Document
... mental abilities. His theory, though incorrect, nevertheless proposed that different mental abilities were modular. ...
... mental abilities. His theory, though incorrect, nevertheless proposed that different mental abilities were modular. ...
Chapter2 - cfhssocialstudies
... mental abilities. His theory, though incorrect, nevertheless proposed that different mental abilities were modular. ...
... mental abilities. His theory, though incorrect, nevertheless proposed that different mental abilities were modular. ...
Neuroscience: The Biological Bases of Behavior
... Broca was treating a patient who had been unable to speak for 30 years. After the patient died, lesions on the left side of the frontal lobe identified the probable cause of the speech deficiency. Since then, many cases have shown this area of the motor cortex (now called Broca’s area) plays an impo ...
... Broca was treating a patient who had been unable to speak for 30 years. After the patient died, lesions on the left side of the frontal lobe identified the probable cause of the speech deficiency. Since then, many cases have shown this area of the motor cortex (now called Broca’s area) plays an impo ...
Chapter 6
... are their functions? (7) 9. How many neurons are in the mammalian brain? 10. The three main components of a neuron are the cell body, dendrites, and axon. What are the functions of each component? (7) 11. _____________ are the contact points where one neuron communicates with another. (7) 12. Many a ...
... are their functions? (7) 9. How many neurons are in the mammalian brain? 10. The three main components of a neuron are the cell body, dendrites, and axon. What are the functions of each component? (7) 11. _____________ are the contact points where one neuron communicates with another. (7) 12. Many a ...
BIOPSYCHOLOGY notes
... nervous system neurons that internally communicate and intervene between the sensory inputs and motor outputs. We have billions and billions of these. ...
... nervous system neurons that internally communicate and intervene between the sensory inputs and motor outputs. We have billions and billions of these. ...
Chapter Two
... • Uses the detection of radio frequency signals produced by displaced radio waves in a magnetic field • Creates a detailed anatomical image of the brain ...
... • Uses the detection of radio frequency signals produced by displaced radio waves in a magnetic field • Creates a detailed anatomical image of the brain ...
Memory - CCRI Faculty Web
... hard drive. Memories are NOT in isolated files, but are in overlapping neural networks. The brain’s long-term memory storage does not get full; it gets more elaborately rewired and interconnected. ...
... hard drive. Memories are NOT in isolated files, but are in overlapping neural networks. The brain’s long-term memory storage does not get full; it gets more elaborately rewired and interconnected. ...
Reticular Activating System
... All sensory input that enters brain via the medulla is also sent to neurons of the reticular formation. These neurons may monitor sensory input for importance. May alert higher brain centers when critical input is detected. ...
... All sensory input that enters brain via the medulla is also sent to neurons of the reticular formation. These neurons may monitor sensory input for importance. May alert higher brain centers when critical input is detected. ...
The Biological Basis of Behavior Why should Psychologists be
... cord where the information is passed on to an interneuron (within the spinal cord) and another neuron to the brain. The interneuron relays the message to a motor (efferent) neuron which signals the muscle to contract and move the finger. A short time later, the brain finally receives the signal and ...
... cord where the information is passed on to an interneuron (within the spinal cord) and another neuron to the brain. The interneuron relays the message to a motor (efferent) neuron which signals the muscle to contract and move the finger. A short time later, the brain finally receives the signal and ...
The Nervous System
... nervous system (CNS), and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The PNS gathers information from inside and outside the body. The CNS receives and analyzes this information and initiates responses. The PNS then picks up and carries the response signals. This information is transmitted throughout the ...
... nervous system (CNS), and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The PNS gathers information from inside and outside the body. The CNS receives and analyzes this information and initiates responses. The PNS then picks up and carries the response signals. This information is transmitted throughout the ...
Lecture - Chapter 13: Central Nervous System - dr
... c. What is the path it takes through the brain and spinal cord. 7. What are the 5 lobes of the brain, what are they named after, what functional regions are found in each? 8. Define the following: a. Sulcus b. Gyrus c. Fissure 9. What major structure separates the left cerebral hemisphere from the r ...
... c. What is the path it takes through the brain and spinal cord. 7. What are the 5 lobes of the brain, what are they named after, what functional regions are found in each? 8. Define the following: a. Sulcus b. Gyrus c. Fissure 9. What major structure separates the left cerebral hemisphere from the r ...
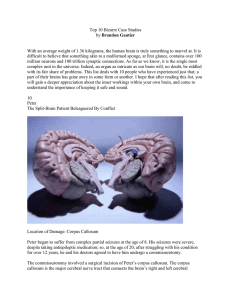
Top 10 Bizarre Case Studies
... only one of many visual agnosias (an agnosia is a failure of recognition). Other visual agnosias include: movement agnosia, object agnosia and color agnosia. R.P. can usually recognize a face is a face, but generally cannot tell exactly whose face it is. R.P. does not report any other recognition pr ...
