Biotechnology Notes
... • Test DNA to detect genetic diseases – determines risk of having or passing on a genetic ...
... • Test DNA to detect genetic diseases – determines risk of having or passing on a genetic ...
Recombinant DNA - Richmond School District
... inserted into the plasmid will only work if it DOESN’T have any introns. One way to do this is to synthesize the gene in a machine. Another method is to isolate the mRNA for the gene and use “REVERSE TRANSCRIPTASE” to make a DNA copy of it. (= complementary DNA (cDNA)) v. detailed animation of the ...
... inserted into the plasmid will only work if it DOESN’T have any introns. One way to do this is to synthesize the gene in a machine. Another method is to isolate the mRNA for the gene and use “REVERSE TRANSCRIPTASE” to make a DNA copy of it. (= complementary DNA (cDNA)) v. detailed animation of the ...
Apple Molecular Biology: Animation 1
... Cloning can mean several things. Most people associate cloning with 'copying'. In molecular biology, cloning can be a process of recreating individuals from their own DNA but a more common use of cloning refers to the insertion of a short piece of DNA into a bacterial plasmid for replication purpose ...
... Cloning can mean several things. Most people associate cloning with 'copying'. In molecular biology, cloning can be a process of recreating individuals from their own DNA but a more common use of cloning refers to the insertion of a short piece of DNA into a bacterial plasmid for replication purpose ...
Advances in Genetics
... • Inbred organisms have alleles very similar to their parents • This increases the chance of a genetic disorder showing in the offspring ...
... • Inbred organisms have alleles very similar to their parents • This increases the chance of a genetic disorder showing in the offspring ...
Prezentace aplikace PowerPoint
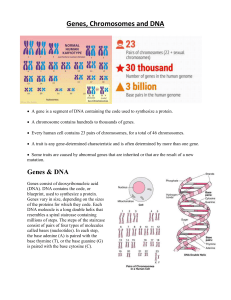
... A gene – what is it? • It is a molecular unit of heredity of a living organism. Genes are found in our chromosomes, which parents pass on to offspring in their sex cells in reproduction. Different versions of the same gene are called alleles and these can determine features like eye colour and the ...
... A gene – what is it? • It is a molecular unit of heredity of a living organism. Genes are found in our chromosomes, which parents pass on to offspring in their sex cells in reproduction. Different versions of the same gene are called alleles and these can determine features like eye colour and the ...
Paradigm Shifts in Biomedical Research
... Cell Cycle Checkpoints and Cancer Checkpoints ensure that cells complete one event before proceeding to the next event Cancer is a disease of uncontrolled cell growth, sloppy DNA replication and errors in chromosome segregation ...
... Cell Cycle Checkpoints and Cancer Checkpoints ensure that cells complete one event before proceeding to the next event Cancer is a disease of uncontrolled cell growth, sloppy DNA replication and errors in chromosome segregation ...
Genes and genomes
... of A, T, C, and G. These unique combinations code for a particular amino acid, much as letters join together to form words. ...
... of A, T, C, and G. These unique combinations code for a particular amino acid, much as letters join together to form words. ...
Chapter 12 DNA Analysis Checkpoint Answers In the nucleus of the
... 8. Blood, semen, saliva, hair follicular tissue, bone 9. Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism ...
... 8. Blood, semen, saliva, hair follicular tissue, bone 9. Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism ...
Prescott`s Microbiology, 9th Edition Chapter 17 – Recombinant DNA
... pUC encodes resistance to ampicillin and enables blue/white cloning selection. pBeloBAC11 encodes resistance to chloramphenicol and also enables blue/white cloning selection. This BAC differs from pUC19 in that it contains genes that ensure a replication complex will be formed (repE), as well as gen ...
... pUC encodes resistance to ampicillin and enables blue/white cloning selection. pBeloBAC11 encodes resistance to chloramphenicol and also enables blue/white cloning selection. This BAC differs from pUC19 in that it contains genes that ensure a replication complex will be formed (repE), as well as gen ...
word play - Discovery Education
... 8. A rod-shaped structure of tightly coiled DNA found in the cell nucleus of plants and animals. 11. A combination of atoms, and also the basic building-block of DNA and RNA. Each molecule has its own shape and attaches only to certain other molecules to form the DNA helix. 12. A winding shape, simi ...
... 8. A rod-shaped structure of tightly coiled DNA found in the cell nucleus of plants and animals. 11. A combination of atoms, and also the basic building-block of DNA and RNA. Each molecule has its own shape and attaches only to certain other molecules to form the DNA helix. 12. A winding shape, simi ...
Genes Chromosomes and DNA
... A trait is any gene-determined characteristic and is often determined by more than one gene. Some traits are caused by abnormal genes that are inherited or that are the result of a new mutation. ...
... A trait is any gene-determined characteristic and is often determined by more than one gene. Some traits are caused by abnormal genes that are inherited or that are the result of a new mutation. ...
Biotech unit Objectives
... Be able to explain the methods of the cell repairing mutations. Be able to explain the key genes and processes in cancer cell formation. Chapter 20 Key Terms Plasmid Thermocycler Streak plate DNA fingerprinting Blunt ends Gene library Lambda DNA Ti plasmid ...
