Week 2 Lecture Notes
... an AP in a single neuron. A single EPSP has, in general, very little effect on the state of a neuron (this makes computational sense). On average, the dendrite of a cortical pyramidal cell receives ~10000 synaptic contacts, of which several hundred to a thousand are active at any given time. The add ...
... an AP in a single neuron. A single EPSP has, in general, very little effect on the state of a neuron (this makes computational sense). On average, the dendrite of a cortical pyramidal cell receives ~10000 synaptic contacts, of which several hundred to a thousand are active at any given time. The add ...
bio12_sm_11_1
... transmission of neural messages by efferent neurons to effectors (muscles or glands) where action appropriate to the stimulus occurs. 2. The nodes of Ranvier are gaps between sections of the myelin sheath, which expose the neuron to extracellular fluid. The alternating exposure and insulation from t ...
... transmission of neural messages by efferent neurons to effectors (muscles or glands) where action appropriate to the stimulus occurs. 2. The nodes of Ranvier are gaps between sections of the myelin sheath, which expose the neuron to extracellular fluid. The alternating exposure and insulation from t ...
Vortex Model of the Brain - Center for Integrated Human Brain Science
... There is no doubt that discrete neuronal networks play an essential role in brain function. Nevertheless, many fundamental questions regarding how the brain works remain unanswered. What is the neuronal substrate of consciousness? Why do anesthetic effects diminish at higher atmospheric pressure? Ho ...
... There is no doubt that discrete neuronal networks play an essential role in brain function. Nevertheless, many fundamental questions regarding how the brain works remain unanswered. What is the neuronal substrate of consciousness? Why do anesthetic effects diminish at higher atmospheric pressure? Ho ...
cognition and language fem 4102
... likely to encounter new information that may overwrite existing memories. There are two types process involved in this theory. The first is retroactive interference where new learned information would disrupt an older memory. The second process is proactive interference information that has already ...
... likely to encounter new information that may overwrite existing memories. There are two types process involved in this theory. The first is retroactive interference where new learned information would disrupt an older memory. The second process is proactive interference information that has already ...
1. The diagram below is of a nerve cell or neuron. i. Add the following
... 3. The connection between adjacent neurons. ...
... 3. The connection between adjacent neurons. ...
Reward” and “Punishment” Function of the Limbic System
... found in the central gray area surrounding the aqueduct of Sylvius. Less potent punishment areas are found in the amygdala and hippocampus Stimulation in these areas causes the animal to show all the signs of displeasure, fear, terror, pain, punishment, and even sickness. Strong stimulation of the p ...
... found in the central gray area surrounding the aqueduct of Sylvius. Less potent punishment areas are found in the amygdala and hippocampus Stimulation in these areas causes the animal to show all the signs of displeasure, fear, terror, pain, punishment, and even sickness. Strong stimulation of the p ...
internal stimuli
... Reflexes • A reflex is an automatic response that occurs very rapidly and without conscious control. • The contraction of skeletal muscles is usually controlled by the brain, but in reflexes the muscles react with the involvement of the spinal cord only – not the brain. This protects us from danger ...
... Reflexes • A reflex is an automatic response that occurs very rapidly and without conscious control. • The contraction of skeletal muscles is usually controlled by the brain, but in reflexes the muscles react with the involvement of the spinal cord only – not the brain. This protects us from danger ...
Language Processing in the Brain
... Researchers are not sure. There are many possibilities, depending on where the person’s other, conventional language abilities are located: in the left hemisphere, the right he More generally speaking, the right hemisphere seems to show a predilection for spatial tasks and for recognizing faces and ...
... Researchers are not sure. There are many possibilities, depending on where the person’s other, conventional language abilities are located: in the left hemisphere, the right he More generally speaking, the right hemisphere seems to show a predilection for spatial tasks and for recognizing faces and ...
