physiological role of neuropeptide y in sympathetic neurotransmission
... frequency of nerve stimulation. The Y2 agonists not only inhibited the evoked release of NE but also the nerve stimulation induced increase in perfusion pressure. In contrast Y1 selective agonists facilitated the increase in perfusion pressure. In contrast to the prejunctional inhibitory effect of N ...
... frequency of nerve stimulation. The Y2 agonists not only inhibited the evoked release of NE but also the nerve stimulation induced increase in perfusion pressure. In contrast Y1 selective agonists facilitated the increase in perfusion pressure. In contrast to the prejunctional inhibitory effect of N ...
Nervous System Organization and Components
... are two systems that serve as means of internal communication within the organism. The nervous system acts rapidly, for a short duration and endocrine system acts slowly, for a long duration. Both systems integrate and coordinate activities to assure proper body function. These systems allow for com ...
... are two systems that serve as means of internal communication within the organism. The nervous system acts rapidly, for a short duration and endocrine system acts slowly, for a long duration. Both systems integrate and coordinate activities to assure proper body function. These systems allow for com ...
research Nerve Cells, Axons, Dendrites, and Synapses: The
... This article first appeared in Center for Neuroskills’ Inside View newsletter. It is reprinted in part with permission. ...
... This article first appeared in Center for Neuroskills’ Inside View newsletter. It is reprinted in part with permission. ...
Nervous system
... Depending upon the type of neuron, axons can be covered with a thin layer of myelin, like an insulated electrical wire. Myelin is made of fat, and it helps to speed transmission of a nerve impulse down a long axon. ...
... Depending upon the type of neuron, axons can be covered with a thin layer of myelin, like an insulated electrical wire. Myelin is made of fat, and it helps to speed transmission of a nerve impulse down a long axon. ...
Lesson 33 - UBC Zoology
... There are dorsal and ventral extensions of the grey matter - the dorsal and ventral horns. The dorsal horn contains the cell bodies of neurons receiving incoming sensory information, which they distribute elsewhere in the cord or to the brain. The ventral horns contain cell bodies of motor neurons ...
... There are dorsal and ventral extensions of the grey matter - the dorsal and ventral horns. The dorsal horn contains the cell bodies of neurons receiving incoming sensory information, which they distribute elsewhere in the cord or to the brain. The ventral horns contain cell bodies of motor neurons ...
What is a neuron?
... Schwann cells - supporting cells of the PNS that myelinate axons • Myelin sheath – whitish lipoprotein that surrounds and insulates the axon (nerve fiber) • Neurilemma - external layer containing bulk of cytoplasm with nucleus and organelles (cell membrane) ...
... Schwann cells - supporting cells of the PNS that myelinate axons • Myelin sheath – whitish lipoprotein that surrounds and insulates the axon (nerve fiber) • Neurilemma - external layer containing bulk of cytoplasm with nucleus and organelles (cell membrane) ...
What is a neuron?
... Schwann cells - supporting cells of the PNS that myelinate axons • Myelin sheath – whitish lipoprotein that surrounds and insulates the axon (nerve fiber) • Neurilemma - external layer containing bulk of cytoplasm with nucleus and organelles (cell membrane) ...
... Schwann cells - supporting cells of the PNS that myelinate axons • Myelin sheath – whitish lipoprotein that surrounds and insulates the axon (nerve fiber) • Neurilemma - external layer containing bulk of cytoplasm with nucleus and organelles (cell membrane) ...
Ch 35 PowerPoint - Damien Rutkoski
... the fluid-filled cochlea. The cochlea is lined with tiny hair cells that are pushed back and forth by these pressure waves. In response to these movements, the hair cells produce nerve impulses that are sent to the brain through the auditory nerve. ...
... the fluid-filled cochlea. The cochlea is lined with tiny hair cells that are pushed back and forth by these pressure waves. In response to these movements, the hair cells produce nerve impulses that are sent to the brain through the auditory nerve. ...
Chapter 5b
... – Positively charged sodium – Positively charged potassium – Negatively charged chloride ions – Other negatively charged proteins. ...
... – Positively charged sodium – Positively charged potassium – Negatively charged chloride ions – Other negatively charged proteins. ...
the nervous system
... • Cells carry messages from one part of the body to another • The messages in the nervous system are electrical signals called impulses • The cells that transmit the impulses are called neurons – Made of: ...
... • Cells carry messages from one part of the body to another • The messages in the nervous system are electrical signals called impulses • The cells that transmit the impulses are called neurons – Made of: ...
File
... associated with peripheral and central nerve damage in the legs and spinal cord • Management—symptomatic, involving treating the underlying cause or contributing factor, if known • Nonmedical treatment • Drug therapy effective for some patients ...
... associated with peripheral and central nerve damage in the legs and spinal cord • Management—symptomatic, involving treating the underlying cause or contributing factor, if known • Nonmedical treatment • Drug therapy effective for some patients ...
The human Nervous system is the most complex system in the
... Myelin sheath formation begins in the CNS of the human embryo at about 4 months gestational age with the formation of most sheaths by the age of 1 year. The final myelin sheath thickness being achieved by the time of physical maturity. There are three types of oligodendrocytes: light, medium, and da ...
... Myelin sheath formation begins in the CNS of the human embryo at about 4 months gestational age with the formation of most sheaths by the age of 1 year. The final myelin sheath thickness being achieved by the time of physical maturity. There are three types of oligodendrocytes: light, medium, and da ...
bio12_sm_11_1
... 3. The nervous system cells that provide a supporting role rather than a transmitting role are the Schwann cells, which produce the myelin sheath, and the glial cells, which provide nutritional and structural support for neurons. They facilitate the transmission of nerve impulses via neurons but do ...
