* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download biology syllabus 2017
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
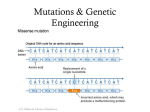
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Biology Mr. Dougherty Voice Mail 627-6375 Course Syllabus [email protected] Biology is an introductory course designed to explore the nature of the physical world as it relates to the living. This course will focus on the diversity of organisms from genetics through ecology In this class there will be an emphasis on academic activities and laboratory exercises that promote problem solving, refine laboratory procedure, and reinforce fundamental reading, writing and math skills. Our students will be involved in outdoor field studies and will be encouraged and rewarded for the exploration of personal avenues of interest in science. GRADING: A running total for each semester usually in the range of 600pts Homework exercises 6@ 25pts 150pts Class Activities 2@ 25pts 50pts Laboratories 2@ 50pts 100pts Test 3@ 100pts 300pts In general I will work to accommodate a roughly 40/60 weight for Test/other assessments Students are encouraged to submit late work and/or resubmit incomplete for partial credit CLASSROOM EXPECTATIONS: Students are expected to come to class prepared to participate. Students will be expected to manage class materials appropriately. Students are expected to contribute to an atmosphere of respect. COURSE CONTENT SCOPE & SEQUENCE: A. Introduction to Biology 1. Demonstrate an understanding of the difference between living and nonliving. a) Define and explain the following concepts/terms:reproduction, following concepts organization,growth, development, obtaining and using energy, metabolism, responding to the environment/stimuli, homeostasis. b) Identify things as living/nonliving based on a set of criteria. 2. Perform a case study of a biological issue such as the zebra mussel problem in the U.S. a) Explain the concept of a case study analysis. b) Read and interpret a scientific case study. B. Biochemistry 1. Explain how atoms form chemical bonds. a) Use the periodic chart to calculate the number of electrons in an atom. b) Knowing the number of electrons in an atom, showing the correct arrangement of valence electrons. c) Show how bonds are formed based on the arrangement of valence electrons in atoms. 2. Explain the relation of organic compounds to organisms. a) Define and provide examples of basic organic compounds. b) Describe how biological compounds are used by organisms. 3. Demonstrate the effects of environmental factors on enzyme function. a) Show the effects of temperature, concentration, and pH on the functioning of enzymes. 4. Demonstrate the properties of water and relate the importance of water to biological functions. a) Show examples of how each property of water can be used for the functioning of organisms. 5. Explain the formation of acidic and basic solutions based on the dissociation of water; a) Show when acid and base solutions would form b) Explain the effects of pH on the functioning of life processes in organisms. C. Cell Structure and Function 1. Understand the relationship between cell structure and function. a) Identify cellular structures and state their functions. b) Explain how structures perform their functions. c) Identify and explain the levels of cellular organization. d) Identify, describe, and compare the various types of cell transport and their purposes. 2. Distinguish between various types of cells based on cellular characteristics. a) State and identify the differences between plant and animal cells; between prokaryotes and eukaryotes. b) Identify examples of plant, animal, prokaryotic, and eukaryotic cells. D. Cellular Reproduction 1. Understand the role of the cell cycle as it relates to growth, development, and reproduction. a) Identify the phases of the cell cycle, the structures involved, and what is happening in each phase. b) Compare and contrast mitosis in plant and animal cells. c) Compare and contrast cell division in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. d) Compare and contrast mitosis and meiosis. e) Compare and contrast meiosis in males and females. f) Explain the limits for cell growth and the need to multiply in numbers rather than grow. E. Genetics 1. Explain and demonstrate how genetic traits are transmitted and expressed. a) Identify the relationship between genes, chromosomes, and DNA. b) Explain the principles of dominance, segregation, and independent assortment. c) Explain the inheritance of traits due to incomplete dominance, codominance, and sex-linkage. d) Apply the rules of probability to solve genetic problems. 2. Understand the impact of genetic technology. a) Investigate issues such as cloning, recombinant DNA, genetic engineering, and/or gene therapy. F. DNA and protein synthesis 1. Explain the role of DNA in heredity, gene expression, and organism function. a) Compare and contrast structure of DNA and RNA. b) List and model the steps of DNA replication and protein synthesis. 2. Analyze the effect of mutations on organism development and function. a) Identify types of gene and chromosome mutations. b) Show how gene and chromosome mutations affect protein synthesis, cell division, the turning on and off of genes, and may lead to disorders/diseases. G. Evolution 1. Understand how scientists use various types of evidence to determine evolutionary relationships. a) Identify and describe types of evidence for evolution. b) Determine evolutionary relationships between organisms, and analyze varying results. 2. Understand the conditions under which new species evolve. a) Explain the role of mutations in organism variation. b) Compare and contrast adaptations and variations. c) Identify the types of adaptations that occur. d) Explain the role of the environment in natural selection. e) Explain adaptive radiation, geographic and reproductive isolation, and genetic drift. f) Compare the rates at which evolution occurs and explain why the variation in rates occurs. 3. Describe the origin of the Earth’s life forms. a) Describe experiments showing how life on Earth originated. 4. Explore the origins of modern humans. a) Identify characteristics shared by all primates and all hominids. b) Identify characteristics of ancient hominids. c) Compare ancient hominids to modern humans, identify changes that have occurred in the following areas, and identify theories to explain why those changes occurred. H. Taxonomy 1. Understand the relationship between structure and function of living organisms. a) Identify structures of various organisms and their corresponding functions. b) Identify and describe the various life processes performed by living organisms, and explain how organisms perform those life processes. 2. Describe how organisms are classified. a) Name the taxa used to classify organisms. b) Describe the major characteristics of each kingdom of life; of each phyla of invertebrates; of chordates