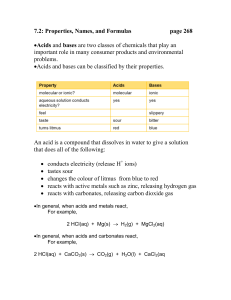
7.2: Properties, Names, and Formulas page 268 •Acids and bases
... 7.2: Properties, Names, and Formulas ...
... 7.2: Properties, Names, and Formulas ...
UNIT 7 – CHEMICAL REACTIONS
... rearranged during the course of a reaction. 3. Atoms and mass are conserved in chemical reactions. 4. Coefficients written in front of the reactants and products indicate the amounts of each that are present. 5. When trying to write a correct equation, _______________ change the products or reactant ...
... rearranged during the course of a reaction. 3. Atoms and mass are conserved in chemical reactions. 4. Coefficients written in front of the reactants and products indicate the amounts of each that are present. 5. When trying to write a correct equation, _______________ change the products or reactant ...
OXIDATION NUMBERS
... In reactions involving simple ions, it is usually easy to tell whether electrons are lost or gained, but it is less easy to tell when complex ions or covalent molecules are involved. Oxidation number is a useful concept for helping to decide in these more awkward cases. ...
... In reactions involving simple ions, it is usually easy to tell whether electrons are lost or gained, but it is less easy to tell when complex ions or covalent molecules are involved. Oxidation number is a useful concept for helping to decide in these more awkward cases. ...
Chemistry
... Learning chemistry requires both the assimilation of many concepts and the development of analytical skills. In this text, we have provided you with numerous tools to help you succeed in both tasks. If you are going to succeed in your chemistry course, you will have to develop good study habits. Sci ...
... Learning chemistry requires both the assimilation of many concepts and the development of analytical skills. In this text, we have provided you with numerous tools to help you succeed in both tasks. If you are going to succeed in your chemistry course, you will have to develop good study habits. Sci ...
Electronic Structure - Chemistry Teaching Resources
... (orientation) and ms (spin) are needed to uniquely describe every electron in an atom. Aug 2016 ...
... (orientation) and ms (spin) are needed to uniquely describe every electron in an atom. Aug 2016 ...
Chapter 4: Oxidation and Reduction MH5 4
... balancing of redox equations. They simplify the electron bookkeeping. Each atom in a compound can be assigned an oxidation number. Rules for assigning Oxidation Numbers : 1. Any allotrope of any element in the free state has an oxidation number of zero. (i.e. C(Diamond) , C(Graphite) , C(Gas) for C ...
... balancing of redox equations. They simplify the electron bookkeeping. Each atom in a compound can be assigned an oxidation number. Rules for assigning Oxidation Numbers : 1. Any allotrope of any element in the free state has an oxidation number of zero. (i.e. C(Diamond) , C(Graphite) , C(Gas) for C ...
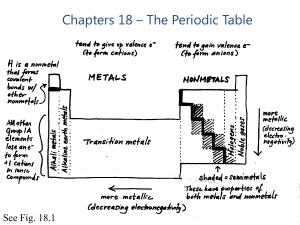
Chapters 18 – The Periodic Table
... ignited, the potassium chlorate decomposes to give oxygen, which in turn causes the phosphorus sulfide to burn more vigorously. The head of safety matches are made of an oxidizing agent such as potassium chlorate, mixed with sulfur, fillers and glass powder. The side of the box contains red phosphor ...
... ignited, the potassium chlorate decomposes to give oxygen, which in turn causes the phosphorus sulfide to burn more vigorously. The head of safety matches are made of an oxidizing agent such as potassium chlorate, mixed with sulfur, fillers and glass powder. The side of the box contains red phosphor ...
The concept of pH and pKa
... stronger acid than the hydronium (H3O+) ion • the dissociation reaction (strictly HX+H2O↔H3O++X− but simplified as HX↔H++X−) goes to completion, i.e. no unreacted acid remains in solution • Dissolving the strong acid HCl (hydrochloric acid) in water: – HCl(aq) → H+ + Cl− ...
