biology syllabus 2017
... a) Investigate issues such as cloning, recombinant DNA, genetic engineering, and/or gene therapy. F. DNA and protein synthesis 1. Explain the role of DNA in heredity, gene expression, and organism function. a) Compare and contrast structure of DNA and RNA. b) List and model the steps of DNA replicat ...
... a) Investigate issues such as cloning, recombinant DNA, genetic engineering, and/or gene therapy. F. DNA and protein synthesis 1. Explain the role of DNA in heredity, gene expression, and organism function. a) Compare and contrast structure of DNA and RNA. b) List and model the steps of DNA replicat ...
single cells
... abnormalities, and studies of cellular structure and function. Chromosomes in three-dimensionally preserved nuclei can be "painted" using FISH. In clinical research, FISH can be used for prenatal diagnosis of inherited chromosomal aberrations, postnatal diagnosis of carriers of genetic disease, diag ...
... abnormalities, and studies of cellular structure and function. Chromosomes in three-dimensionally preserved nuclei can be "painted" using FISH. In clinical research, FISH can be used for prenatal diagnosis of inherited chromosomal aberrations, postnatal diagnosis of carriers of genetic disease, diag ...
Chapter 7: Microbial Genetics 10/8/2015
... (similar) DNA sequences: • DNA with “same” genes • facilitated by special proteins • original DNA is lost ...
... (similar) DNA sequences: • DNA with “same” genes • facilitated by special proteins • original DNA is lost ...
b) Inheritance - iGCSE Science Courses
... 3.13 understand that the nucleus of a cell contains chromosomes on which genes are located 3.14 understand that a gene is a section of a molecule of DNA and that a gene codes for a specific protein 3.15 describe a DNA molecule as two strands coiled to form a double helix, the strands being linked by ...
... 3.13 understand that the nucleus of a cell contains chromosomes on which genes are located 3.14 understand that a gene is a section of a molecule of DNA and that a gene codes for a specific protein 3.15 describe a DNA molecule as two strands coiled to form a double helix, the strands being linked by ...
Biology 30 Review Assignment Part 2
... (Record all three digits of your answer in the numerical-response section on the answer sheet.) ...
... (Record all three digits of your answer in the numerical-response section on the answer sheet.) ...
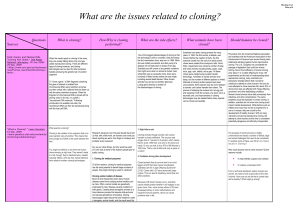
What is cloning?
... by the research community and the news media, Clonaid never provided any evidence to confirm the existence of this clone or the other 12 human clones it purportedly created. In 2004, a group led by Woo-Suk Hwang of Seoul National University in South Korea published a paper in the journal Science in ...
... by the research community and the news media, Clonaid never provided any evidence to confirm the existence of this clone or the other 12 human clones it purportedly created. In 2004, a group led by Woo-Suk Hwang of Seoul National University in South Korea published a paper in the journal Science in ...
Dr Ishtiaq Transcription
... cell or stage of development. In other words exons could be skipped or added. This means that variations of a protein (called isoforms) can be produced from the same gene. ...
... cell or stage of development. In other words exons could be skipped or added. This means that variations of a protein (called isoforms) can be produced from the same gene. ...
Blueprint of Life by Ahmad Shah Idil
... organisms and that all living things have a common ancestor in some initial form of primitive life. ...
... organisms and that all living things have a common ancestor in some initial form of primitive life. ...
Available - Ggu.ac.in
... VNTR (or Variable number tandem repeat) etc., Some of the techniques developed for DNA manipulation are used to detect DNA variations known as restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLPs). A. Some one per thousand base pairs (bp = nucleotide pairs) varies in the population, i.e. instead of an A ...
... VNTR (or Variable number tandem repeat) etc., Some of the techniques developed for DNA manipulation are used to detect DNA variations known as restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLPs). A. Some one per thousand base pairs (bp = nucleotide pairs) varies in the population, i.e. instead of an A ...
Lectures 1 & 2 (2010.03.05 & 2010.03.06)
... (A) The cloverleaf structure, a convention used to show the complementary base-pairing (red lines). The ANTICODON is the sequence of three nucleotides that base-pairs with a CODON in mRNA. The amino acid matching the codon/anticodon pair is attached at the 3′ end of the tRNA. tRNAs contain some unus ...
... (A) The cloverleaf structure, a convention used to show the complementary base-pairing (red lines). The ANTICODON is the sequence of three nucleotides that base-pairs with a CODON in mRNA. The amino acid matching the codon/anticodon pair is attached at the 3′ end of the tRNA. tRNAs contain some unus ...
ENVIRONMENTAL RISK MANAGEMENT AUTHORITY DECISION
... Changes to controls: Addition of footnotes to the containment facility references and the Australian/New Zealand containment facility references to “future proof” the decision Standardise the wording of the breach of containment control Removal of the control regarding inspection of facilities ...
... Changes to controls: Addition of footnotes to the containment facility references and the Australian/New Zealand containment facility references to “future proof” the decision Standardise the wording of the breach of containment control Removal of the control regarding inspection of facilities ...
No Slide Title
... molecules into suitable host 3) identify hosts which have taken up your recombinant molecules 4) Extract DNA ...
... molecules into suitable host 3) identify hosts which have taken up your recombinant molecules 4) Extract DNA ...
013368718X_CH10_143-158.indd
... 8. Griffith’s experiments showed that some chemical compound in cells must be responsible for bacterial ...
... 8. Griffith’s experiments showed that some chemical compound in cells must be responsible for bacterial ...
Why don’t antibodies get rid of HIV?
... • DNA replication ensures that genetic information is passed on unchanged from a cell to its descendents. • The major thing cells do with genetic information is use it to encode PROTEINS. • Every cell contains all of an organism’s genes, so each cell could (in theory) make every protein. But which p ...
