Somatic nervous system
... muscle fiber could either be excitatory or inhibitory. For vertebrates, however, the response of a muscle fiber to a neurotransmitter (always acetylcholine (ACh)) can only be excitatory. ...
... muscle fiber could either be excitatory or inhibitory. For vertebrates, however, the response of a muscle fiber to a neurotransmitter (always acetylcholine (ACh)) can only be excitatory. ...
Chapter 2 Vocabulary
... 30. The __________________ , the oldest and innermost region of the brain, is an extension of the spinal cord and is the central core of the brain; its structures direct automatic survival functions. (p. 61) 31. Located in the brainstem, the __________________ controls breathing and heartbeat. (p. 6 ...
... 30. The __________________ , the oldest and innermost region of the brain, is an extension of the spinal cord and is the central core of the brain; its structures direct automatic survival functions. (p. 61) 31. Located in the brainstem, the __________________ controls breathing and heartbeat. (p. 6 ...
Chapters 31 and 34 - Nervous Endocrine
... Nerve Transmission • Messages are electrical and chemical signals • An electric charge is conducted down a neuron (Dendrite to axon) – Axon is covered in an insulating layer called a myelin sheath to speed up impulses ...
... Nerve Transmission • Messages are electrical and chemical signals • An electric charge is conducted down a neuron (Dendrite to axon) – Axon is covered in an insulating layer called a myelin sheath to speed up impulses ...
Overview
... Other diseases affecting the nervous system are Parkinsons, seizures, multiple sclerosis, meningitis, and Cerebral vascular accident commonly called a stroke, (which also affects the circulatory system). Infections and tumors may also occur causing illness affecting the nervous system. ...
... Other diseases affecting the nervous system are Parkinsons, seizures, multiple sclerosis, meningitis, and Cerebral vascular accident commonly called a stroke, (which also affects the circulatory system). Infections and tumors may also occur causing illness affecting the nervous system. ...
The Nervous System - Needham.K12.ma.us
... – Speeds up breathing and heart rate – Stops digestion and urination – Dilates Pupils • Parasympathetic—Normal Body Maintenance – Moderates breathing and heart rate – Allows for digestion and urination – Constricts Pupils ...
... – Speeds up breathing and heart rate – Stops digestion and urination – Dilates Pupils • Parasympathetic—Normal Body Maintenance – Moderates breathing and heart rate – Allows for digestion and urination – Constricts Pupils ...
Neurons and the General Layout of the Nervous System - U
... myelin sheaths of axons in the CNS and PNS are oligodendroglia and Schwann cells, respectively • Only Schwann cells are regenerative. Damage is permanent if it occurs in oligodendroglia (cause of Parkinson’s, degeneration of myelin of dopaminergic neurons) ...
... myelin sheaths of axons in the CNS and PNS are oligodendroglia and Schwann cells, respectively • Only Schwann cells are regenerative. Damage is permanent if it occurs in oligodendroglia (cause of Parkinson’s, degeneration of myelin of dopaminergic neurons) ...
Neurophysiology Complete
... Repolarization: within a millisecond Na and K return to their original state and the resting membrane potentil is restored Absolute refractory period: when the Na gates are open and the neuron is totally insensitive to additional stimuli Relative refractory period: if a very strong stimuli is able t ...
... Repolarization: within a millisecond Na and K return to their original state and the resting membrane potentil is restored Absolute refractory period: when the Na gates are open and the neuron is totally insensitive to additional stimuli Relative refractory period: if a very strong stimuli is able t ...
Nerve sheaths:
... Synaptic vesicles also present where there is synaptic transmission takes place. Multiple sclerosis (MS) affect myelin 1-5times >female ages 43-45 demylination in CNS. ...
... Synaptic vesicles also present where there is synaptic transmission takes place. Multiple sclerosis (MS) affect myelin 1-5times >female ages 43-45 demylination in CNS. ...
Physio Lab 5 PhysioEx 3
... hold the cloth, then take it off when the patient falls asleep, and put it back on when they wake up. This is because ether only temperately blocks VGCs. Within 6 minutes, the action potential returns. Question (#6) is about curare, an anesthesia from tree sap. It is used by South American Indians o ...
... hold the cloth, then take it off when the patient falls asleep, and put it back on when they wake up. This is because ether only temperately blocks VGCs. Within 6 minutes, the action potential returns. Question (#6) is about curare, an anesthesia from tree sap. It is used by South American Indians o ...
Anatomy, composition and physiology of neuron, dendrite, axon,and
... Specificity and modifiability of neuronal connections ...
... Specificity and modifiability of neuronal connections ...
the brain - Cloudfront.net
... 2% of your body but uses _____ of your energy when you are at rest. A. 10% C. 50% B. 20% D. 75% 4. The more you repeat something the more brain space is dedicated to it. For example, in musicians the part of the brain that controls fingers used to play an instrument is up to 130% larger than in a no ...
... 2% of your body but uses _____ of your energy when you are at rest. A. 10% C. 50% B. 20% D. 75% 4. The more you repeat something the more brain space is dedicated to it. For example, in musicians the part of the brain that controls fingers used to play an instrument is up to 130% larger than in a no ...
Current concepts in central nervous system regeneration
... until their projecting axons and dendrites reach their target tissue.4 Thus, a neurotrophic factor has a neurotrophic function, in addition to its neurotropic role, axon guidance.5 Since the distance axons are required to grow varies between populations of neurons, the timing of specific neurotrophi ...
