RT-PCR lab
... sequence. • Next, you have to make enough copies of the tiny trace amount of cDNA to sequence ...
... sequence. • Next, you have to make enough copies of the tiny trace amount of cDNA to sequence ...
Genetics - Mr. Coleman's Biology
... A mutation is a change in the order of the nitrogenous bases of DNA. Some mutations are harmless, some are damaging to the organism, and some are fatal (causing the organism not to develop). ...
... A mutation is a change in the order of the nitrogenous bases of DNA. Some mutations are harmless, some are damaging to the organism, and some are fatal (causing the organism not to develop). ...
File
... A mutation is a change in the order of the nitrogenous bases of DNA. Some mutations are harmless, some are damaging to the organism, and some are fatal (causing the organism not to develop). ...
... A mutation is a change in the order of the nitrogenous bases of DNA. Some mutations are harmless, some are damaging to the organism, and some are fatal (causing the organism not to develop). ...
DNA polymerase
... When the process is complete, two DNA molecules have been formed identical to each other and to the parent molecule Errors during replication are rare, as each cell contains a family of more than thirty enzymes to ensure the accurate replication of DNA DNA polymerase makes very few errors, and most ...
... When the process is complete, two DNA molecules have been formed identical to each other and to the parent molecule Errors during replication are rare, as each cell contains a family of more than thirty enzymes to ensure the accurate replication of DNA DNA polymerase makes very few errors, and most ...
chap-4 - Workforce3One
... – Problems - Bacteria may recognize the proteins as foreign and destroy them – Posttranslational modifications are different in bacteria – Bacterial environment may not permit correct protein folding – Very high levels of cloned eukaryotic proteins can be expressed in useless insoluble form ...
... – Problems - Bacteria may recognize the proteins as foreign and destroy them – Posttranslational modifications are different in bacteria – Bacterial environment may not permit correct protein folding – Very high levels of cloned eukaryotic proteins can be expressed in useless insoluble form ...
RNA - Ms Kim`s Biology Class
... 8. Why is DNA replication called "semi-conservative"? __________________________________________ 9. The two sides of the DNA helix are held together by ________________________ 10. What are the DNA base pairing rules? What are the RNA base pairing rules? DNA ______________________ RNA ______________ ...
... 8. Why is DNA replication called "semi-conservative"? __________________________________________ 9. The two sides of the DNA helix are held together by ________________________ 10. What are the DNA base pairing rules? What are the RNA base pairing rules? DNA ______________________ RNA ______________ ...
Control of Gene Expression
... be controlled as the larvae are more easily located. Produces “genetically modified organisms” ...
... be controlled as the larvae are more easily located. Produces “genetically modified organisms” ...
Wzór streszczenia/Abstract form:
... Oxidative stress influences DNA and other biomolecules damage via oxidative changes to their chemical structure. These changes are believed to increase the risk of cancer, heart disease and aging processes. It has been demonstrated that antioxidants such as ascorbic acid, tocopherols and flavonoids ...
... Oxidative stress influences DNA and other biomolecules damage via oxidative changes to their chemical structure. These changes are believed to increase the risk of cancer, heart disease and aging processes. It has been demonstrated that antioxidants such as ascorbic acid, tocopherols and flavonoids ...
Biology 303 EXAM II 3/14/00 NAME
... did her father. Which of her parents underwent nondisjunction during meiosis, giving rise to the gamete responsible for the syndrome? ...
... did her father. Which of her parents underwent nondisjunction during meiosis, giving rise to the gamete responsible for the syndrome? ...
Bio 93 Quiz 4: Master Copy
... A) The twisting nature of DNA creates nonparallel strands. B) The 5' to 3' direction of one strand runs counter to the 5' to 3' direction of the other strand. C) Base pairings create unequal spacing between the two DNA strands. D) One strand is positively charged and the other is negatively charged. ...
... A) The twisting nature of DNA creates nonparallel strands. B) The 5' to 3' direction of one strand runs counter to the 5' to 3' direction of the other strand. C) Base pairings create unequal spacing between the two DNA strands. D) One strand is positively charged and the other is negatively charged. ...
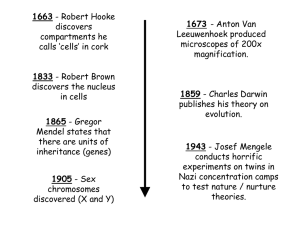
Timeline
... 1989 - First birth using PGD 1978 - First ‘test-tube’ baby produced using IVF 1995 - Plan to sequence human genome began 2000 - In US first ‘saviour sibling’ produced using PGD ...
... 1989 - First birth using PGD 1978 - First ‘test-tube’ baby produced using IVF 1995 - Plan to sequence human genome began 2000 - In US first ‘saviour sibling’ produced using PGD ...
DNA - heredity2
... • Affects the haemoglobin • Most common form is caused by a recessive trait on chromosome 11, a single base change (T A) which makes the 6th codon Val not Glu on the β-globin polypeptide • Causes RBCs to form a sickle shape when the concentration of oxygen is low ...
... • Affects the haemoglobin • Most common form is caused by a recessive trait on chromosome 11, a single base change (T A) which makes the 6th codon Val not Glu on the β-globin polypeptide • Causes RBCs to form a sickle shape when the concentration of oxygen is low ...
Within minutes, 2nd Generation ATP® tests answer the question
... requires a trained technician and results can be somewhat subjective. Take the guess-work completely out of the equation and get a true picture of the situation at hand through DNA quantification, which will definitively identify all foaming and filamentous bacteria. Anaerobic Digester Gas Productio ...
