Two Effects of the Environment on Physiological Processes
... their activities in response to new situations or changes in the environment. The brain is more plastic in early life. The brain can rearrange the connections between neurons The brain can generate new neurons throughout life Learning can increase/decrease neurotransmission between specific ...
... their activities in response to new situations or changes in the environment. The brain is more plastic in early life. The brain can rearrange the connections between neurons The brain can generate new neurons throughout life Learning can increase/decrease neurotransmission between specific ...
The Information Processing Approach to Cognition
... processing of information. The frontal lobes of the cerebral cortex is the structure associated with working memory. For example, you are processing the words you read on the screen in your frontal lobes. However, if I ask, "What is your telephone number?" your brain immediately calls that from long ...
... processing of information. The frontal lobes of the cerebral cortex is the structure associated with working memory. For example, you are processing the words you read on the screen in your frontal lobes. However, if I ask, "What is your telephone number?" your brain immediately calls that from long ...
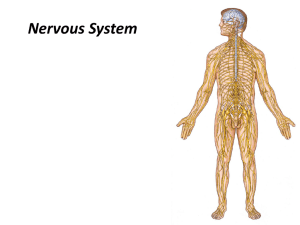
The Nervous System
... person has repeated seizures over time. A seizure is the physical findings or changes in behavior that occur after an episode of abnormal electrical activity in the brain. Treatment for epilepsy may involve surgery or medication. A diagnosis would consist of an MRI. If epilepsy seizures are due to a ...
... person has repeated seizures over time. A seizure is the physical findings or changes in behavior that occur after an episode of abnormal electrical activity in the brain. Treatment for epilepsy may involve surgery or medication. A diagnosis would consist of an MRI. If epilepsy seizures are due to a ...
Brain Presentation1
... normally in the brain through the synthesis of a neurotransmitter called GABA. Some of the greatest concentrations of GHB are found in the substantia nigra, thalamus and hypothalamus. When GHB is ingested by a user, it affects several different neurotransmitter systems in the brain: •GHB can increas ...
... normally in the brain through the synthesis of a neurotransmitter called GABA. Some of the greatest concentrations of GHB are found in the substantia nigra, thalamus and hypothalamus. When GHB is ingested by a user, it affects several different neurotransmitter systems in the brain: •GHB can increas ...
2006 natl fx fnd abstract - University of Illinois Archives
... important ideas you can try to put them back. Good luck! Also, do you mind if my name goes before Robert’s? ...
... important ideas you can try to put them back. Good luck! Also, do you mind if my name goes before Robert’s? ...
The free
... neurotransmitter have distinct roles; for example, ‘dopamine signals the error in reward prediction, serotonin controls the time scale of reward prediction, noradrenalin controls the randomness in action selection, and acetylcholine controls the speed of memory update. This contrasts with a single r ...
... neurotransmitter have distinct roles; for example, ‘dopamine signals the error in reward prediction, serotonin controls the time scale of reward prediction, noradrenalin controls the randomness in action selection, and acetylcholine controls the speed of memory update. This contrasts with a single r ...
Nervous System - Belle Vernon Area School District
... F. Cerebral palsy – general, defects in motor functions from several types of brain damage or birth related injury. G. Parkinsons – muscular rigidity, lack of movement H. Stroke I. Alzheimer’s disease – mental deterioration (dementia). J. Epilepsy – group of brain disorders that cause seizures K. He ...
... F. Cerebral palsy – general, defects in motor functions from several types of brain damage or birth related injury. G. Parkinsons – muscular rigidity, lack of movement H. Stroke I. Alzheimer’s disease – mental deterioration (dementia). J. Epilepsy – group of brain disorders that cause seizures K. He ...
HOW WE ENCODE - arcadiapsych
... something – But no explicit memory – memory of facts and experiences that one can consciously know and “declare” ...
... something – But no explicit memory – memory of facts and experiences that one can consciously know and “declare” ...
The Nervous System
... -Depolarization of one area causes depolarization of the next area so the nerve impulse continues down the neuron -Wave of depolarization only moves in 1 directions from the dendrites to the cell body to the axon -Original stimulation must be above threshold level in order for an impulse to be start ...
... -Depolarization of one area causes depolarization of the next area so the nerve impulse continues down the neuron -Wave of depolarization only moves in 1 directions from the dendrites to the cell body to the axon -Original stimulation must be above threshold level in order for an impulse to be start ...
to-BBB and Lundbeck to join forces on brain delivery of
... Thanks to the advances of biotechnology, therapeutic antibodies have become well-established treatment modalities to address many systemic diseases. The blood-brain barrier (BBB) is unfortunately a significant obstacle in the treatment of CNS disorders, since it prevents delivery of many drug candid ...
... Thanks to the advances of biotechnology, therapeutic antibodies have become well-established treatment modalities to address many systemic diseases. The blood-brain barrier (BBB) is unfortunately a significant obstacle in the treatment of CNS disorders, since it prevents delivery of many drug candid ...
memory - The Institute of Mathematical Sciences
... time, as they get consolidated they get entrenched in a network of cortical connections. At this point, they have an existence independent of the hippocampus. It is also thought that sleep plays a key role in the process of consolidating memories; not just so that they remain longer, but also their ...