... until their projecting axons and dendrites reach their target tissue.4 Thus, a neurotrophic factor has a neurotrophic function, in addition to its neurotropic role, axon guidance.5 Since the distance axons are required to grow varies between populations of neurons, the timing of specific neurotrophi ...
Human Physiology
... 9b.Students know how the nervous system mediates communication between different parts of the body and the body’s interactions with the environment. 9d.Students know the functions of the nervous system and the role of neurons in transmitting electrochemical impulses. 9e.Students know the roles of se ...
... 9b.Students know how the nervous system mediates communication between different parts of the body and the body’s interactions with the environment. 9d.Students know the functions of the nervous system and the role of neurons in transmitting electrochemical impulses. 9e.Students know the roles of se ...
Complete Nervous System Worksheet
... 3. Name the two divisions of the peripheral nervous system. 4. Name 2 characteristics of motor neurons 5. Name 2 characteristics of sensory neurons 6. Name the parts that make up the C.N.S. 7. What is the name of the sheath that covers some neurons 8. What is the space between two successive neurons ...
... 3. Name the two divisions of the peripheral nervous system. 4. Name 2 characteristics of motor neurons 5. Name 2 characteristics of sensory neurons 6. Name the parts that make up the C.N.S. 7. What is the name of the sheath that covers some neurons 8. What is the space between two successive neurons ...
neurons
... of its membrane and allowing positive ions to rush in. • The neuron then quickly pushes the positively charged ions back out again and closes that section of its membrane. • The neuron then opens the next section of its membrane and allows the positively charged ions to rush in, and quickly pushes t ...
... of its membrane and allowing positive ions to rush in. • The neuron then quickly pushes the positively charged ions back out again and closes that section of its membrane. • The neuron then opens the next section of its membrane and allows the positively charged ions to rush in, and quickly pushes t ...
File
... - Simplest spinal reflex - Monosynaptic reflex - e.g knee jerk 1. Receptor muscle sense the action (e.g hammer on knee) 2. Message sent along afferent nerve axon to spinal cord 3. Afferent synapses with efferent of same muscles 4. Impulse in transmitted along efferent pathway 5. Motor unit contracts ...
... - Simplest spinal reflex - Monosynaptic reflex - e.g knee jerk 1. Receptor muscle sense the action (e.g hammer on knee) 2. Message sent along afferent nerve axon to spinal cord 3. Afferent synapses with efferent of same muscles 4. Impulse in transmitted along efferent pathway 5. Motor unit contracts ...
CHAPTER 3 – THE BIOLOGICAL BASIS OF BEHAVIOUR
... complex mental data and is called the “grey matter” of the brain. The cortex surrounds the cerebrum, with comprises symmetrical hemispheres (left and right). Both the left hemisphere and the right hemisphere have specialised functions (hemisphere lateralisation). The left hemisphere specialises in l ...
... complex mental data and is called the “grey matter” of the brain. The cortex surrounds the cerebrum, with comprises symmetrical hemispheres (left and right). Both the left hemisphere and the right hemisphere have specialised functions (hemisphere lateralisation). The left hemisphere specialises in l ...
1 - UPenn School of Engineering and Applied Science
... for CNS damage in animals. These damaged neuronal cells (and accessory cells) must be enticed to repair themselves otherwise the damaged cells will undergo cell death and result in a net loss in the total number of cells. Experimentally, several types of cells have been used to encourage neuronal c ...
... for CNS damage in animals. These damaged neuronal cells (and accessory cells) must be enticed to repair themselves otherwise the damaged cells will undergo cell death and result in a net loss in the total number of cells. Experimentally, several types of cells have been used to encourage neuronal c ...
File
... systems is done by the nervous system. – Function: controls and coordinates all bodily functions and responds to internal and external stimuli. THINK… COMMUNICATION! ...
... systems is done by the nervous system. – Function: controls and coordinates all bodily functions and responds to internal and external stimuli. THINK… COMMUNICATION! ...
Unit-III-The-Nervous-and-Endocrine-Systems
... Volunteer work is done by choice, so the body’s (or soma’s) voluntary actions are controlled by this nervous system. ...
... Volunteer work is done by choice, so the body’s (or soma’s) voluntary actions are controlled by this nervous system. ...
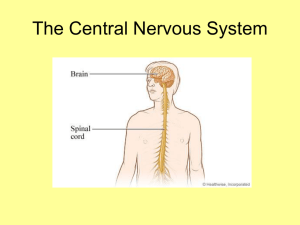
Central nervous system
... • Feel for the flow of events (sense of the present) • Our memory of what just happened “echoes” in our minds for a few seconds ...
... • Feel for the flow of events (sense of the present) • Our memory of what just happened “echoes” in our minds for a few seconds ...
here - TurkoTek
... Labeled Lines- any time a particular afferent nerve fires, the brain interperts the same way. Phantom Pain- the nerves that used to carry info, are still partially intact, so brain interprets it the way it always has. Referred Pain- pain that originated in your internal organs, will experience ...
... Labeled Lines- any time a particular afferent nerve fires, the brain interperts the same way. Phantom Pain- the nerves that used to carry info, are still partially intact, so brain interprets it the way it always has. Referred Pain- pain that originated in your internal organs, will experience ...