... requires a trained technician and results can be somewhat subjective. Take the guess-work completely out of the equation and get a true picture of the situation at hand through DNA quantification, which will definitively identify all foaming and filamentous bacteria. Anaerobic Digester Gas Productio ...
Behavior Genetics and Evolutionary Psychology
... information that makes up the chromosomes. Genes – the biochemical units of heredity that make up the chromosomes; segments of DNA capable of synthesizing a protein Can be active(expressed) or inactive Turned on by environmental events (stress, diet, drugs) When turned on – provides the code ...
... information that makes up the chromosomes. Genes – the biochemical units of heredity that make up the chromosomes; segments of DNA capable of synthesizing a protein Can be active(expressed) or inactive Turned on by environmental events (stress, diet, drugs) When turned on – provides the code ...
Genetic Engineering
... DNA can be made in a lab using a machine called a DNA synthesizer. The scientists can join natural pieces of DNA to synthesized one using enzymes that splice DNA back together They can also combine DNA from two ...
... DNA can be made in a lab using a machine called a DNA synthesizer. The scientists can join natural pieces of DNA to synthesized one using enzymes that splice DNA back together They can also combine DNA from two ...
Chapter 4 Cellular Metabolism
... In __catabolic __ reactions, larger molecules are broken down into smaller ones. The reactions of metabolism are often reversible Which process requires energy? anabolic Which process releases energy? Catabolic The process of joining two molecules by removing water is called __dehydration synthesis_ ...
... In __catabolic __ reactions, larger molecules are broken down into smaller ones. The reactions of metabolism are often reversible Which process requires energy? anabolic Which process releases energy? Catabolic The process of joining two molecules by removing water is called __dehydration synthesis_ ...
DNA Lab Techniques
... • Other 98% (introns) are non-coding • Only about 20,000 to 25,000 genes (expected 100,000) • Proteome – organism’s complete set of proteins • About 8 million single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP) – places where humans differ by a single nucleotide • About ½ of genome comes from transposons (pieces ...
... • Other 98% (introns) are non-coding • Only about 20,000 to 25,000 genes (expected 100,000) • Proteome – organism’s complete set of proteins • About 8 million single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP) – places where humans differ by a single nucleotide • About ½ of genome comes from transposons (pieces ...
File - Down the Rabbit Hole
... 1. Go to ‘What are DNA and Genes?’ a. Explain the relationship between DNA, genes and a genome. b. How do the building blocks of DNA work to create instructions? c. What is it the instructions code for? 2. Go to ‘Build a DNA Molecule’ and build a molecule a. How long would it take you to replicate t ...
... 1. Go to ‘What are DNA and Genes?’ a. Explain the relationship between DNA, genes and a genome. b. How do the building blocks of DNA work to create instructions? c. What is it the instructions code for? 2. Go to ‘Build a DNA Molecule’ and build a molecule a. How long would it take you to replicate t ...
Part II: Recombinant DNA Technology
... a double-stranded cut in the DNA. While recognition sequences vary between 4 and 8 nucleotides, many of them are palindromic, which correspond to nitrogenous base sequences that read the same backwards and forwards. In theory, there are two types of palindromic sequences that can be possible in DNA. ...
... a double-stranded cut in the DNA. While recognition sequences vary between 4 and 8 nucleotides, many of them are palindromic, which correspond to nitrogenous base sequences that read the same backwards and forwards. In theory, there are two types of palindromic sequences that can be possible in DNA. ...
05E-NucleicAcids
... • During preparations for cell division each of the strands serves as a template to order nucleotides into a new complementary strand. • This results in two identical copies of the original double-stranded DNA molecule. • The copies are then distributed to the daughter cells. ...
... • During preparations for cell division each of the strands serves as a template to order nucleotides into a new complementary strand. • This results in two identical copies of the original double-stranded DNA molecule. • The copies are then distributed to the daughter cells. ...
Issues in Biotechnology
... Genetically Modified somatic nuclei could be implanted into unfertilized eggs to create a genetically modified clone ...
... Genetically Modified somatic nuclei could be implanted into unfertilized eggs to create a genetically modified clone ...
Molecular cloning
Molecular cloning is a set of experimental methods in molecular biology that are used to assemble recombinant DNA molecules and to direct their replication within host organisms. The use of the word cloning refers to the fact that the method involves the replication of one molecule to produce a population of cells with identical DNA molecules. Molecular cloning generally uses DNA sequences from two different organisms: the species that is the source of the DNA to be cloned, and the species that will serve as the living host for replication of the recombinant DNA. Molecular cloning methods are central to many contemporary areas of modern biology and medicine.In a conventional molecular cloning experiment, the DNA to be cloned is obtained from an organism of interest, then treated with enzymes in the test tube to generate smaller DNA fragments. Subsequently, these fragments are then combined with vector DNA to generate recombinant DNA molecules. The recombinant DNA is then introduced into a host organism (typically an easy-to-grow, benign, laboratory strain of E. coli bacteria). This will generate a population of organisms in which recombinant DNA molecules are replicated along with the host DNA. Because they contain foreign DNA fragments, these are transgenic or genetically modified microorganisms (GMO). This process takes advantage of the fact that a single bacterial cell can be induced to take up and replicate a single recombinant DNA molecule. This single cell can then be expanded exponentially to generate a large amount of bacteria, each of which contain copies of the original recombinant molecule. Thus, both the resulting bacterial population, and the recombinant DNA molecule, are commonly referred to as ""clones"". Strictly speaking, recombinant DNA refers to DNA molecules, while molecular cloning refers to the experimental methods used to assemble them.