oxidation and reduction
... Paper copies of the A-Level Chemistry Questionsheets may be copied free of charge by teaching staff or students for use within their school, provided the Photocopy Masters have been purchased by their school. No part of these Questionsheets may be reproduced or transmitted, in any other form or by a ...
... Paper copies of the A-Level Chemistry Questionsheets may be copied free of charge by teaching staff or students for use within their school, provided the Photocopy Masters have been purchased by their school. No part of these Questionsheets may be reproduced or transmitted, in any other form or by a ...
Effect of Ions on the Hydrophobic Interaction between Two Plates
... between two nonpolar, hydrophobic surfaces. Each surface is represented by a plate of 31 single-layer atoms, arranged in a triangular lattice with a bond length of 0.32 nm. The shape of the plate is disklike, with a diameter of about 2.1 nm (see Figure 1). The Lennard-Jones (LJ) parameters of the pl ...
... between two nonpolar, hydrophobic surfaces. Each surface is represented by a plate of 31 single-layer atoms, arranged in a triangular lattice with a bond length of 0.32 nm. The shape of the plate is disklike, with a diameter of about 2.1 nm (see Figure 1). The Lennard-Jones (LJ) parameters of the pl ...
Corrosion - iMechanica
... 3. Cathodic Protection: Measure the weight and volume of each material sample listed below. Dip each in diluted acid solution (Must specify) and measure the loss of weight due to corrosion. Then, take a zinc piece, polish it, measure its weight and volume and couple it with another steel piece by me ...
... 3. Cathodic Protection: Measure the weight and volume of each material sample listed below. Dip each in diluted acid solution (Must specify) and measure the loss of weight due to corrosion. Then, take a zinc piece, polish it, measure its weight and volume and couple it with another steel piece by me ...
Chapter 10. Chemical Bonding II. Molecular Geometry and
... 1. The number of MO's equal the number of AO's used to make the MO's 2. The more stable the bonding MO, the less stable the antibonding MO 3. MO's fill from low to high energies 4. In stable molecules, the number of electrons in bonding MO's > electrons in antibonding MO's 5. Maximum of 2 electrons ...
... 1. The number of MO's equal the number of AO's used to make the MO's 2. The more stable the bonding MO, the less stable the antibonding MO 3. MO's fill from low to high energies 4. In stable molecules, the number of electrons in bonding MO's > electrons in antibonding MO's 5. Maximum of 2 electrons ...
Electrochemistry
... and charges. (Look at medium) Step 4: Add the two half-reactions together and balance the final equation by inspection. The electrons on both sides must cancel. (Be sure they are equal) Step 5: Verify that the equation contains the same type and numbers of atoms and the same charges on both sides of ...
... and charges. (Look at medium) Step 4: Add the two half-reactions together and balance the final equation by inspection. The electrons on both sides must cancel. (Be sure they are equal) Step 5: Verify that the equation contains the same type and numbers of atoms and the same charges on both sides of ...
Cold interactions between an Yb ion and a Li atom
... Before presenting our potential-energy curves, and permanent and transition dipole moments, we first compare the computed atomic results to the best available experimental data. Our predicted position of the nonrelativistic 2 P state of the Li atom is 14 910 cm−1 , to be compared with the experiment ...
... Before presenting our potential-energy curves, and permanent and transition dipole moments, we first compare the computed atomic results to the best available experimental data. Our predicted position of the nonrelativistic 2 P state of the Li atom is 14 910 cm−1 , to be compared with the experiment ...
Elements, their Symbol, Atomic Number and Molar Mass
... 8. Which parameter gives the combining capacity of an element? 9. In what form atoms of a solid exist? 10. What is the smallest particle of a compound capable of stable existence? 11. What is a charged particle called? 12. What unit represents weight of ...
... 8. Which parameter gives the combining capacity of an element? 9. In what form atoms of a solid exist? 10. What is the smallest particle of a compound capable of stable existence? 11. What is a charged particle called? 12. What unit represents weight of ...
Chapter 2
... • This screen being projected on is matter. • All the materials you can hold or touch is ...
... • This screen being projected on is matter. • All the materials you can hold or touch is ...
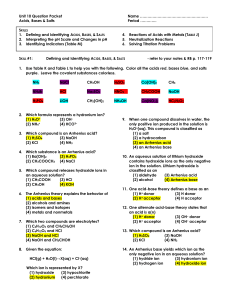
Acid Base Equilibria
... Weak acid: one that only partially dissociates in aqueous solution and therefore exists in the solution as a mixture of acid molecules component ions: For example, HF dissociates in water to give H+ and F-. It is a weak acid with a dissociation equation that is HF (aq) ↔ H+ (aq) + F-(aq) Note the us ...
