PCA9544A 1. General description 4-channel I
... interrupt output. When an interrupt is generated by any device, it will be detected by the PCA9544A and the interrupt output will be driven LOW. The channel need not be active for detection of the interrupt. A bit is also set in the control byte. Bits 7:4 of the control byte correspond to channel 3 ...
... interrupt output. When an interrupt is generated by any device, it will be detected by the PCA9544A and the interrupt output will be driven LOW. The channel need not be active for detection of the interrupt. A bit is also set in the control byte. Bits 7:4 of the control byte correspond to channel 3 ...
NX3P1108 1. General description Logic controlled high-side power switch
... Product specification — The information and data provided in a Product data sheet shall define the specification of the product as agreed between NXP Semiconductors and its customer, unless NXP Semiconductors and customer have explicitly agreed otherwise in writing. In no event however, shall an agr ...
... Product specification — The information and data provided in a Product data sheet shall define the specification of the product as agreed between NXP Semiconductors and its customer, unless NXP Semiconductors and customer have explicitly agreed otherwise in writing. In no event however, shall an agr ...
Hot Swap Controller and Digital Power Monitor with Soft Start Pin ADM1177
... lockout (UVLO) circuit resets the ADM1177 when a low supply voltage is detected. Current Sense Input Pin. A sense resistor between the VCC pin and the SENSE pin sets the analog current limit. The hot swap operation of the ADM1177 controls the external FET gate to maintain the (VCC − VSENSE) voltage ...
... lockout (UVLO) circuit resets the ADM1177 when a low supply voltage is detected. Current Sense Input Pin. A sense resistor between the VCC pin and the SENSE pin sets the analog current limit. The hot swap operation of the ADM1177 controls the external FET gate to maintain the (VCC − VSENSE) voltage ...
37.0-40.0 GHz GaAs Receiver (USB) SMT, 7x7 mm R1008-QB Features
... Additionally, a fixed bias of VG2=-0.5V is required to bias the mixer and doubler. Adjusting VG2 above or below this value can adversely affect conversion gain, image rejection and intercept point performance. It is recommended to use active biasing to keep the currents constant as the RF power and ...
... Additionally, a fixed bias of VG2=-0.5V is required to bias the mixer and doubler. Adjusting VG2 above or below this value can adversely affect conversion gain, image rejection and intercept point performance. It is recommended to use active biasing to keep the currents constant as the RF power and ...
Application Note - Galco Industrial Electronics
... When a positive gate voltage is first applied, a gate current flows until the gate capacitance is charged and the gate voltage rises to the “on” level. When the gate voltage is removed, the charges injected into the collector bulk region must be removed before high voltage can be blocked. The IGBT s ...
... When a positive gate voltage is first applied, a gate current flows until the gate capacitance is charged and the gate voltage rises to the “on” level. When the gate voltage is removed, the charges injected into the collector bulk region must be removed before high voltage can be blocked. The IGBT s ...
AD8319 数据手册DataSheet 下载
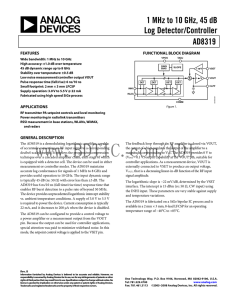
... The feedback loop through an RF amplifier is closed via VOUT, the output of which regulates the output of the amplifier to a magnitude corresponding to VSET. The AD8319 provides 0 V to (VPOS − 0.1 V) output capability at the VOUT pin, suitable for controller applications. As a measurement device, VO ...
... The feedback loop through an RF amplifier is closed via VOUT, the output of which regulates the output of the amplifier to a magnitude corresponding to VSET. The AD8319 provides 0 V to (VPOS − 0.1 V) output capability at the VOUT pin, suitable for controller applications. As a measurement device, VO ...
LT3751 - High Voltage Capacitor Charger Controller with Regulation
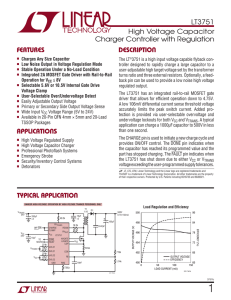
... Note 5: Refer to Block Diagram for VTRANS and VDRAIN definitions. Note 6: Low noise regulation of the output voltage requires a resistive voltage divider from output voltage to FB pin. FB pin should not be grounded in this configuration. Refer to the Typical Application diagram for proper FB pin con ...
... Note 5: Refer to Block Diagram for VTRANS and VDRAIN definitions. Note 6: Low noise regulation of the output voltage requires a resistive voltage divider from output voltage to FB pin. FB pin should not be grounded in this configuration. Refer to the Typical Application diagram for proper FB pin con ...
Conductive Polymer Aluminum Solid Capacitors Application Note
... high ripple current capability, so that the switching power supply can be downsized by reducing the number of capacitors. In the meantime, the downsizing can be made by reducing the size of the output inductor. However, reducing the output inductance leads up to an increase in the ripple current, wh ...
... high ripple current capability, so that the switching power supply can be downsized by reducing the number of capacitors. In the meantime, the downsizing can be made by reducing the size of the output inductor. However, reducing the output inductance leads up to an increase in the ripple current, wh ...
