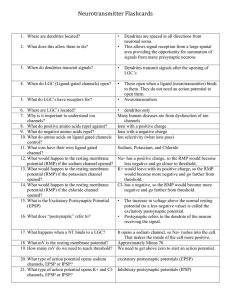
to find the lecture notes for lecture 6 nervous tissue click here
... active zone -upon receipt of AP into these bulbs -causes the opening of voltagegated Ca2+ channels -the influx of calcium promotes the “docking” of the synaptic vesicle with the PM and the exocytosis of their contents -the synaptic vesicle components are recycled for future use ...
... active zone -upon receipt of AP into these bulbs -causes the opening of voltagegated Ca2+ channels -the influx of calcium promotes the “docking” of the synaptic vesicle with the PM and the exocytosis of their contents -the synaptic vesicle components are recycled for future use ...
Motor Systems - University of Sunderland
... – SS use oxidative metabolism, are weak, do not appear to fatigue, have a role in maintaining posture. – FR are fatigue-resistant, use both oxidative and nonoxidative enzymes, are stronger, and their motoneurons have intermediate input resistance and rheobase (current threshold for initiating a spik ...
... – SS use oxidative metabolism, are weak, do not appear to fatigue, have a role in maintaining posture. – FR are fatigue-resistant, use both oxidative and nonoxidative enzymes, are stronger, and their motoneurons have intermediate input resistance and rheobase (current threshold for initiating a spik ...
Chapter 2 Lecture Notes Module 4 – Neural and Hormonal Systems
... ______________________ - endocrine glands located on top of each kidney that secrete over 30 different hormones to deal with stress, regulate salt intake, and provide a secondary source of sex hormones affecting the sexual changes that occur during adolescence. ...
... ______________________ - endocrine glands located on top of each kidney that secrete over 30 different hormones to deal with stress, regulate salt intake, and provide a secondary source of sex hormones affecting the sexual changes that occur during adolescence. ...
2.2 Electrical Communication Study Guide by Hisrich
... 2.2.i How can biomedical professionals help treat, cure and improve the quality of life of those suffering from nervous system disorders? The main person that treats neurological disorders is a Neurologist (one who studies nerves). That’s a special kind of doctor that specializes in the nervous syst ...
... 2.2.i How can biomedical professionals help treat, cure and improve the quality of life of those suffering from nervous system disorders? The main person that treats neurological disorders is a Neurologist (one who studies nerves). That’s a special kind of doctor that specializes in the nervous syst ...
File
... T6.5.4 - An action potential consists of depolarization and repolarization of the neuron. Action potentials are rapid changes in membrane potentials. This consists of a rapid depolarization (change from negative to positive when sodium diffuses into the neuron) and a rapid repolarization (change ...
... T6.5.4 - An action potential consists of depolarization and repolarization of the neuron. Action potentials are rapid changes in membrane potentials. This consists of a rapid depolarization (change from negative to positive when sodium diffuses into the neuron) and a rapid repolarization (change ...
The Electrochemical Impulse
... Binding depolarizes the membrane of the dendrites Na+ channels open, and the action potential is reintiated Inhibitory effect Opens K + channels in the membrane, so K + diffuses out The inner surface becomes even more negative in relation to the outer the membrane is hyperpolarized makes ...
... Binding depolarizes the membrane of the dendrites Na+ channels open, and the action potential is reintiated Inhibitory effect Opens K + channels in the membrane, so K + diffuses out The inner surface becomes even more negative in relation to the outer the membrane is hyperpolarized makes ...
Hair cells
... -This process is called echolocation The invention of sonar (sound navigation and ...
... -This process is called echolocation The invention of sonar (sound navigation and ...
Answers to End-of-Chapter Questions – Brooker et al ARIS site
... 8. The speed of transmission of an action potential along an axon is influenced by a. the presence of myelin. b. an increased concentration of Ca2+. c. the diameter of the axon. d. all of the above. e. a and c only. Answer: e. The speed of an action potential is influenced by the presence of myelin ...