... stronger acid than the hydronium (H3O+) ion • the dissociation reaction (strictly HX+H2O↔H3O++X− but simplified as HX↔H++X−) goes to completion, i.e. no unreacted acid remains in solution • Dissolving the strong acid HCl (hydrochloric acid) in water: – HCl(aq) → H+ + Cl− ...
Lecture3_Module_19
... the distribution of species will depend on factors such as concentrations, stoichiometry, pH and ionic strength The calculations become very complex where a metal cation have the opportunity to bind to more than one type of ligands ...
... the distribution of species will depend on factors such as concentrations, stoichiometry, pH and ionic strength The calculations become very complex where a metal cation have the opportunity to bind to more than one type of ligands ...
Document
... The bulb in Figure 4.6(a) is only dimly lit because acetic acid is a weak acid and therefore a weak electrolyte [recall Figure 4.3(c)]. The situation in (b) is similar because ammonia is a weak base and therefore also ionizes only slightly. When the two solutions are mixed, which is what has been do ...
... The bulb in Figure 4.6(a) is only dimly lit because acetic acid is a weak acid and therefore a weak electrolyte [recall Figure 4.3(c)]. The situation in (b) is similar because ammonia is a weak base and therefore also ionizes only slightly. When the two solutions are mixed, which is what has been do ...
More Reaction Information
... anions and cations are separated from each other. This is called dissociation. Na2S(aq) 2 Na+(aq) + S2–(aq) When compounds containing polyatomic ions dissociate, the polyatomic group stays together as one ion. Na2SO4(aq) 2 Na+(aq) + SO42−(aq) When strong acids dissolve in water, the molecule ion ...
... anions and cations are separated from each other. This is called dissociation. Na2S(aq) 2 Na+(aq) + S2–(aq) When compounds containing polyatomic ions dissociate, the polyatomic group stays together as one ion. Na2SO4(aq) 2 Na+(aq) + SO42−(aq) When strong acids dissolve in water, the molecule ion ...
Recording Measurements
... 40. According to Reference Table J, which of these metals will react most readily with 1.0 M HCl to produce H2(g)? (1) Ca (2) K (3) Mg (4) Zn 41. Under standard conditions, which metal will react with 0.1 M HCl to liberate hydrogen gas? (1) Ag (2) Au (3) Cu (4) Mg 42. Because tap water is slightly a ...
... 40. According to Reference Table J, which of these metals will react most readily with 1.0 M HCl to produce H2(g)? (1) Ca (2) K (3) Mg (4) Zn 41. Under standard conditions, which metal will react with 0.1 M HCl to liberate hydrogen gas? (1) Ag (2) Au (3) Cu (4) Mg 42. Because tap water is slightly a ...
section_3.2
... Atoms of one element can combine with atoms of another element to form compounds. A given compound always has the same relative numbers and types of atoms. This is called the law of constant composition ...
... Atoms of one element can combine with atoms of another element to form compounds. A given compound always has the same relative numbers and types of atoms. This is called the law of constant composition ...
Chemistry - Pearson School
... Learning chemistry requires both the assimilation of many concepts and the development of analytical skills. In this text, we have provided you with numerous tools to help you succeed in both tasks. If you are going to succeed in your chemistry course, you will have to develop good study habits. Sci ...
... Learning chemistry requires both the assimilation of many concepts and the development of analytical skills. In this text, we have provided you with numerous tools to help you succeed in both tasks. If you are going to succeed in your chemistry course, you will have to develop good study habits. Sci ...
Practice Qs - Unit 10 Acid Base
... 40. According to Reference Table J, which of these metals will react most readily with 1.0 M HCl to produce H2(g)? (1) Ca (2) K (3) Mg (4) Zn 41. Under standard conditions, which metal will react with 0.1 M HCl to liberate hydrogen gas? (1) Ag (2) Au (3) Cu (4) Mg 42. Because tap water is slightly a ...
... 40. According to Reference Table J, which of these metals will react most readily with 1.0 M HCl to produce H2(g)? (1) Ca (2) K (3) Mg (4) Zn 41. Under standard conditions, which metal will react with 0.1 M HCl to liberate hydrogen gas? (1) Ag (2) Au (3) Cu (4) Mg 42. Because tap water is slightly a ...