... only one of many visual agnosias (an agnosia is a failure of recognition). Other visual agnosias include: movement agnosia, object agnosia and color agnosia. R.P. can usually recognize a face is a face, but generally cannot tell exactly whose face it is. R.P. does not report any other recognition pr ...
Neuroscience and Behavior
... Right-Left Differences in the Intact Brain People with intact brains also show left-right hemispheric differences in mental abilities. A number of brain scan studies show normal individuals engage their right brain when completing a perceptual task and their left brain when carrying out a linguisti ...
... Right-Left Differences in the Intact Brain People with intact brains also show left-right hemispheric differences in mental abilities. A number of brain scan studies show normal individuals engage their right brain when completing a perceptual task and their left brain when carrying out a linguisti ...
Option A Cerebral Cortex and Senses
... – Reasoning, language, complex thought, visual processing, motor movement , memory, speech ...
... – Reasoning, language, complex thought, visual processing, motor movement , memory, speech ...
Unit_2_-_Biological_Bases_of_Behavior
... displayed proudly at Harvard University’s medical school! For real! ...
... displayed proudly at Harvard University’s medical school! For real! ...
presentation source - Arkansas Tech Faculty Web Sites
... with age. The number of spaces increases by one unit every other year beginning at age three. Juan Pascual-Leon, 1970 The m-space capacity of individuals increases at about this rate but can vary up or down by up to two units for each age group. ...
... with age. The number of spaces increases by one unit every other year beginning at age three. Juan Pascual-Leon, 1970 The m-space capacity of individuals increases at about this rate but can vary up or down by up to two units for each age group. ...
Brain Awareness Day - Lakehead Science Education (Matt Roy)
... What do Smell and Taste have in common? • They are both chemical senses! – Molecules in the air or our mouths dissolve and bind to receptors which send signals to the brain! ...
... What do Smell and Taste have in common? • They are both chemical senses! – Molecules in the air or our mouths dissolve and bind to receptors which send signals to the brain! ...
Bridget Lecture 2 Notes The Neurons o Functional classes (CNS
... ▪ In Dendrites: passive propagation ● Lose power ▪ In Axons: Active Propagation ● Myelin sheath isolate the axon and preserve voltage ● Regenerate the voltage at the nodes of Ranvier Rate Law o Greater the stimulant the greater the number of action potentials o Spontaneous (weak) vs. Elicite ...
... ▪ In Dendrites: passive propagation ● Lose power ▪ In Axons: Active Propagation ● Myelin sheath isolate the axon and preserve voltage ● Regenerate the voltage at the nodes of Ranvier Rate Law o Greater the stimulant the greater the number of action potentials o Spontaneous (weak) vs. Elicite ...
PRACTICE QUIZ
... 10. The main difference between gustatory receptor cells and olfactory receptor cells is that _______________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ 11. Nasal mucus is produced by ______________________________________________________________ 12. Olfac ...
... 10. The main difference between gustatory receptor cells and olfactory receptor cells is that _______________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ 11. Nasal mucus is produced by ______________________________________________________________ 12. Olfac ...
Outline12 CNS - Napa Valley College
... - deep gray matter areas, involved in subconscious motor control and other functions e. Limbic system - “emotional brain” amygdala - center of strong emotions (fear, anger); role in memory processing hippocampus - major role in consolidation of long-term memory ...
... - deep gray matter areas, involved in subconscious motor control and other functions e. Limbic system - “emotional brain” amygdala - center of strong emotions (fear, anger); role in memory processing hippocampus - major role in consolidation of long-term memory ...
Memory
... o The effect of articulatory suppression: if asked to say something aloud while rehearsing material in phonological loop, the memory for the rehearsed material is impaired. The three part structure was recently (2000) given a fourth component by Baddeley – episodic buffer. It’s considered necessary ...
... o The effect of articulatory suppression: if asked to say something aloud while rehearsing material in phonological loop, the memory for the rehearsed material is impaired. The three part structure was recently (2000) given a fourth component by Baddeley – episodic buffer. It’s considered necessary ...
Unit 7 Cognition
... 7: Contrast the recall, recognition, and explicit memory, and identify the main brain structure associated with each. ...
... 7: Contrast the recall, recognition, and explicit memory, and identify the main brain structure associated with each. ...
Objectives included for the test File
... by relay neurons, and from the CNS to effectors by motor neurons. Define resting potential and action potential (depolarization and repolarization). Explain how a nerve impulse passes along a non-myelinated neuron. Include the movement of Na+ and K+ ions to create a resting potential and an action p ...
... by relay neurons, and from the CNS to effectors by motor neurons. Define resting potential and action potential (depolarization and repolarization). Explain how a nerve impulse passes along a non-myelinated neuron. Include the movement of Na+ and K+ ions to create a resting potential and an action p ...