... Be able to explain the methods of the cell repairing mutations. Be able to explain the key genes and processes in cancer cell formation. Chapter 20 Key Terms Plasmid Thermocycler Streak plate DNA fingerprinting Blunt ends Gene library Lambda DNA Ti plasmid ...
Name: Genetics Study Guide
... and your notes. Use these to review the questions on this study guide. Be prepared for the review on Weds. Look for the notes downloads on my Blog. ...
... and your notes. Use these to review the questions on this study guide. Be prepared for the review on Weds. Look for the notes downloads on my Blog. ...
Introduction to biotechnology - Indiana University School of Informatics
... 2. DNA cloning either through the use of cloning vectors or the polymerase chain reaction, whereby a single DNA molecule can be copied to generate many billions of identical molecules. 3. Nucleic acid hybridization, which makes it possible to find a specific sequence of DNA or RNA with great accurac ...
... 2. DNA cloning either through the use of cloning vectors or the polymerase chain reaction, whereby a single DNA molecule can be copied to generate many billions of identical molecules. 3. Nucleic acid hybridization, which makes it possible to find a specific sequence of DNA or RNA with great accurac ...
20 Scientists 2016
... -Thomas Malthus: In his Essay on the Principle of Population, predicts that the human population will grow faster than the space and food supplies needed to sustain it. -Jean-Baptiste Lamarck: Through the use or disuse of organs, organisms acquired or lost certain traits in their lifetime. -Charles ...
... -Thomas Malthus: In his Essay on the Principle of Population, predicts that the human population will grow faster than the space and food supplies needed to sustain it. -Jean-Baptiste Lamarck: Through the use or disuse of organs, organisms acquired or lost certain traits in their lifetime. -Charles ...
biotechnology
... DNA determine the sequences of the 3 billion chemical base pairs that make up human DNA ...
... DNA determine the sequences of the 3 billion chemical base pairs that make up human DNA ...
Document
... Hereditary- Genetically transmitted or transmittable from parent to offspring. DNA- Consists of genetic differences called genes that are carried through from the parent to the child. RNA- A polymeric constituent of all living cells and many viruses. Chromosomes- A circular strand of DNA in bacteri ...
... Hereditary- Genetically transmitted or transmittable from parent to offspring. DNA- Consists of genetic differences called genes that are carried through from the parent to the child. RNA- A polymeric constituent of all living cells and many viruses. Chromosomes- A circular strand of DNA in bacteri ...
Characteristics of Living Things
... Contain DNA Grow and develop Respond to their environment (stimuli) Made of cells Evolve (as a group) ...
... Contain DNA Grow and develop Respond to their environment (stimuli) Made of cells Evolve (as a group) ...
Molecuar Structure of DNA Questions
... 5. How many DNA nucleotides are there? List them. Also indicate which are purines, and which are pyrimidines. ...
... 5. How many DNA nucleotides are there? List them. Also indicate which are purines, and which are pyrimidines. ...
Genetic Engineering
... These are enzymes that scientists use in genetic engineering The enzyme recognizes a site on the DNA which is made of 4 to 6 bases. The enzyme will cut DNA at these recognition sites. These recognition sites are palindromes. Cutting DNA at recognition sites is the first step in many types of DNA tec ...
... These are enzymes that scientists use in genetic engineering The enzyme recognizes a site on the DNA which is made of 4 to 6 bases. The enzyme will cut DNA at these recognition sites. These recognition sites are palindromes. Cutting DNA at recognition sites is the first step in many types of DNA tec ...
Molecular cloning
Molecular cloning is a set of experimental methods in molecular biology that are used to assemble recombinant DNA molecules and to direct their replication within host organisms. The use of the word cloning refers to the fact that the method involves the replication of one molecule to produce a population of cells with identical DNA molecules. Molecular cloning generally uses DNA sequences from two different organisms: the species that is the source of the DNA to be cloned, and the species that will serve as the living host for replication of the recombinant DNA. Molecular cloning methods are central to many contemporary areas of modern biology and medicine.In a conventional molecular cloning experiment, the DNA to be cloned is obtained from an organism of interest, then treated with enzymes in the test tube to generate smaller DNA fragments. Subsequently, these fragments are then combined with vector DNA to generate recombinant DNA molecules. The recombinant DNA is then introduced into a host organism (typically an easy-to-grow, benign, laboratory strain of E. coli bacteria). This will generate a population of organisms in which recombinant DNA molecules are replicated along with the host DNA. Because they contain foreign DNA fragments, these are transgenic or genetically modified microorganisms (GMO). This process takes advantage of the fact that a single bacterial cell can be induced to take up and replicate a single recombinant DNA molecule. This single cell can then be expanded exponentially to generate a large amount of bacteria, each of which contain copies of the original recombinant molecule. Thus, both the resulting bacterial population, and the recombinant DNA molecule, are commonly referred to as ""clones"". Strictly speaking, recombinant DNA refers to DNA molecules, while molecular cloning refers to the experimental methods used to assemble them.