EQ2.5 - major divisions of the nervous system
... What are the major divisions of the nervous system, and what are their basic functions? The two major divisions of the nervous system are the central and the peripheral nervous system. The central nervous system is divided in two parts : the brain and the spinal chord. The Peripheral nervous system ...
... What are the major divisions of the nervous system, and what are their basic functions? The two major divisions of the nervous system are the central and the peripheral nervous system. The central nervous system is divided in two parts : the brain and the spinal chord. The Peripheral nervous system ...
Ch. 7: The Nervous System
... 7. If 2 or more nerves converge onto one, the addition of their impulses may be enough to trigger the larger nerve to continue the impulse on toward the CNS. 8. The CNS receives the signal and interprets the information, then it makes a decision. 9. The CNS sends an impulse out through a motor nerve ...
... 7. If 2 or more nerves converge onto one, the addition of their impulses may be enough to trigger the larger nerve to continue the impulse on toward the CNS. 8. The CNS receives the signal and interprets the information, then it makes a decision. 9. The CNS sends an impulse out through a motor nerve ...
Neuron communication
... • First, neurotransmitters are received by the dendrites. • Then, the information is processed by the soma. • Next, an action potential occurs, sending information down the axon. • Finally, neurotransmitters are released at the axon terminal for the next neuron to ...
... • First, neurotransmitters are received by the dendrites. • Then, the information is processed by the soma. • Next, an action potential occurs, sending information down the axon. • Finally, neurotransmitters are released at the axon terminal for the next neuron to ...
Visual Processing - Baby Watch Early Intervention
... way that young children with brain injury can’t. • Brain injury to young children may affect the visual brain in similar ways. • But in the very young child, brain plasticity may help the visual brain rewire to some degree around the lesions. • Depending on where, when or how much damage occurred, v ...
... way that young children with brain injury can’t. • Brain injury to young children may affect the visual brain in similar ways. • But in the very young child, brain plasticity may help the visual brain rewire to some degree around the lesions. • Depending on where, when or how much damage occurred, v ...
Organization of the Nervous system. Physiology of neurons and glial
... To the unaided eye, the most striking feature of the human brain is its curvy pattern of bumps and grooves. But within those curves is a latticework of nerve fibers that cross each other at roughly right angles (method used here is called diffusion spectrum imaging that infer the position of nerve f ...
... To the unaided eye, the most striking feature of the human brain is its curvy pattern of bumps and grooves. But within those curves is a latticework of nerve fibers that cross each other at roughly right angles (method used here is called diffusion spectrum imaging that infer the position of nerve f ...
Single Unit Recording
... electrode introduced into the brain of a living animal will detect electrical activity that is generated by the neurons adjacent to the electrode tip. If the electrode is a microelectrode, with a tip size of 3 to 10 micrometers, the electrode will often isolate the activity of a single neuron. The a ...
... electrode introduced into the brain of a living animal will detect electrical activity that is generated by the neurons adjacent to the electrode tip. If the electrode is a microelectrode, with a tip size of 3 to 10 micrometers, the electrode will often isolate the activity of a single neuron. The a ...
Chapter 11: Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue
... admits to drinking 10 to 12 cups of coffee daily. His doctor (knowing that caffeine lowers the threshold of neurons) suggests he reduce his intake of coffee. Given that caffeine lowers the threshold of neurons, how might this explain Mr. Jacobson’s symptoms? ...
... admits to drinking 10 to 12 cups of coffee daily. His doctor (knowing that caffeine lowers the threshold of neurons) suggests he reduce his intake of coffee. Given that caffeine lowers the threshold of neurons, how might this explain Mr. Jacobson’s symptoms? ...
Amnesia at the movies - University of Toronto Mississauga
... Priming – Primary Sensory Cortex Procedural Memory - Striate ...
... Priming – Primary Sensory Cortex Procedural Memory - Striate ...
Nerve impulses and Synapses Electro
... • While metabotropic receptors are not ion channels themselves, they can, and often do, open or close ion channels indirectly via a second messenger cascade. • The first step in the cascade is invariably the activation of a Gprotein. • There are different types of G-proteins, and they can trigger di ...