... time, as they get consolidated they get entrenched in a network of cortical connections. At this point, they have an existence independent of the hippocampus. It is also thought that sleep plays a key role in the process of consolidating memories; not just so that they remain longer, but also their ...
Memory_Ch7_all - Arizona State University
... People were, at first. But then a bunch of new tasks were tried and a people discovered a circularity in the argument What makes a level “deep”? It leads to better memory. And why care about “depth”? It can predict memory. ...
... People were, at first. But then a bunch of new tasks were tried and a people discovered a circularity in the argument What makes a level “deep”? It leads to better memory. And why care about “depth”? It can predict memory. ...
File Now
... paradoxically both main neurotransmitter for memory and main one responsible for cell death ...
... paradoxically both main neurotransmitter for memory and main one responsible for cell death ...
1 - U-System
... - deficit in long-term memory including retrograde and anterograde amnesia; trouble learning facts, but no trouble learning new skills - amnesia is usually caused by bilateral damage in one of two specific places – the medial temporal lobe (including subcortical structures, such as the amygdala and ...
... - deficit in long-term memory including retrograde and anterograde amnesia; trouble learning facts, but no trouble learning new skills - amnesia is usually caused by bilateral damage in one of two specific places – the medial temporal lobe (including subcortical structures, such as the amygdala and ...
Biopsychology, Neuroscience, Physiological Psychology
... The motor cortex, an arch-shaped region at the rear of the frontal lobes, controls voluntary muscle movements on the opposite side of the body. Body parts requiring the most precise control occupy the greatest amount of cortical space. In an effort to find the source of motor control, researchers ha ...
... The motor cortex, an arch-shaped region at the rear of the frontal lobes, controls voluntary muscle movements on the opposite side of the body. Body parts requiring the most precise control occupy the greatest amount of cortical space. In an effort to find the source of motor control, researchers ha ...
BRAIN COMPUTER INTERFACING ARMY RESCUE USING
... Because the brain sends out a level of electrical energy the correct technology certainly could use this energy to power action operations. The knowledge of brain waves and of energy that sends a signal from one neuron to another is not new. Scientists and doctors have used equipment to measure brai ...
... Because the brain sends out a level of electrical energy the correct technology certainly could use this energy to power action operations. The knowledge of brain waves and of energy that sends a signal from one neuron to another is not new. Scientists and doctors have used equipment to measure brai ...
Nervous system
... electrochemical signals -- they are something like the gates and wires in a computer. pulses travel to the dendrite into the cell body and then onto the axon. Some nerves are covered by a special sheath called myelin, which increases the conductivity of the neuron. ...
... electrochemical signals -- they are something like the gates and wires in a computer. pulses travel to the dendrite into the cell body and then onto the axon. Some nerves are covered by a special sheath called myelin, which increases the conductivity of the neuron. ...
Unit 3B Study Guide
... 6. Define cerebral cortex. Name the four lobes that make up the cortex and state their locations. 7. Name the three functional divisions of the cortex and describe their functions. 8. Name and describe the role of the areas in the association cortex involved in understanding and producing language. ...
... 6. Define cerebral cortex. Name the four lobes that make up the cortex and state their locations. 7. Name the three functional divisions of the cortex and describe their functions. 8. Name and describe the role of the areas in the association cortex involved in understanding and producing language. ...
How Psychologists Study the Brain
... require a contrast medium to provide clearer images. Different tissues react differently to the magnetic current and this produces various images. No ionizing radiation is used in MRI. MRI cannot be done if the person has certain metal devices inside their body (such as a pacemaker, implanted port o ...
... require a contrast medium to provide clearer images. Different tissues react differently to the magnetic current and this produces various images. No ionizing radiation is used in MRI. MRI cannot be done if the person has certain metal devices inside their body (such as a pacemaker, implanted port o ...
First The Nervous System is Composed of Two Parts Peripheral
... • Also smoothes out muscle movement so it is not jerky. • Is extremely important for controlling rapid movement such as startle responses • Is also important for maintaining body balance ...
... • Also smoothes out muscle movement so it is not jerky. • Is extremely important for controlling rapid movement such as startle responses • Is also important for maintaining body balance ...
Human Memory - Fort Bend ISD
... Kandel observed that the amount of neurotransmitters released into the synapses between the nerve cells that controlled the withdrawal reflex increased as the snails learned the ...
... Kandel observed that the amount of neurotransmitters released into the synapses between the nerve cells that controlled the withdrawal reflex increased as the snails learned the ...
Storage and Retrieval
... • When you look at the words you see both its color and meaning. • When they are in conflict you must make a choice • Experience has taught you that word meaning is more important than color so you retrieve that information. • You are not always in complete control of what you pay attention to. ...
... • When you look at the words you see both its color and meaning. • When they are in conflict you must make a choice • Experience has taught you that word meaning is more important than color so you retrieve that information. • You are not always in complete control of what you pay attention to. ...