AP Chemistry Syllabus - HSANA AP Chemistry
... Assigned problems are begun in class and finished at home. Solutions to problems are reviewed in class in teacher-lead and student-lead sessions A spirit of family is created between students. Students are allowed at times to help or peer teach other students. All students in the class take the A ...
... Assigned problems are begun in class and finished at home. Solutions to problems are reviewed in class in teacher-lead and student-lead sessions A spirit of family is created between students. Students are allowed at times to help or peer teach other students. All students in the class take the A ...
Matter and Measurement
... Rules to assign oxidation numbers 1) The oxidation state on any atom in its elemental form is zero (H2, O2, Na(s)) 2) The sum of the oxidation states of all atoms in a neutral compound is zero (CH4, NH3) 3) The sum of the oxidation states of all atoms in an ion is equal to the charge on the ion (NO ...
... Rules to assign oxidation numbers 1) The oxidation state on any atom in its elemental form is zero (H2, O2, Na(s)) 2) The sum of the oxidation states of all atoms in a neutral compound is zero (CH4, NH3) 3) The sum of the oxidation states of all atoms in an ion is equal to the charge on the ion (NO ...
1999 Advanced Placement Chemistry Exam
... (B) Evaporation to dryness 50. In the periodic table, as the atomic number increases from 11 to 17, what happens to the atomic radius? (A) It remains constant. (B) It increases only. (C) It increases, then decreases. (D) It decreases only. (E) It decreases, then increases. 51. Which of the following ...
... (B) Evaporation to dryness 50. In the periodic table, as the atomic number increases from 11 to 17, what happens to the atomic radius? (A) It remains constant. (B) It increases only. (C) It increases, then decreases. (D) It decreases only. (E) It decreases, then increases. 51. Which of the following ...
AP `99 Multiple Choice
... (B) Evaporation to dryness 50. In the periodic table, as the atomic number increases from 11 to 17, what happens to the atomic radius? (A) It remains constant. (B) It increases only. (C) It increases, then decreases. (D) It decreases only. (E) It decreases, then increases. 51. Which of the following ...
... (B) Evaporation to dryness 50. In the periodic table, as the atomic number increases from 11 to 17, what happens to the atomic radius? (A) It remains constant. (B) It increases only. (C) It increases, then decreases. (D) It decreases only. (E) It decreases, then increases. 51. Which of the following ...
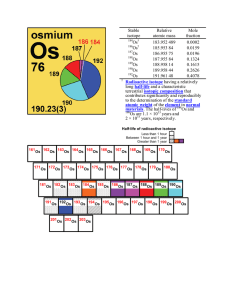
Stable isotope Relative atomic mass Mole fraction Os 183.952 489
... and an equal but opposite (positive) charge. proton – an elementary particle having a rest mass of about 1.673 × 10–27 kg, slightly less than that of a neutron, and a positive electric charge equal and opposite to that of the electron. The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom is the atomic nu ...
... and an equal but opposite (positive) charge. proton – an elementary particle having a rest mass of about 1.673 × 10–27 kg, slightly less than that of a neutron, and a positive electric charge equal and opposite to that of the electron. The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom is the atomic nu ...
sample - Bright Red Publishing
... Note: Benzene is normally drawn as but it can be useful to show the delocalisation as a system of alternating single and double bonds as shown above. In both structures electrons are delocalised around the benzene rings. In the structure on the right hand side delocalisation can occur across the cen ...
... Note: Benzene is normally drawn as but it can be useful to show the delocalisation as a system of alternating single and double bonds as shown above. In both structures electrons are delocalised around the benzene rings. In the structure on the right hand side delocalisation can occur across the cen ...
Chemistry - cloudfront.net
... bonding) 30. know which metals need Roman numerals in the names for their ionic compounds and be able to work from a formula back to a name containing a Roman numeral 31. understand the nature of covalent bonding that holds together non-metal atoms 32. be able to name covalent compounds given a name ...
... bonding) 30. know which metals need Roman numerals in the names for their ionic compounds and be able to work from a formula back to a name containing a Roman numeral 31. understand the nature of covalent bonding that holds together non-metal atoms 32. be able to name covalent compounds given a name ...