... • While metabotropic receptors are not ion channels themselves, they can, and often do, open or close ion channels indirectly via a second messenger cascade. • The first step in the cascade is invariably the activation of a Gprotein. • There are different types of G-proteins, and they can trigger di ...
ALHT106 – Psychology for Allied Health
... Thorndike – Connectionism stimulus à response (pre Skinner) 1. Law of effect – behaviour followed by pleasant consequences likely to be repeated (vice versa) 2. Law of readiness – series of responses can be chained together to satisfy some goal which will result in annoyance if blocked 3. Law of ...
... Thorndike – Connectionism stimulus à response (pre Skinner) 1. Law of effect – behaviour followed by pleasant consequences likely to be repeated (vice versa) 2. Law of readiness – series of responses can be chained together to satisfy some goal which will result in annoyance if blocked 3. Law of ...
Computer-generated holograms of three
... be constructed by the CGH can be represented in the computer by mathematical or graphical descriptions, or by their spatial samples. The physical interference between light waves is replaced by mathematical computation. However, synthesizing CGHs of 3D images is usually a heavy computational task. T ...
... be constructed by the CGH can be represented in the computer by mathematical or graphical descriptions, or by their spatial samples. The physical interference between light waves is replaced by mathematical computation. However, synthesizing CGHs of 3D images is usually a heavy computational task. T ...
Slide ()
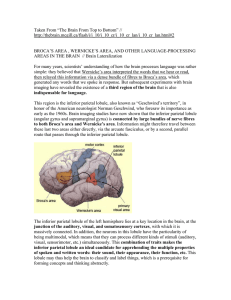
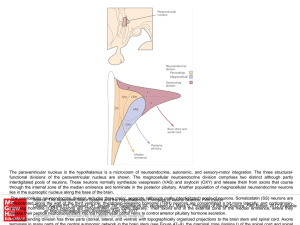
... concentrated along the wall of the third ventricle; thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) neurons are concentrated a bit more laterally; and corticotropinCitation: Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM, Siegelbaum SA, Hudspeth AJ, Mack S. Principles of Neural Science, Fifth Editon; 2012 Available releasi ...
... concentrated along the wall of the third ventricle; thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) neurons are concentrated a bit more laterally; and corticotropinCitation: Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM, Siegelbaum SA, Hudspeth AJ, Mack S. Principles of Neural Science, Fifth Editon; 2012 Available releasi ...
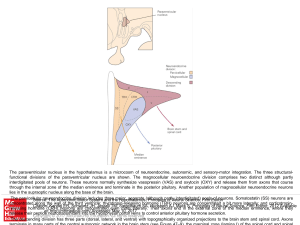
Slide ()
... concentrated along the wall of the third ventricle; thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) neurons are concentrated a bit more laterally; and corticotropinCitation: Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM, Siegelbaum SA, Hudspeth AJ, Mack S. Principles of Neural Science, Fifth Editon; 2012 Available releasi ...
... concentrated along the wall of the third ventricle; thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) neurons are concentrated a bit more laterally; and corticotropinCitation: Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM, Siegelbaum SA, Hudspeth AJ, Mack S. Principles of Neural Science, Fifth Editon; 2012 Available releasi ...
Introduction to Neural Networks
... small amount of local memory. The units are connected by communication channels (“connections”) which usually carry numeric data, encoded by any of various means. The units operate only on their local data and on the inputs they receive via the connections. Usenet newsgroup comp.ai.neural-nets ...
... small amount of local memory. The units are connected by communication channels (“connections”) which usually carry numeric data, encoded by any of various means. The units operate only on their local data and on the inputs they receive via the connections. Usenet newsgroup comp.ai.neural-nets ...
Neurons and how they communicate
... send a message to another neuron It does so through an electro-chemical process called action potential or neuronal firing ...
... send a message to another neuron It does so through an electro-chemical process called action potential or neuronal firing ...