Genetic Engineering
... Plasmid is removed from bacteria cell (host cell) Plasmid is cut with restriction enzymes A gene is inserted into the plasmid Plasmid is returned to the cell When cell replicates it clones the gene The bacteria then infects other cells, giving them the gene (bacteria cell is called a transgenic orga ...
... Plasmid is removed from bacteria cell (host cell) Plasmid is cut with restriction enzymes A gene is inserted into the plasmid Plasmid is returned to the cell When cell replicates it clones the gene The bacteria then infects other cells, giving them the gene (bacteria cell is called a transgenic orga ...
Genetic Engineering
... Plasmid is removed from bacteria cell (host cell) Plasmid is cut with restriction enzymes A gene is inserted into the plasmid Plasmid is returned to the cell When cell replicates it clones the gene The bacteria then infects other cells, giving them the gene (bacteria cell is called a transgenic orga ...
... Plasmid is removed from bacteria cell (host cell) Plasmid is cut with restriction enzymes A gene is inserted into the plasmid Plasmid is returned to the cell When cell replicates it clones the gene The bacteria then infects other cells, giving them the gene (bacteria cell is called a transgenic orga ...
SBI 3CI Diagnostic Quiz October 10, 2014 – Microbiology Name
... A vaccine is a dead version of the actual disease. Gene therapy will remove defective cells from your body. 2 members of the same species don’t always produce fertile offspring Vaccines are considered a form of passive immunity. Recombinant DNA is DNA that has been spliced open and strands of DNA ad ...
... A vaccine is a dead version of the actual disease. Gene therapy will remove defective cells from your body. 2 members of the same species don’t always produce fertile offspring Vaccines are considered a form of passive immunity. Recombinant DNA is DNA that has been spliced open and strands of DNA ad ...
ANNEX B: Selected Biotechnology Terms
... Cloning – the process of preparing a largely identical group of organisms, cells, viruses, or nucleic acid molecules (including genes or gene fragments) descending from a single common ancestor Escherichia coli (E. coli) – a common type of bacteria found in the human intestine and aids in digestion. ...
... Cloning – the process of preparing a largely identical group of organisms, cells, viruses, or nucleic acid molecules (including genes or gene fragments) descending from a single common ancestor Escherichia coli (E. coli) – a common type of bacteria found in the human intestine and aids in digestion. ...
GE & Profiling iQuiz
... When the DNA from individuals is analysed a unique DNA profile is made and a result similar to a bar code is obtained. This DNA profile formation is also known as genetic ...
... When the DNA from individuals is analysed a unique DNA profile is made and a result similar to a bar code is obtained. This DNA profile formation is also known as genetic ...
GBE 214 TECNIQUES IN MOLECULAR BIOLOGY
... The course covers the definitions and applications of biotechnology and genetic engineering, describe the correct way for experiments design, sampling, collection of results, their analysis and interpretation, error detection and correction. The techniques presented in this course would provide stud ...
... The course covers the definitions and applications of biotechnology and genetic engineering, describe the correct way for experiments design, sampling, collection of results, their analysis and interpretation, error detection and correction. The techniques presented in this course would provide stud ...
Unit 4 Part2 wksht3
... UNIT 4 PART 2 WORKSHEET 3 1. Genetic engineering involves isolating, removing, and recombining genes. What is used to cut the DNA at a specific place to remove a gene? ___________________________________________ ...
... UNIT 4 PART 2 WORKSHEET 3 1. Genetic engineering involves isolating, removing, and recombining genes. What is used to cut the DNA at a specific place to remove a gene? ___________________________________________ ...
Frontiers of Genetics
... species, into a single DNA molecule • Bacteria have small circular pieces of DNA called plasmids separate from their larger single chromosome • Plasmids can replicate and pass between bacterial cells allowing gene sharing – associated with antibacterial resistance ...
... species, into a single DNA molecule • Bacteria have small circular pieces of DNA called plasmids separate from their larger single chromosome • Plasmids can replicate and pass between bacterial cells allowing gene sharing – associated with antibacterial resistance ...
DNA Personal Ads
... sequence is really dull, and I’m ready to move on to more exciting things. I’m looking for my true love, mRNA. (transcription) ...
... sequence is really dull, and I’m ready to move on to more exciting things. I’m looking for my true love, mRNA. (transcription) ...