... 8. The speed of transmission of an action potential along an axon is influenced by a. the presence of myelin. b. an increased concentration of Ca2+. c. the diameter of the axon. d. all of the above. e. a and c only. Answer: e. The speed of an action potential is influenced by the presence of myelin ...
File
... - Simplest spinal reflex - Monosynaptic reflex - e.g knee jerk 1. Receptor muscle sense the action (e.g hammer on knee) 2. Message sent along afferent nerve axon to spinal cord 3. Afferent synapses with efferent of same muscles 4. Impulse in transmitted along efferent pathway 5. Motor unit contracts ...
... - Simplest spinal reflex - Monosynaptic reflex - e.g knee jerk 1. Receptor muscle sense the action (e.g hammer on knee) 2. Message sent along afferent nerve axon to spinal cord 3. Afferent synapses with efferent of same muscles 4. Impulse in transmitted along efferent pathway 5. Motor unit contracts ...
Neural Tissue – Chapter 12
... membrane. The arrival of positive charges shifts the transmembrane potential toward 0 mV. This is called depolarization. Step Two: At the resting potential, sodium ions are drawn to the outer surface of the cell membrane, attracted by the excess of negative ions on the inside of the membrane. As the ...
... membrane. The arrival of positive charges shifts the transmembrane potential toward 0 mV. This is called depolarization. Step Two: At the resting potential, sodium ions are drawn to the outer surface of the cell membrane, attracted by the excess of negative ions on the inside of the membrane. As the ...
The nervous system - Sonoma Valley High School
... An impulse begins when a neuron is stimulated strong ...
... An impulse begins when a neuron is stimulated strong ...
Nervous System
... Rapid opening of 1st. Voltage-gated channels cause Na+ to enter & cause depolarization. When depolarization reaches a threshold, the membrane potential reverses & AP is generated. The second voltage gated K+ channel open allowing K+ to flow out. The slower opening of voltage-gated K+ channels & ...
... Rapid opening of 1st. Voltage-gated channels cause Na+ to enter & cause depolarization. When depolarization reaches a threshold, the membrane potential reverses & AP is generated. The second voltage gated K+ channel open allowing K+ to flow out. The slower opening of voltage-gated K+ channels & ...
Nerve tissue for stu..
... C. Myelinated axons in the central nervous system (CNS) – myelin sheath is formed by processes of oligodendrocytes. One inetrnodal segment is formed by one process of oligodendrocyte. One oligodendrocyte can form more internodal segments by its processes. D. Non-myelinated axons in the CNS – axons a ...
... C. Myelinated axons in the central nervous system (CNS) – myelin sheath is formed by processes of oligodendrocytes. One inetrnodal segment is formed by one process of oligodendrocyte. One oligodendrocyte can form more internodal segments by its processes. D. Non-myelinated axons in the CNS – axons a ...
Nervous System Notes
... negative to positive. Causes neurotransmitters(chemicals) to be released at the terminal, to stimulate the next neuron in the chain. ...
... negative to positive. Causes neurotransmitters(chemicals) to be released at the terminal, to stimulate the next neuron in the chain. ...
Anatomy Physiology Final Exam Review
... a. Muscle Fascicle Muscle fiber Mofibril Muscle filament b. Fascicle Muscle Muscle fiber Myofibril Fascicle c. Fascicle Muscle fiber Myofibril Muscle filament Muscle d. Muscle Muscle fiber Myofibril Muscle Muscle filament 24. Which one of the following does not take p ...
... a. Muscle Fascicle Muscle fiber Mofibril Muscle filament b. Fascicle Muscle Muscle fiber Myofibril Fascicle c. Fascicle Muscle fiber Myofibril Muscle filament Muscle d. Muscle Muscle fiber Myofibril Muscle Muscle filament 24. Which one of the following does not take p ...