... • DNA replication ensures that genetic information is passed on unchanged from a cell to its descendents. • The major thing cells do with genetic information is use it to encode PROTEINS. • Every cell contains all of an organism’s genes, so each cell could (in theory) make every protein. But which p ...
A Protein - Cygnus Technologies
... qualification and validation that should be performed by each laboratory. At a minimum each laboratory is urged to perform a spike and recovery study for each sample type to be tested in the assay. Each laboratory technician should also demonstrate competency in the assay by performing a similar pre ...
... qualification and validation that should be performed by each laboratory. At a minimum each laboratory is urged to perform a spike and recovery study for each sample type to be tested in the assay. Each laboratory technician should also demonstrate competency in the assay by performing a similar pre ...
Microarray - Clemson University
... • Conventional expression analysis only allows the study of the expression of a single gene in a single experiment • The highly parallel nature of microarrays allows the simultaneous study of the expression of thousands or even tens of thousands of different genes in a single experiment • Microarray ...
... • Conventional expression analysis only allows the study of the expression of a single gene in a single experiment • The highly parallel nature of microarrays allows the simultaneous study of the expression of thousands or even tens of thousands of different genes in a single experiment • Microarray ...
3.1 Class Notes Powerpoint
... protein that is used within a cell. Proteins are made up of hundreds of amino acids in a specific sequence. When they get “out of order’ a mutation occurs. ...
... protein that is used within a cell. Proteins are made up of hundreds of amino acids in a specific sequence. When they get “out of order’ a mutation occurs. ...
Human cloning - 10EssentialScience
... Physicians from the American Medical Association and scientists with the American Association for the Advancement of Science have issued formal public statements advising against human reproductive cloning. The U.S. Congress has considered the passage of legislation that could ban human cloning. Due ...
... Physicians from the American Medical Association and scientists with the American Association for the Advancement of Science have issued formal public statements advising against human reproductive cloning. The U.S. Congress has considered the passage of legislation that could ban human cloning. Due ...
MS Word - VCU Secrets of the Sequence
... transmitted faithfully when cells multiply in a process known as semi-conservative replication. The two strands of DNA separate and each acts as a template for the synthesis (or replication) of a new strand. New bases are paired with the template strand, and are then connected to one another to form ...
... transmitted faithfully when cells multiply in a process known as semi-conservative replication. The two strands of DNA separate and each acts as a template for the synthesis (or replication) of a new strand. New bases are paired with the template strand, and are then connected to one another to form ...
BACULOVIRUS MEDIATED PRODUCTION OF INFECTIOUS
... study aims to construct full-length cDNA clones of IMNV and test for their infectivity in an insect cell line using reverse genetic methodologies. To construct the full length IMNV cDNA clones, genomic RNA of the virus was extracted from IMNV-infected shrimp and converted to cDNA before they were am ...
... study aims to construct full-length cDNA clones of IMNV and test for their infectivity in an insect cell line using reverse genetic methodologies. To construct the full length IMNV cDNA clones, genomic RNA of the virus was extracted from IMNV-infected shrimp and converted to cDNA before they were am ...
Biology 2
... chromosome consists of 2 genetically identical sister chromatids. • Prophase I – most complex. Accounts for 90% of meiosis. In a process called SYNAPSIS, homologous chromosomes (each composed of two sister chromatids) pair up. They form a structure called a TETRAD. Each TETRAD has four chromatids. D ...
... chromosome consists of 2 genetically identical sister chromatids. • Prophase I – most complex. Accounts for 90% of meiosis. In a process called SYNAPSIS, homologous chromosomes (each composed of two sister chromatids) pair up. They form a structure called a TETRAD. Each TETRAD has four chromatids. D ...
9.9 Forensic Chemistry
... In their normal state atoms do not emit light, but if an atom is given extra energy by either heat or electricity, the electrons within the atom are excited into a higher energy level. When the electrons fall back down to their ground state (lowest energy level, the atoms are normally in this state) ...
... In their normal state atoms do not emit light, but if an atom is given extra energy by either heat or electricity, the electrons within the atom are excited into a higher energy level. When the electrons fall back down to their ground state (lowest energy level, the atoms are normally in this state) ...
Molecular cloning
Molecular cloning is a set of experimental methods in molecular biology that are used to assemble recombinant DNA molecules and to direct their replication within host organisms. The use of the word cloning refers to the fact that the method involves the replication of one molecule to produce a population of cells with identical DNA molecules. Molecular cloning generally uses DNA sequences from two different organisms: the species that is the source of the DNA to be cloned, and the species that will serve as the living host for replication of the recombinant DNA. Molecular cloning methods are central to many contemporary areas of modern biology and medicine.In a conventional molecular cloning experiment, the DNA to be cloned is obtained from an organism of interest, then treated with enzymes in the test tube to generate smaller DNA fragments. Subsequently, these fragments are then combined with vector DNA to generate recombinant DNA molecules. The recombinant DNA is then introduced into a host organism (typically an easy-to-grow, benign, laboratory strain of E. coli bacteria). This will generate a population of organisms in which recombinant DNA molecules are replicated along with the host DNA. Because they contain foreign DNA fragments, these are transgenic or genetically modified microorganisms (GMO). This process takes advantage of the fact that a single bacterial cell can be induced to take up and replicate a single recombinant DNA molecule. This single cell can then be expanded exponentially to generate a large amount of bacteria, each of which contain copies of the original recombinant molecule. Thus, both the resulting bacterial population, and the recombinant DNA molecule, are commonly referred to as ""clones"". Strictly speaking, recombinant DNA refers to DNA molecules, while molecular cloning refers to the experimental methods used to assemble them.