Brooker Chapter 17
... This phenomenon, called exon shuffling, may lead to the evolution of genes with more diverse functions Copyright ©The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display ...
... This phenomenon, called exon shuffling, may lead to the evolution of genes with more diverse functions Copyright ©The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display ...
Biology Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms Lab
... Now that you’ve isolated your DNA, amplified the TAS2R38 gene and Greg has performed a restriction digest on the DNA with the HaeIII enzyme, we are ready to run our products out on a gel. Now, if you recall from lecture, all we did during PCR was amplify a single fragment of known length into millio ...
... Now that you’ve isolated your DNA, amplified the TAS2R38 gene and Greg has performed a restriction digest on the DNA with the HaeIII enzyme, we are ready to run our products out on a gel. Now, if you recall from lecture, all we did during PCR was amplify a single fragment of known length into millio ...
11-17-11 DNA Lecture - Kings County Criminal Bar Association
... results with lower levels of male perpetrator DNA because there is not a concern about heterozygote allele loss via stochastic PCR amplification; number of male contributors can be determined • Courts have already widely accepted STR typing, instrumentation, and software for analysis (Y-STR markers ...
... results with lower levels of male perpetrator DNA because there is not a concern about heterozygote allele loss via stochastic PCR amplification; number of male contributors can be determined • Courts have already widely accepted STR typing, instrumentation, and software for analysis (Y-STR markers ...
Biology 1 Notes Chapter 12 - DNA and RNA Prentice Hall pages
... The four bases (letters) of mRNA (A, U, G, and C) are read three letters at a time (and translated) to determine the order in which amino acids are added to a protein. ...
... The four bases (letters) of mRNA (A, U, G, and C) are read three letters at a time (and translated) to determine the order in which amino acids are added to a protein. ...
Investigating a Eukaryotic Genome
... fragment from the yeast genome obtained from the EcoRI digest into the pBS plasmid. They then transform E. coli cells with this recombinant plasmid and plate the cells onto LB/ampicillin plates. Since the plasmid contains a gene that codes for an ampicillin resistance protein, only E. coli cells tha ...
... fragment from the yeast genome obtained from the EcoRI digest into the pBS plasmid. They then transform E. coli cells with this recombinant plasmid and plate the cells onto LB/ampicillin plates. Since the plasmid contains a gene that codes for an ampicillin resistance protein, only E. coli cells tha ...
Gene Transfer
... of the β-lactamase protein if successfully transformed into suitable bacteria. In the presence of the ampicillin, the transformed bacteria would have a strong selective advantage over susceptible bacteria. The looping out of DNA could occur by homologous recombination within the chromosome between a ...
... of the β-lactamase protein if successfully transformed into suitable bacteria. In the presence of the ampicillin, the transformed bacteria would have a strong selective advantage over susceptible bacteria. The looping out of DNA could occur by homologous recombination within the chromosome between a ...
22.0GeneticDisorders
... 2. Proteins determine the physical traits of an organism 3. In humans, DNA is organized into 23 pairs of homologous chromosomes B. DNA Structure 1. The basic building block of DNA is a nucleotide 2. Nucleotide chains are held together to form a double helix 3. Nucleotides are represented using the l ...
... 2. Proteins determine the physical traits of an organism 3. In humans, DNA is organized into 23 pairs of homologous chromosomes B. DNA Structure 1. The basic building block of DNA is a nucleotide 2. Nucleotide chains are held together to form a double helix 3. Nucleotides are represented using the l ...
References - Proceedings of the Royal Society B
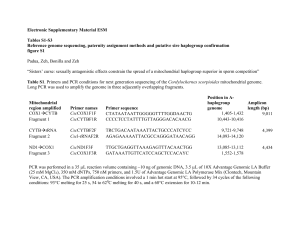
... CYTB gene Cytb424-449 (5’ – GGWTAYGTWYTWCCWTGRGGWCARAT – 3’ and Cytb876-847 (5’ – GCRTAWGCRAAWARRAARTAYCAYTCWGG – 3’) [2]. COXI and CYTB are located approximately opposite one another in the circular mitochondrial genome, and primers from these two genes can be used to amplify the entire genome in t ...
... CYTB gene Cytb424-449 (5’ – GGWTAYGTWYTWCCWTGRGGWCARAT – 3’ and Cytb876-847 (5’ – GCRTAWGCRAAWARRAARTAYCAYTCWGG – 3’) [2]. COXI and CYTB are located approximately opposite one another in the circular mitochondrial genome, and primers from these two genes can be used to amplify the entire genome in t ...
