BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTORS (BJTS)
... metal–oxide–semiconductor. The words "complementary-symmetry" refer to the fact that the typical digital design style with CMOS uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistors (MOSFETs) for logic functions. ...
... metal–oxide–semiconductor. The words "complementary-symmetry" refer to the fact that the typical digital design style with CMOS uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistors (MOSFETs) for logic functions. ...
UNIT 5: Low – Power CMOS Logic Circuits
... • The first source of leakage current occurs when the source or drain of an N-transistor (P-transistor) is at Vdd (Gnd}. • PN-junctions are fonned at the source or drain of transistors because of a parasitic effect of the bulk CMOS device structure. ...
... • The first source of leakage current occurs when the source or drain of an N-transistor (P-transistor) is at Vdd (Gnd}. • PN-junctions are fonned at the source or drain of transistors because of a parasitic effect of the bulk CMOS device structure. ...
MS Word
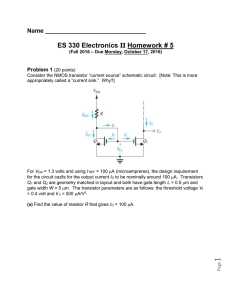
... V/m. The input bias current ID1 = 100 A. [Note: The gate-to-source voltage vgs, and currents ii and io are all small-signal quantities.] ...
... V/m. The input bias current ID1 = 100 A. [Note: The gate-to-source voltage vgs, and currents ii and io are all small-signal quantities.] ...
NEW COMPLEMENTARY BiCMOS DIGITAL GATES FOR LOW
... Nanyang Technological University, Nanyang Avenue, Singapore 639798 ...
... Nanyang Technological University, Nanyang Avenue, Singapore 639798 ...
ECE - 703 - NIT Arunachal Pradesh
... (i) IEEE Solid State Circuits Society Newsletter (ii) Springer (iii)Electronics Letter (iv) IEEE Magazines on Semiconductor Manufacturing (v) IEEE Magazines on Consumer Electronics 7. Mode of Teaching: J.C Bose/S. N. Bose (please tick). J.C. Bose Model 8. If the course is of practices, list the expe ...
... (i) IEEE Solid State Circuits Society Newsletter (ii) Springer (iii)Electronics Letter (iv) IEEE Magazines on Semiconductor Manufacturing (v) IEEE Magazines on Consumer Electronics 7. Mode of Teaching: J.C Bose/S. N. Bose (please tick). J.C. Bose Model 8. If the course is of practices, list the expe ...
(Analog) VLSI Circuit Design Fall 2016
... • Distance learning office hours will be held via Zoom (similar to WebEx) at the same time. Email me if you want to meet and I will set up the session. ...
... • Distance learning office hours will be held via Zoom (similar to WebEx) at the same time. Email me if you want to meet and I will set up the session. ...
lab1
... carefully chosen to get a decent amplification. The transistors NMOS and PMOS are obtained from the Fairchild library of devices (Fairchild.olb). For PMOS, make sure that the bulk is connected to Source (VDD). 2 Using time-domain analysis in the PSPICE program, determine the gain of the CMOS amplif ...
... carefully chosen to get a decent amplification. The transistors NMOS and PMOS are obtained from the Fairchild library of devices (Fairchild.olb). For PMOS, make sure that the bulk is connected to Source (VDD). 2 Using time-domain analysis in the PSPICE program, determine the gain of the CMOS amplif ...
PSPICE tutorial: MOSFETs
... difference between the “3” and “4” versions. The “4” versions have 4 terminals (D, S, G + body) – the body connection must be wired up explicitly. In the “3” version, the body is already connected to the source and so there are only three connections (D, S, and G). As you might expect, an MbreakN4 c ...
... difference between the “3” and “4” versions. The “4” versions have 4 terminals (D, S, G + body) – the body connection must be wired up explicitly. In the “3” version, the body is already connected to the source and so there are only three connections (D, S, and G). As you might expect, an MbreakN4 c ...