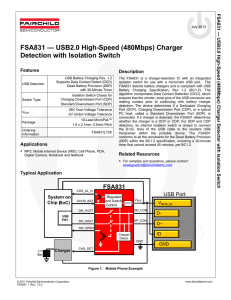
FSA831 — USB2.0 High-Speed (480Mbps) Charger Detection with Isolation Switch FSA83
... the 30-minute timer, then GOOD_BAT changes to LOW; SW_OPEN changes to Hi-Z and the counter continues counting until the 30 minutes expires. If GOOD_BAT then returns to HIGH, SW_OPEN changes to LOW and finishes out the 30-minute time. ...
... the 30-minute timer, then GOOD_BAT changes to LOW; SW_OPEN changes to Hi-Z and the counter continues counting until the 30 minutes expires. If GOOD_BAT then returns to HIGH, SW_OPEN changes to LOW and finishes out the 30-minute time. ...
TS9001 - Silicon Labs
... orders of magnitude higher supply current when switching. Because of this behavior, additional power supply bypass capacitance may be required to provide additional charge storage during switching. The design of the TS9001-1’s rail-to-rail output stage implements a technique that virtually eliminate ...
... orders of magnitude higher supply current when switching. Because of this behavior, additional power supply bypass capacitance may be required to provide additional charge storage during switching. The design of the TS9001-1’s rail-to-rail output stage implements a technique that virtually eliminate ...
lecture1423722706
... 1. Take a moment to study the problem ―in total‖ and make a brief mental sketch of the overall approach you plan to use. The result may be time- and energy-saving shortcuts. 2. Next examine each region of the network independently before tying them together in series-parallel combinations. This will ...
... 1. Take a moment to study the problem ―in total‖ and make a brief mental sketch of the overall approach you plan to use. The result may be time- and energy-saving shortcuts. 2. Next examine each region of the network independently before tying them together in series-parallel combinations. This will ...
LTC3541-1
... a linear regulator. It can be used to provide up to two output voltages from a single input voltage making the LTC3541-1 ideal for applications with limited board space. The combination and configuration of these major blocks within the LTC3541-1 is determined by way of the control pins ENBUCK and E ...
... a linear regulator. It can be used to provide up to two output voltages from a single input voltage making the LTC3541-1 ideal for applications with limited board space. The combination and configuration of these major blocks within the LTC3541-1 is determined by way of the control pins ENBUCK and E ...
Current-Fed Switched Inverter
... inverter for a reliable, versatile, and low-distortion ac inversion. The recently developed Z-source inverter (ZSI) possesses these qualities. However, the realization of ZSI comes at a cost of higher passive component count as it needs two sets of passive filters. A switched boost inverter (SBI) ha ...
... inverter for a reliable, versatile, and low-distortion ac inversion. The recently developed Z-source inverter (ZSI) possesses these qualities. However, the realization of ZSI comes at a cost of higher passive component count as it needs two sets of passive filters. A switched boost inverter (SBI) ha ...
DRV5033 Digital-Omnipolar-Switch Hall Effect Sensor
... The DRV5033 device is a chopper-stabilized hall sensor with a digital omnipolar switch output for magnetic sensing applications. The DRV5033 device can be powered with a supply voltage between 2.5 and 38 V, and will survive –22 V reverse battery conditions continuously. Note that the DRV5033 device ...
... The DRV5033 device is a chopper-stabilized hall sensor with a digital omnipolar switch output for magnetic sensing applications. The DRV5033 device can be powered with a supply voltage between 2.5 and 38 V, and will survive –22 V reverse battery conditions continuously. Note that the DRV5033 device ...
MAX19793 1500MHz to 6000MHz Dual Analog Voltage Variable
... Both attenuators share a common analog control and can be cascaded together to yield 46.6dB of total attenuation range with a typical combined linear control slope of 16.8dB/ V (5V operation). ...
... Both attenuators share a common analog control and can be cascaded together to yield 46.6dB of total attenuation range with a typical combined linear control slope of 16.8dB/ V (5V operation). ...
CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS) /ˈsiːmɒs/ is a technology for constructing integrated circuits. CMOS technology is used in microprocessors, microcontrollers, static RAM, and other digital logic circuits. CMOS technology is also used for several analog circuits such as image sensors (CMOS sensor), data converters, and highly integrated transceivers for many types of communication. In 1963, while working for Fairchild Semiconductor, Frank Wanlass patented CMOS (US patent 3,356,858).CMOS is also sometimes referred to as complementary-symmetry metal–oxide–semiconductor (or COS-MOS).The words ""complementary-symmetry"" refer to the fact that the typical design style with CMOS uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistors (MOSFETs) for logic functions.Two important characteristics of CMOS devices are high noise immunity and low static power consumption.Since one transistor of the pair is always off, the series combination draws significant power only momentarily during switching between on and off states. Consequently, CMOS devices do not produce as much waste heat as other forms of logic, for example transistor–transistor logic (TTL) or NMOS logic, which normally have some standing current even when not changing state. CMOS also allows a high density of logic functions on a chip. It was primarily for this reason that CMOS became the most used technology to be implemented in VLSI chips.The phrase ""metal–oxide–semiconductor"" is a reference to the physical structure of certain field-effect transistors, having a metal gate electrode placed on top of an oxide insulator, which in turn is on top of a semiconductor material. Aluminium was once used but now the material is polysilicon. Other metal gates have made a comeback with the advent of high-k dielectric materials in the CMOS process, as announced by IBM and Intel for the 45 nanometer node and beyond.