GHSGT Ecology/Genetics Review (EcoGenReview)
... A. Each meiotic division produces four sperm cells and one egg cell. Sperm are motile while the egg can not move on its own. B. The egg cell is much larger than a sperm cell. C. The number of chromosomes found in a human sperm is different from the number found in a human egg cell. D. A and B 14. Ha ...
... A. Each meiotic division produces four sperm cells and one egg cell. Sperm are motile while the egg can not move on its own. B. The egg cell is much larger than a sperm cell. C. The number of chromosomes found in a human sperm is different from the number found in a human egg cell. D. A and B 14. Ha ...
Learned about mutations
... INTRODUCTION: Each time a cell divides, it must make a copy of its DNA during a process known as DNA replication. Sometimes during replication, an error is made that causes changes in the mRNA and proteins that are made using that DNA. These errors or changes are called mutations. A mutation is defi ...
... INTRODUCTION: Each time a cell divides, it must make a copy of its DNA during a process known as DNA replication. Sometimes during replication, an error is made that causes changes in the mRNA and proteins that are made using that DNA. These errors or changes are called mutations. A mutation is defi ...
7.014 Problem Set 3
... 2. You have finished your summer internship at the Venter Institute, but you are interested in studying more about the species that you characterized over the summer. Dr. Venter has agreed to let you take the three species that you studied (M, I and T) back to MIT with you so you can investigate the ...
... 2. You have finished your summer internship at the Venter Institute, but you are interested in studying more about the species that you characterized over the summer. Dr. Venter has agreed to let you take the three species that you studied (M, I and T) back to MIT with you so you can investigate the ...
DNA Replication in Bacteria
... That is, there are long sequences of bases within the protein-coding sequences of the gene that do not code for amino acids in the final protein product. ...
... That is, there are long sequences of bases within the protein-coding sequences of the gene that do not code for amino acids in the final protein product. ...
Document
... How do the Jurassic Park scientists manipulate the dinosaur DNA to make transgenic dinosaurs? They fill in the “gaps” in the dinosaur DNA with frog DNA What type of egg do they use to allow the dinosaurs to develop in? (Very quiet, in the background) They use unfertilized ostrich eggs (This is why t ...
... How do the Jurassic Park scientists manipulate the dinosaur DNA to make transgenic dinosaurs? They fill in the “gaps” in the dinosaur DNA with frog DNA What type of egg do they use to allow the dinosaurs to develop in? (Very quiet, in the background) They use unfertilized ostrich eggs (This is why t ...
By controlling Protein Synthesis
... called the central dogma of biology. – Write the central dogma of biology as a flow chart – What role does each of these structures play in protein synthesis? • DNA • mRNA • RNA polymerase • Spliceosomes ...
... called the central dogma of biology. – Write the central dogma of biology as a flow chart – What role does each of these structures play in protein synthesis? • DNA • mRNA • RNA polymerase • Spliceosomes ...
Hemophilia - Genomics Help
... creating a Multiple Cloning Site (MCS) in their AdEasy vector. This is a short stretch of DNA sequence that contains several restriction enzyme sites, which do not occur anywhere else in the vector (unique sites). So if you cut the vector with any one of these enzymes (or any combination of two of t ...
... creating a Multiple Cloning Site (MCS) in their AdEasy vector. This is a short stretch of DNA sequence that contains several restriction enzyme sites, which do not occur anywhere else in the vector (unique sites). So if you cut the vector with any one of these enzymes (or any combination of two of t ...
Powerpoint template for scientific posters (Swarthmore
... •To find mutations in exon 8 and 17, samples were prepared for sequencing. •PCR was used to amplify the section of DNA (exon 8 or 17) of the CKIT gene. •The PCR reaction “master mix” consisted of Taq (DNA polymerase), Taq buffer, primers (to flag the exon), dNTP (nucleotides), and the AML sample. •T ...
... •To find mutations in exon 8 and 17, samples were prepared for sequencing. •PCR was used to amplify the section of DNA (exon 8 or 17) of the CKIT gene. •The PCR reaction “master mix” consisted of Taq (DNA polymerase), Taq buffer, primers (to flag the exon), dNTP (nucleotides), and the AML sample. •T ...
Proteins, Carbohydrates, and Lipids
... increasingly complex task that requires active, continuing maintenance of digital media. This challenge has focused some interest on DNA as an attractive target for information storage1 because of its capacity for high-density information encoding, longevity under easily achieved conditions2–4 and p ...