Effects of Warm Up and Cool Down
... the following bone conditions: – Osteoporosis and how this affects physical activity – Growth plate and how this affects physical activity – Osteoarthritis and how this affects physical ...
... the following bone conditions: – Osteoporosis and how this affects physical activity – Growth plate and how this affects physical activity – Osteoarthritis and how this affects physical ...
Neurons & the Nervous System
... (sends the message) • Refractory period: phase after firing an impulse, neuron will not fire • All-or-none principle: neuron will fire or not fire, no in-between ...
... (sends the message) • Refractory period: phase after firing an impulse, neuron will not fire • All-or-none principle: neuron will fire or not fire, no in-between ...
neuroplasticity 2016
... • Sometimes only some of the axon branches of a neuron are damaged • The presynaptic cell body still makes the usual amount of neurotransmitter, but now the neurotransmitter is distributed to less presynaptic terminals • Therefore, each terminal receives more neurotransmitter, and more neurotransmit ...
... • Sometimes only some of the axon branches of a neuron are damaged • The presynaptic cell body still makes the usual amount of neurotransmitter, but now the neurotransmitter is distributed to less presynaptic terminals • Therefore, each terminal receives more neurotransmitter, and more neurotransmit ...
Case Studies in a Physiology Course on the Autonomic Nervous
... Ganglionic nicotinic neurotransmission. The ganglionic transmitter of both the sympathetic and the parasympathetic division is acetylcholine (ACh). ACh is synthesised in the ganglionic axon from choline (Ch) that is actively transported into the axon by means of a high affinity choline uptake trans ...
... Ganglionic nicotinic neurotransmission. The ganglionic transmitter of both the sympathetic and the parasympathetic division is acetylcholine (ACh). ACh is synthesised in the ganglionic axon from choline (Ch) that is actively transported into the axon by means of a high affinity choline uptake trans ...
Lies outside the central nervous system
... Promotes all internal responses associated with a relaxed state. Causes the pupil of the eye to contract, promotes digestion of food and slows down the heartbeat The neurotransmitter released during this is acetylcholine (Ach) ...
... Promotes all internal responses associated with a relaxed state. Causes the pupil of the eye to contract, promotes digestion of food and slows down the heartbeat The neurotransmitter released during this is acetylcholine (Ach) ...
Neuromuscular junction

A neuromuscular junction (sometimes called a myoneural junction) is a junction between nerve and muscle; it is a chemical synapse formed by the contact between the presynaptic terminal of a motor neuron and the postsynaptic membrane of a muscle fiber. It is at the neuromuscular junction that a motor neuron is able to transmit a signal to the muscle fiber, causing muscle contraction.Muscles require innervation to function—and even just to maintain muscle tone, avoiding atrophy. Synaptic transmission at the neuromuscular junction begins when an action potential reaches the presynaptic terminal of a motor neuron, which activates voltage-dependent calcium channels to allow calcium ions to enter the neuron. Calcium ions bind to sensor proteins (synaptotagmin) on synaptic vesicles, triggering vesicle fusion with the cell membrane and subsequent neurotransmitter release from the motor neuron into the synaptic cleft. In vertebrates, motor neurons release acetylcholine (ACh), a small molecule neurotransmitter, which diffuses across the synaptic cleft and binds to nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) on the cell membrane of the muscle fiber, also known as the sarcolemma. nAChRs are ionotropic receptors, meaning they serve as ligand-gated ion channels. The binding of ACh to the receptor can depolarize the muscle fiber, causing a cascade that eventually results in muscle contraction.Neuromuscular junction diseases can be of genetic and autoimmune origin. Genetic disorders, such as Duchenne muscular dystrophy, can arise from mutated structural proteins that comprise the neuromuscular junction, whereas autoimmune diseases, such as myasthenia gravis, occur when antibodies are produced against nicotinic acetylcholine receptors on the sarcolemma.