 8.0 x 1024 atoms C) 159 atoms D) 4.21 atoms E) 342 atoms 8. Which of the following compounds is a strong electrolyte? A) H2O B) N2 C) CH3COOH (acetic acid) D) CH3CH2OH (ethanol) E) KOH 9. Based on the solubility ...
... 7. How many carbon atoms are there in 10 lbs of sugar, C12H22O11? A) 9.6 x 1025 atoms B) 8.0 x 1024 atoms C) 159 atoms D) 4.21 atoms E) 342 atoms 8. Which of the following compounds is a strong electrolyte? A) H2O B) N2 C) CH3COOH (acetic acid) D) CH3CH2OH (ethanol) E) KOH 9. Based on the solubility ...
Unit 3 Notes
... Increasing the pressure will cause the equilibrium to move to ............................. the pressure. The equilibrium will move to .............................. the number of gas particles. The equilibrium moves to the .................. producing more ........................ and less ........ ...
... Increasing the pressure will cause the equilibrium to move to ............................. the pressure. The equilibrium will move to .............................. the number of gas particles. The equilibrium moves to the .................. producing more ........................ and less ........ ...
CHAPTER 1, MATTER AND CHANGE Section 1, Chemistry Is a
... Six branches of chemistry: organic chemistry, inorganic chemistry, physical chemistry, analytical chemistry, biochemistry, and theoretical chemistry. A chemical is any substance that has a definite composition. Section 2, Matter and Its Properties Mass is a measure of the amount of matter. (Use a ba ...
... Six branches of chemistry: organic chemistry, inorganic chemistry, physical chemistry, analytical chemistry, biochemistry, and theoretical chemistry. A chemical is any substance that has a definite composition. Section 2, Matter and Its Properties Mass is a measure of the amount of matter. (Use a ba ...
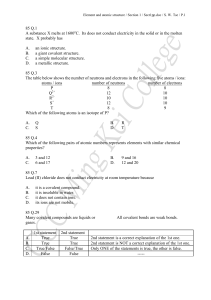
85 Q.1 A substance X melts at 1600oC. Its does
... X Which of the following statements are correct? (1) There is one electron in the outermost shell of an atom of X. (2) There are five electrons in the outermost shell of an atom of Y. (3) There are eight electrons in the outermost shell of an atom of Z. A. C. ...
... X Which of the following statements are correct? (1) There is one electron in the outermost shell of an atom of X. (2) There are five electrons in the outermost shell of an atom of Y. (3) There are eight electrons in the outermost shell of an atom of Z. A. C. ...
Stuff Matters Handout
... object. Matter is sometimes related to light and electromagnetic radiation. Even though matter can be found all over the Universe, you only find it in a few forms. As of 1995, scientists have identified five physical states of matter (we will be concerned with only three). Each of those states is so ...
... object. Matter is sometimes related to light and electromagnetic radiation. Even though matter can be found all over the Universe, you only find it in a few forms. As of 1995, scientists have identified five physical states of matter (we will be concerned with only three). Each of those states is so ...
chemistry I review pwrpt.
... •Varied chemical makeup from sample to sample. • 2 or more substances physically combined •Homo or Hetero Mixtures • Pizza and salt water ...
... •Varied chemical makeup from sample to sample. • 2 or more substances physically combined •Homo or Hetero Mixtures • Pizza and salt water ...
C5H12 + 8 O2 → 5 CO2 + 6 H2O
... e.g. oxidation number for Cl2 is ___, for Fe is ___. 2. The oxidation number of a monatomic ion equals _____________. e.g. oxidation number for Cl– is ___, for Fe2+ is ___. 3. Some elements have the same oxidation number in almost all their compounds, and can be used as __________ to determine the o ...
... e.g. oxidation number for Cl2 is ___, for Fe is ___. 2. The oxidation number of a monatomic ion equals _____________. e.g. oxidation number for Cl– is ___, for Fe2+ is ___. 3. Some elements have the same oxidation number in almost all their compounds, and can be used as __________ to determine the o ...
Chapter 12: Intermolecular Attractions and the Properties of Liquids
... (a) The negative ends of water dipoles surround a cation. (b) The positive ends of water dipoles surround an anion. The attractions can be quite strong because the ions have full charges. ...