... 3. The nervous system cells that provide a supporting role rather than a transmitting role are the Schwann cells, which produce the myelin sheath, and the glial cells, which provide nutritional and structural support for neurons. They facilitate the transmission of nerve impulses via neurons but do ...
Final Exam - UF Psychology
... 4. Two competing theories of color vision are the __trichromatic theory_____________, which is based on the relative activity of the different kinds of retinal cones, and the __opponent process theory_______________, which is suggested by receptive fields with center-surround antagonism of complemen ...
... 4. Two competing theories of color vision are the __trichromatic theory_____________, which is based on the relative activity of the different kinds of retinal cones, and the __opponent process theory_______________, which is suggested by receptive fields with center-surround antagonism of complemen ...
The Nervous System
... TOPIC: The Nervous System AIM: How does the Nervous System help maintain Homeostasis? HW: TEXT BOOK READ PAGES 558-562. Do Vocabulary Definitions for words on page 558 ...
... TOPIC: The Nervous System AIM: How does the Nervous System help maintain Homeostasis? HW: TEXT BOOK READ PAGES 558-562. Do Vocabulary Definitions for words on page 558 ...
Nervous System and Senses - Avon Community School Corporation
... › Sensory (afferent)- carry messages to CNS › Motor (efferent)- carry messages from CNS ...
... › Sensory (afferent)- carry messages to CNS › Motor (efferent)- carry messages from CNS ...
methods of neuroanatomy
... Reigned 20 years, now obsolete. Weakness: fiber of passage problem (i.e., inability to tell whether labeling is attributable to direct effects on cell bodies at the lesion site or instead to damage to axons that pass through the lesion but originate elsewhere). Autoradiography: emerges in 1970's. Ex ...
... Reigned 20 years, now obsolete. Weakness: fiber of passage problem (i.e., inability to tell whether labeling is attributable to direct effects on cell bodies at the lesion site or instead to damage to axons that pass through the lesion but originate elsewhere). Autoradiography: emerges in 1970's. Ex ...
Stopping nerve cell over-activity: a new drug target
... NMDA ‘receptors’ are parts of nerve cells that respond to glutamate. Preventing NMDA receptors from working could be a useful drug treatment for Parkinson’s that might stop nerve cell over-activity. But recent research has shown that the dopamineproducing cells affected in Parkinson’s have NMDA rece ...
... NMDA ‘receptors’ are parts of nerve cells that respond to glutamate. Preventing NMDA receptors from working could be a useful drug treatment for Parkinson’s that might stop nerve cell over-activity. But recent research has shown that the dopamineproducing cells affected in Parkinson’s have NMDA rece ...
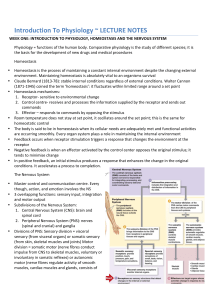
Introduction To Physiology ~ LECTURE NOTES
... (1871-‐1945) coined the term ‘homeostasis’: it fluctuates within limited range around a set point Homeostasis mechanisms: 1. Receptor-‐ sensitive to environmental change 2. Control centre-‐ receives and processes ...
... (1871-‐1945) coined the term ‘homeostasis’: it fluctuates within limited range around a set point Homeostasis mechanisms: 1. Receptor-‐ sensitive to environmental change 2. Control centre-‐ receives and processes ...
Nervous Systems
... • Feel good with dopamine and serotonin – Natural reward system appeared early in evolution; reinforce behaviors favorable to ...
... • Feel good with dopamine and serotonin – Natural reward system appeared early in evolution; reinforce behaviors favorable to ...
AP Psychology - Ms. Hofmann`s Website
... Open your textbook to page 59. Study the Nervous System image. Then click on the Autonomic Nervous System under the Peripheral Nervous system on this website. Read the two scenarios on the right that begin with, “It’s a nice sunny day…” Draw yourself in each of these situations and in the caption ex ...
... Open your textbook to page 59. Study the Nervous System image. Then click on the Autonomic Nervous System under the Peripheral Nervous system on this website. Read the two scenarios on the right that begin with, “It’s a nice sunny day…” Draw yourself in each of these situations and in the caption ex ...
AP Psychology – Unit 3 – Biological Bases of Behavior
... d. do none of the above. 31. The branching extensions of nerve cells that receive incoming signals from sensory receptors or from other neurons are called the: a. axons. b. synapses. c. dendrites. d. neurotransmitters. 32. Sheila was able to jerk her hand out of the scalding water before sensing any ...
... d. do none of the above. 31. The branching extensions of nerve cells that receive incoming signals from sensory receptors or from other neurons are called the: a. axons. b. synapses. c. dendrites. d. neurotransmitters. 32. Sheila was able to jerk her hand out of the scalding water before sensing any ...
1 - My Blog
... d. do none of the above. 31. The branching extensions of nerve cells that receive incoming signals from sensory receptors or from other neurons are called the: a. axons. b. synapses. c. dendrites. d. neurotransmitters. 32. Sheila was able to jerk her hand out of the scalding water before sensing any ...
... d. do none of the above. 31. The branching extensions of nerve cells that receive incoming signals from sensory receptors or from other neurons are called the: a. axons. b. synapses. c. dendrites. d. neurotransmitters. 32. Sheila was able to jerk her hand out of the scalding water before sensing any ...