Discovery of DNA
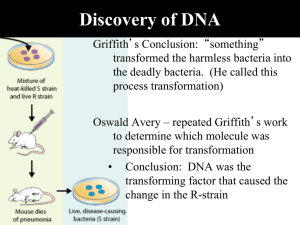
... Discovery of DNA Alfred Hershey & Martha Chase • Question: Are genes made of DNA or proteins? • What they knew: viruses use other organisms to reproduce Viruses only contain DNA and a protein coat. Whichever virus particle enters the cell must be the material that makes up genes (DNA). ...
... Discovery of DNA Alfred Hershey & Martha Chase • Question: Are genes made of DNA or proteins? • What they knew: viruses use other organisms to reproduce Viruses only contain DNA and a protein coat. Whichever virus particle enters the cell must be the material that makes up genes (DNA). ...
biotechnology - Wikispaces.net
... transferring the nucleus from the cell of an adult sheep into the cytoplasm of an eunucleated fertilized egg. The egg was then transplanted into the uterus of a surrogate mother where it developed like a normal zygote into a lamb, which grew into a ...
... transferring the nucleus from the cell of an adult sheep into the cytoplasm of an eunucleated fertilized egg. The egg was then transplanted into the uterus of a surrogate mother where it developed like a normal zygote into a lamb, which grew into a ...
Clone
... enzymes, leaving sticky ends Artificial plasmids can be constructed by linking new DNA fragments to the sticky ends of plasmid ...
... enzymes, leaving sticky ends Artificial plasmids can be constructed by linking new DNA fragments to the sticky ends of plasmid ...
Genetic Engineering pp 2014
... DNA between those traits. These cause the DNA fragments separated by electrophoresis to be different sizes, creating a ...
... DNA between those traits. These cause the DNA fragments separated by electrophoresis to be different sizes, creating a ...
PCR - University of Hawaii
... • mutations are changes to the base pair sequence of genetic material (either DNA or RNA). Mutations can be caused by copying errors in the genetic material during cell division and by exposure to ultraviolet or ionizing radiation, chemical mutagens, or viruses ...
... • mutations are changes to the base pair sequence of genetic material (either DNA or RNA). Mutations can be caused by copying errors in the genetic material during cell division and by exposure to ultraviolet or ionizing radiation, chemical mutagens, or viruses ...
BIOTECHNOLOGY
... • the use of living systems and organisms to develop or make useful products. It can also be any technological application such as artificial selection, genetic engineering, DNA fingerprinting and cloning that uses biological systems and living organisms to make or modify products or processes for s ...
... • the use of living systems and organisms to develop or make useful products. It can also be any technological application such as artificial selection, genetic engineering, DNA fingerprinting and cloning that uses biological systems and living organisms to make or modify products or processes for s ...
Molecular cloning
Molecular cloning is a set of experimental methods in molecular biology that are used to assemble recombinant DNA molecules and to direct their replication within host organisms. The use of the word cloning refers to the fact that the method involves the replication of one molecule to produce a population of cells with identical DNA molecules. Molecular cloning generally uses DNA sequences from two different organisms: the species that is the source of the DNA to be cloned, and the species that will serve as the living host for replication of the recombinant DNA. Molecular cloning methods are central to many contemporary areas of modern biology and medicine.In a conventional molecular cloning experiment, the DNA to be cloned is obtained from an organism of interest, then treated with enzymes in the test tube to generate smaller DNA fragments. Subsequently, these fragments are then combined with vector DNA to generate recombinant DNA molecules. The recombinant DNA is then introduced into a host organism (typically an easy-to-grow, benign, laboratory strain of E. coli bacteria). This will generate a population of organisms in which recombinant DNA molecules are replicated along with the host DNA. Because they contain foreign DNA fragments, these are transgenic or genetically modified microorganisms (GMO). This process takes advantage of the fact that a single bacterial cell can be induced to take up and replicate a single recombinant DNA molecule. This single cell can then be expanded exponentially to generate a large amount of bacteria, each of which contain copies of the original recombinant molecule. Thus, both the resulting bacterial population, and the recombinant DNA molecule, are commonly referred to as ""clones"". Strictly speaking, recombinant DNA refers to DNA molecules, while molecular cloning refers to the experimental methods used to assemble them.