Digital Logic Topics - Agricultural engineering
... for this purpose than a conventional op-amp. • Devices actually used in digital logic are much simpler internally than an Op Amp ...
... for this purpose than a conventional op-amp. • Devices actually used in digital logic are much simpler internally than an Op Amp ...
ECE 311 - Electronics ABET Outcomes Test
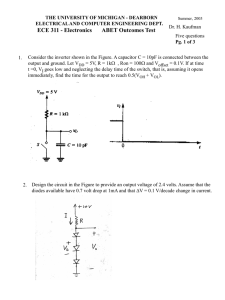
... 6. The circuit shown in the Figure is intended to supply current to floating loads (those for which both terminals are ungrounded) while making the greatest possible use of the available power supply. (a) Assuming ideal op amps, sketch the voltage waveforms at nodes B and C for a 1-V peak –to-peak s ...
... 6. The circuit shown in the Figure is intended to supply current to floating loads (those for which both terminals are ungrounded) while making the greatest possible use of the available power supply. (a) Assuming ideal op amps, sketch the voltage waveforms at nodes B and C for a 1-V peak –to-peak s ...
1 - University of California, Berkeley
... (a) Keep the Wp/Wn ratio of the Pseudo-NMOS stage 2:1, find the delay for a low-to-high transition at the output, tpLH, in terms of Cunit and Runit. (b) Use Cunit=2fF, find the optimal S that minimize the low-to-high delay by taking derivative of your result in part (a). (c) Use tp0=0.69*Runit*Cunit ...
... (a) Keep the Wp/Wn ratio of the Pseudo-NMOS stage 2:1, find the delay for a low-to-high transition at the output, tpLH, in terms of Cunit and Runit. (b) Use Cunit=2fF, find the optimal S that minimize the low-to-high delay by taking derivative of your result in part (a). (c) Use tp0=0.69*Runit*Cunit ...
Abstract - Logic Mind Technologies
... of the prescaler is improved in two aspects. First, by adopting a new pseudo divide-by-2/3 prescaler, the minimum working period is effectively reduced by half a NOR gate's delay. Second, by changing the connection of TSPC D-Flip-Flops, the minimum working period is further reduced by half an invert ...
... of the prescaler is improved in two aspects. First, by adopting a new pseudo divide-by-2/3 prescaler, the minimum working period is effectively reduced by half a NOR gate's delay. Second, by changing the connection of TSPC D-Flip-Flops, the minimum working period is further reduced by half an invert ...
CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS) /ˈsiːmɒs/ is a technology for constructing integrated circuits. CMOS technology is used in microprocessors, microcontrollers, static RAM, and other digital logic circuits. CMOS technology is also used for several analog circuits such as image sensors (CMOS sensor), data converters, and highly integrated transceivers for many types of communication. In 1963, while working for Fairchild Semiconductor, Frank Wanlass patented CMOS (US patent 3,356,858).CMOS is also sometimes referred to as complementary-symmetry metal–oxide–semiconductor (or COS-MOS).The words ""complementary-symmetry"" refer to the fact that the typical design style with CMOS uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistors (MOSFETs) for logic functions.Two important characteristics of CMOS devices are high noise immunity and low static power consumption.Since one transistor of the pair is always off, the series combination draws significant power only momentarily during switching between on and off states. Consequently, CMOS devices do not produce as much waste heat as other forms of logic, for example transistor–transistor logic (TTL) or NMOS logic, which normally have some standing current even when not changing state. CMOS also allows a high density of logic functions on a chip. It was primarily for this reason that CMOS became the most used technology to be implemented in VLSI chips.The phrase ""metal–oxide–semiconductor"" is a reference to the physical structure of certain field-effect transistors, having a metal gate electrode placed on top of an oxide insulator, which in turn is on top of a semiconductor material. Aluminium was once used but now the material is polysilicon. Other metal gates have made a comeback with the advent of high-k dielectric materials in the CMOS process, as announced by IBM and Intel for the 45 nanometer node and beyond.