... (a) The negative ends of water dipoles surround a cation. (b) The positive ends of water dipoles surround an anion. The attractions can be quite strong because the ions have full charges. ...
Chapter 5HW_Ans
... b) reduced c) redox reactions go together as one species losses (electrons or hydrogen in oxidation or gains oxygen) and concomitantly the other species gains (electrons or hydrogen) in reduction. ...
... b) reduced c) redox reactions go together as one species losses (electrons or hydrogen in oxidation or gains oxygen) and concomitantly the other species gains (electrons or hydrogen) in reduction. ...
Examination
... 18 Which process is a chemical change? (1) evaporating an alcohol (2) subliming of iodine (3) melting an ice cube (4) rusting of iron 19 Which term represents an intermolecular force in a sample of water? (1) hydrogen bonding (2) covalent bonding (3) metallic bonding (4) ionic bonding ...
... 18 Which process is a chemical change? (1) evaporating an alcohol (2) subliming of iodine (3) melting an ice cube (4) rusting of iron 19 Which term represents an intermolecular force in a sample of water? (1) hydrogen bonding (2) covalent bonding (3) metallic bonding (4) ionic bonding ...
solute
... soluble – substance that will dissolve in a solvent insoluble – substance that will not dissolve in a solvent miscible – when 2 liquids will dissolve in each other in any proportion (ex: water and ethanol) ...
... soluble – substance that will dissolve in a solvent insoluble – substance that will not dissolve in a solvent miscible – when 2 liquids will dissolve in each other in any proportion (ex: water and ethanol) ...
File
... B. When two moles of this ketone are burned, 8. moles of water are formed. What is the molecular formula of the ketone? ...
... B. When two moles of this ketone are burned, 8. moles of water are formed. What is the molecular formula of the ketone? ...
CHEM1001 2012-J-2 June 2012 22/01(a) • Complete the following
... An equilibrium mixture in a 1.00 L vessel was found to contain [SO2(g)] = 0.800 M, [NO2(g)] = 0.100 M, [SO3(g)] = 0.600 M and [NO(g)] = 0.400 M. If the volume and temperature are kept constant, what amount of NO(g) needs to be added to the reaction vessel to give an equilibrium concentration of NO2( ...
... An equilibrium mixture in a 1.00 L vessel was found to contain [SO2(g)] = 0.800 M, [NO2(g)] = 0.100 M, [SO3(g)] = 0.600 M and [NO(g)] = 0.400 M. If the volume and temperature are kept constant, what amount of NO(g) needs to be added to the reaction vessel to give an equilibrium concentration of NO2( ...
401
... only slightly. Since φ0 is common to all the cfs as seen from Eq. (7), we would be able to have this local picture even for the exact wave function. Thus, the FC theory as expressed by Eqs. (5) and (7) implies that each electron is captured essentially within the exponential region around the nucleu ...
... only slightly. Since φ0 is common to all the cfs as seen from Eq. (7), we would be able to have this local picture even for the exact wave function. Thus, the FC theory as expressed by Eqs. (5) and (7) implies that each electron is captured essentially within the exponential region around the nucleu ...
Solubility Rules The following rules are used in several chemistry
... The strong bases are: NaOH, LiOH, KOH, Li2 O. When you look at the solubility chart, you will notice that other bases, such as Ca(OH) 2 and Ba(OH)2, are said to be soluble as well. However, except for the strong bases listed, all other bases are only SLIGHTLY soluble. Slightly soluble compounds mean ...
... The strong bases are: NaOH, LiOH, KOH, Li2 O. When you look at the solubility chart, you will notice that other bases, such as Ca(OH) 2 and Ba(OH)2, are said to be soluble as well. However, except for the strong bases listed, all other bases are only SLIGHTLY soluble. Slightly soluble compounds mean ...
Naming Binary Molecular Compounds
... • Calculate the formula mass or molar mass of any given compound. • Use molar mass to convert between mass in grams and amount in moles of a chemical compound. • Calculate the # of molecules, formula units, or ions in a given molar amount of a chemical compound. •Calculate the % composition of a giv ...
... • Calculate the formula mass or molar mass of any given compound. • Use molar mass to convert between mass in grams and amount in moles of a chemical compound. • Calculate the # of molecules, formula units, or ions in a given molar amount of a chemical compound. •Calculate the % composition of a giv ...