... increasingly complex task that requires active, continuing maintenance of digital media. This challenge has focused some interest on DNA as an attractive target for information storage1 because of its capacity for high-density information encoding, longevity under easily achieved conditions2–4 and p ...
Recombination and Genetic Engineering
... exist in a host E. coli cell, it must integrate into the host chromosome which it does by means of a sitespecific recombination reaction. ...
... exist in a host E. coli cell, it must integrate into the host chromosome which it does by means of a sitespecific recombination reaction. ...
Genetic-Exchange - Microbiology and Immunology Online
... 1. To explain the mechanisms of gene transfer in bacteria. 2. To describe the nature of transposable genetic elements and plasmids. 3. To discuss the significance of gene transfer, transposable genetic elements and plasmids. ...
... 1. To explain the mechanisms of gene transfer in bacteria. 2. To describe the nature of transposable genetic elements and plasmids. 3. To discuss the significance of gene transfer, transposable genetic elements and plasmids. ...
final review
... 154. How many types of amino acids are used to make proteins? ________ 155. How many DNA nucleotides make an order for one amino acid? ______ 156. a. How many mRNA nucleotides are translated into one amino acid? ___ b. What do you call this triplet of nucleotides? __________ 157. When RNA is being m ...
... 154. How many types of amino acids are used to make proteins? ________ 155. How many DNA nucleotides make an order for one amino acid? ______ 156. a. How many mRNA nucleotides are translated into one amino acid? ___ b. What do you call this triplet of nucleotides? __________ 157. When RNA is being m ...
Bacterial Transformation and Transfection Bacterial transformation is
... to isolate cells containing those recombinant molecules from each other and from those containing the non-recombinant vector. The E. coli lacZ operon has been incorporated into several cloning vectors, including plasmid pUC and bacteriophage M13. The polylinker regions of these vectors was engineere ...
... to isolate cells containing those recombinant molecules from each other and from those containing the non-recombinant vector. The E. coli lacZ operon has been incorporated into several cloning vectors, including plasmid pUC and bacteriophage M13. The polylinker regions of these vectors was engineere ...
Using Fruit Flies to Investigate a Cancer Metastasis
... and humans are responsible for the opposite phenotypes. With this result, we will, in the future, mutate specific amino acids within the WPD loop to confirm these are the amino acids that cause the phenotype. If hPRL-3 doesn’t have a oncogenic phenotype, then we know that the differences in the fly ...
... and humans are responsible for the opposite phenotypes. With this result, we will, in the future, mutate specific amino acids within the WPD loop to confirm these are the amino acids that cause the phenotype. If hPRL-3 doesn’t have a oncogenic phenotype, then we know that the differences in the fly ...
Lab Investigation: Examining a Single Gene
... • Keeping in mind what a cell does when it replicates its DNA, make a list of steps involved in replicating DNA: ...
... • Keeping in mind what a cell does when it replicates its DNA, make a list of steps involved in replicating DNA: ...
Molecular cloning
Molecular cloning is a set of experimental methods in molecular biology that are used to assemble recombinant DNA molecules and to direct their replication within host organisms. The use of the word cloning refers to the fact that the method involves the replication of one molecule to produce a population of cells with identical DNA molecules. Molecular cloning generally uses DNA sequences from two different organisms: the species that is the source of the DNA to be cloned, and the species that will serve as the living host for replication of the recombinant DNA. Molecular cloning methods are central to many contemporary areas of modern biology and medicine.In a conventional molecular cloning experiment, the DNA to be cloned is obtained from an organism of interest, then treated with enzymes in the test tube to generate smaller DNA fragments. Subsequently, these fragments are then combined with vector DNA to generate recombinant DNA molecules. The recombinant DNA is then introduced into a host organism (typically an easy-to-grow, benign, laboratory strain of E. coli bacteria). This will generate a population of organisms in which recombinant DNA molecules are replicated along with the host DNA. Because they contain foreign DNA fragments, these are transgenic or genetically modified microorganisms (GMO). This process takes advantage of the fact that a single bacterial cell can be induced to take up and replicate a single recombinant DNA molecule. This single cell can then be expanded exponentially to generate a large amount of bacteria, each of which contain copies of the original recombinant molecule. Thus, both the resulting bacterial population, and the recombinant DNA molecule, are commonly referred to as ""clones"". Strictly speaking, recombinant DNA refers to DNA molecules, while molecular cloning refers to the experimental methods used to assemble them.