... Weak acid: one that only partially dissociates in aqueous solution and therefore exists in the solution as a mixture of acid molecules component ions: For example, HF dissociates in water to give H+ and F-. It is a weak acid with a dissociation equation that is HF (aq) ↔ H+ (aq) + F-(aq) Note the us ...
Part 2. The Quantum Particle in a Box
... width. Thus, molecular energy levels are broadened in a coupled metal-molecule system – the greater the coupling, the greater the broadening of the molecular energy levels. Let‟s assume that there are two electrons in the molecular orbital. Let‟s assume that the lifetime of these electrons on the mo ...
... width. Thus, molecular energy levels are broadened in a coupled metal-molecule system – the greater the coupling, the greater the broadening of the molecular energy levels. Let‟s assume that there are two electrons in the molecular orbital. Let‟s assume that the lifetime of these electrons on the mo ...
Oxidation Reactions of Lanthanide Cations with N2O and O2
... 1980s, periodic patters in the intrinsic chemical reactivity of early first-row and second-row transition-metal ions also became of interest, particularly toward hydrocarbons because of the importance of C-H and C-C bond activation.1-5 Gas-phase reactivities of isolated lanthanide cations began to b ...
... 1980s, periodic patters in the intrinsic chemical reactivity of early first-row and second-row transition-metal ions also became of interest, particularly toward hydrocarbons because of the importance of C-H and C-C bond activation.1-5 Gas-phase reactivities of isolated lanthanide cations began to b ...
New AQA C3 revison guide
... The periodic tables patterns are now known to be based on the structure of the atom. Elements in the periodic table are arranged in order of atomic number (number of protons in the nucleus) The group number of an element shows the number of electrons in the outer shell. The period number shows the n ...
... The periodic tables patterns are now known to be based on the structure of the atom. Elements in the periodic table are arranged in order of atomic number (number of protons in the nucleus) The group number of an element shows the number of electrons in the outer shell. The period number shows the n ...
Test 2
... solids, tell how they are different from each other, and give an example of each. Molecular - have complete molecules at lattice points Ionic - Have ins at lattice points Atomic- Have atoms at lattice points 6. (5 points) What kind of bonding is used to hold a metal lattice together, and how is this ...
... solids, tell how they are different from each other, and give an example of each. Molecular - have complete molecules at lattice points Ionic - Have ins at lattice points Atomic- Have atoms at lattice points 6. (5 points) What kind of bonding is used to hold a metal lattice together, and how is this ...
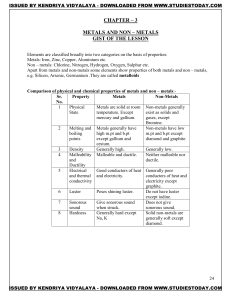
METALS AND NON – METALS Concepts
... ionic bond is formed. Therefore Ionic compound is obtained. 2Na + Cl2 2NaCl Metals react with hydrogen to form metal hydride This reaction takes place only for most reactive metals. 2Na(s) + H2(g) 2NaH(s) ...
... ionic bond is formed. Therefore Ionic compound is obtained. 2Na + Cl2 2NaCl Metals react with hydrogen to form metal hydride This reaction takes place only for most reactive metals. 2Na(s) + H2(g) 2NaH(s) ...
Class notes - Bullis Haiku
... Suppose you want to identify WHICH ions precipitate out of solution in the first 4 groups or are left in solution (Group V). We can actually identify which ions are present based on the solubility of the complex ions. I will show you how you can identify which ions are present in the Group I precipi ...
... Suppose you want to identify WHICH ions precipitate out of solution in the first 4 groups or are left in solution (Group V). We can actually identify which ions are present based on the solubility of the complex ions. I will show you how you can identify which ions are present in the Group I precipi ...
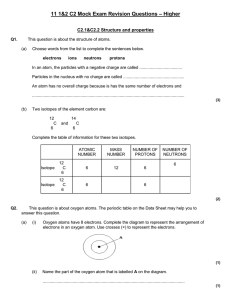
Year 11 C2 Mock Exam Revision Questions
... Magnesium chloride is an ionic compound. What are the names of its ions? ................................................. ions and ................................................. ions ...
... Magnesium chloride is an ionic compound. What are the names of its ions? ................................................. ions and ................................................. ions ...
Topic 4 Formulae, Equations and Mole
... Step 1: Start by finding out how many atoms of each type are on each side of the equation. (Some teachers recommend making a little table listing the numbers of each atom for the left hand side and for the right hand side.) Step 2: Next, look for an element which is in only one chemical on the left ...
... Step 1: Start by finding out how many atoms of each type are on each side of the equation. (Some teachers recommend making a little table listing the numbers of each atom for the left hand side and for the right hand side.) Step 2: Next, look for an element which is in only one chemical on the left ...
Notes 2 Balancing
... • The Law of Conservation of Mass • States that in ordinary chemical or physical changes, mass is neither created nor destroyed. • React vinegar and baking soda • Produces a gas (which “floats” away). • The products including this gas, if captured, is the same mass per mole as the reactants consumed ...
... • The Law of Conservation of Mass • States that in ordinary chemical or physical changes, mass is neither created nor destroyed. • React vinegar and baking soda • Produces a gas (which “floats” away). • The products including this gas, if captured, is the same mass per mole as the reactants consumed ...
Differentiated Chemistry First Term Test Review
... Sulfuric acid reacts with sodium hydroxide to yield sodium sulfate and water. If 37 grams of sulfuric acid react with 30. grams of sodium hydroxide, how many grams of water are produced? (A) 53 g (B) 14 g (C) 37 g (D) 45 g (E) 106 g ...
... Sulfuric acid reacts with sodium hydroxide to yield sodium sulfate and water. If 37 grams of sulfuric acid react with 30. grams of sodium hydroxide, how many grams of water are produced? (A) 53 g (B) 14 g (C) 37 g (D) 45 g (E) 106 g ...
Unit 8 Powerpoint
... Zn(s) + Cu(NO3)2(aq) --> Cu(s) + Zn(NO3)2(aq) Whether one metal will displace another metal from a ...
... Zn(s) + Cu(NO3)2(aq) --> Cu(s) + Zn(NO3)2(aq) Whether one metal will displace another metal from a ...
Review Session Handout from 10/6
... 14. Oxalic acid, H2C2O4, is a toxic substance found in spinach leaves, what is the molarity of a solution made by dissolving 12.0 g of oxalic acid in enough water to give 400.0 mL of solution? How many mL of 0.100 M KOH would you need to titrate 25.0 mL of the oxalic acid solution according to the f ...
... 14. Oxalic acid, H2C2O4, is a toxic substance found in spinach leaves, what is the molarity of a solution made by dissolving 12.0 g of oxalic acid in enough water to give 400.0 mL of solution? How many mL of 0.100 M KOH would you need to titrate 25.0 mL of the oxalic acid solution according to the f ...
KEY - Unit 10 - Practice Questions
... 40. According to Reference Table J, which of these metals will react most readily with 1.0 M HCl to produce H2(g)? (1) Ca (2) K (3) Mg (4) Zn 41. Under standard conditions, which metal will react with 0.1 M HCl to liberate hydrogen gas? (1) Ag (2) Au (3) Cu (4) Mg 42. Because tap water is slightly a ...
... 40. According to Reference Table J, which of these metals will react most readily with 1.0 M HCl to produce H2(g)? (1) Ca (2) K (3) Mg (4) Zn 41. Under standard conditions, which metal will react with 0.1 M HCl to liberate hydrogen gas? (1) Ag (2) Au (3) Cu (4) Mg 42. Because tap water is slightly a ...
PowerPoint - Balancing Equations
... – Chemical reactions occur when bonds between the outermost parts of atoms are formed or broken – Chemical reactions involve changes in matter, the making of new materials with new properties, and energy changes. – Symbols represent elements, formulas describe compounds, chemical equations describe ...
... – Chemical reactions occur when bonds between the outermost parts of atoms are formed or broken – Chemical reactions involve changes in matter, the making of new materials with new properties, and energy changes. – Symbols represent elements, formulas describe compounds, chemical equations describe ...
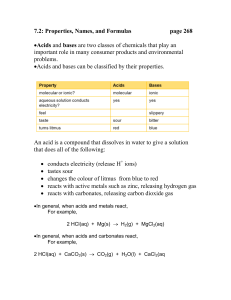
7.2: Properties, Names, and Formulas page 268 •Acids and bases
... 7.2: Properties, Names, and Formulas ...
... 7.2: Properties, Names, and Formulas ...