A Model of Extraforaminal Brachial Plexus Injury in Neonatal Mice
... lesion in neonatal mice clinically mimicking the typical upper trunk injury in humans. While others have developed models of intraforaminal injury in neonatal rats, the current model has three distinct advantages: 1. The postganglionic nature of the lesion more closely recreates the neurologic patho ...
... lesion in neonatal mice clinically mimicking the typical upper trunk injury in humans. While others have developed models of intraforaminal injury in neonatal rats, the current model has three distinct advantages: 1. The postganglionic nature of the lesion more closely recreates the neurologic patho ...
Endocrine System - Brain Mind Forum
... GABA.[16] Correspondingly, glycine is the inhibitory transmitter in the spinal cord. Acetylcholine was the first neurotransmitter discovered in the peripheral and central nervous systems. It activates skeletal muscles in the somatic nervous system and may either excite or inhibit internal organs in ...
... GABA.[16] Correspondingly, glycine is the inhibitory transmitter in the spinal cord. Acetylcholine was the first neurotransmitter discovered in the peripheral and central nervous systems. It activates skeletal muscles in the somatic nervous system and may either excite or inhibit internal organs in ...
PHYSIOLOGICAL PSYCHOLOGY UNIVERSITY OF CALICUT SCHOOL OF DISTANCE EDUCATION BSc Counselling Psychology
... stronger than what is ordinarily necessary. a. Absolute refractory period c. Depolarization b. Relative refractory period d. Excitatory period 95. To complete synaptic transmission, the neurotransmitters attach to receptor molecules embedded in the __________________ . a. Presynaptic membrane c. Cel ...
... stronger than what is ordinarily necessary. a. Absolute refractory period c. Depolarization b. Relative refractory period d. Excitatory period 95. To complete synaptic transmission, the neurotransmitters attach to receptor molecules embedded in the __________________ . a. Presynaptic membrane c. Cel ...
4-S2 - L1 (1)
... • ACh is also a central neurotransmitter – acts at both nicotinic and muscarinic receptors in the brain – mainly excitatory – receptors often present on presynaptic terminals to enhance the release of other transmitters ...
... • ACh is also a central neurotransmitter – acts at both nicotinic and muscarinic receptors in the brain – mainly excitatory – receptors often present on presynaptic terminals to enhance the release of other transmitters ...
C The Electrochemical Impulse
... Acetylcholine and cholinesterase Two neurotransmitters: Acetylcholine (ACh) acts has an excitatory effect on most neurons Causes depolarization ...
... Acetylcholine and cholinesterase Two neurotransmitters: Acetylcholine (ACh) acts has an excitatory effect on most neurons Causes depolarization ...
Nature Versus Nurture
... § This includes strengthening these connections as you might expect Remember that as you interact with others you change the structure of their nervous system and they change yours! § This also includes, yes….. removing and weakening synapses ...
... § This includes strengthening these connections as you might expect Remember that as you interact with others you change the structure of their nervous system and they change yours! § This also includes, yes….. removing and weakening synapses ...
Nervous System
... neurons, sometimes over a considerable distance. In the neurons that make up the nerves running from the spinal cord to your toes, the axons can be as long as three feet! ...
... neurons, sometimes over a considerable distance. In the neurons that make up the nerves running from the spinal cord to your toes, the axons can be as long as three feet! ...
ANS (Ch14)
... • The adrenal medulla, sweat glands, arrector pili muscles, kidneys, and most blood vessels receive only sympathetic fibers • The sympathetic division controls – Thermoregulatory responses to heat – Release of renin from the kidneys – Metabolic effects • Increases metabolic rates of cells • Raises b ...
... • The adrenal medulla, sweat glands, arrector pili muscles, kidneys, and most blood vessels receive only sympathetic fibers • The sympathetic division controls – Thermoregulatory responses to heat – Release of renin from the kidneys – Metabolic effects • Increases metabolic rates of cells • Raises b ...
Unit VIII: Animal Structure and Function, Part II
... 7. Interneurons inhibit other motor neurons (hamstring) 8. Prevents the hamstring from contracting ...
... 7. Interneurons inhibit other motor neurons (hamstring) 8. Prevents the hamstring from contracting ...
Nervous System - Wando High School
... Lack centrioles- cannot perform mitosis Classified by structure and function ...
... Lack centrioles- cannot perform mitosis Classified by structure and function ...
Chapter 8
... Ballistic movement - A habitual, rapid, wellpracticed movement that does not depend on sensory feedback; controlled by the cerebellum. ...
... Ballistic movement - A habitual, rapid, wellpracticed movement that does not depend on sensory feedback; controlled by the cerebellum. ...
Muscle Tissue, Nervous Tissue, and Membranes
... Smooth Muscle: Forms walls of hollow organs and found in ...
... Smooth Muscle: Forms walls of hollow organs and found in ...
muscular system
... Spores of the bacteria C. tetani live in the soil and are found around the world. In the spore form, C. tetani may remain inactive in the soil, but it can remain infectious for more than 40 years. Infection begins when the spores enter the body through an injury or wound. The spores release bacteri ...
... Spores of the bacteria C. tetani live in the soil and are found around the world. In the spore form, C. tetani may remain inactive in the soil, but it can remain infectious for more than 40 years. Infection begins when the spores enter the body through an injury or wound. The spores release bacteri ...
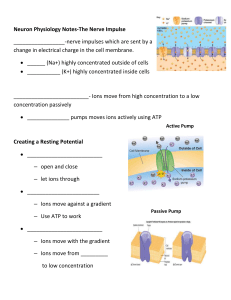
Neuron Physiology Notes
... _________________________- Ions move from high concentration to a low concentration passively ______________ pumps moves ions actively using ATP Active Pump ...
... _________________________- Ions move from high concentration to a low concentration passively ______________ pumps moves ions actively using ATP Active Pump ...
Nervous Dia rams
... The nerve celt that connects sensory and motor neurons The nerve cell that transmits impulses from the brain or spinal cord to a muscle or gland ...
... The nerve celt that connects sensory and motor neurons The nerve cell that transmits impulses from the brain or spinal cord to a muscle or gland ...
ANS and sympathetic division pharm
... Like the muscarinic receptors, adrenergic receptors are also seven transmembrane domain protiens coupled to G Protiens however there are multiple subtypes and actions. There are four major subtypes α1α2β1 and β2. Adrenoceptors respond to catecholamines in an order of potency; for alpha adrenoceptors ...
... Like the muscarinic receptors, adrenergic receptors are also seven transmembrane domain protiens coupled to G Protiens however there are multiple subtypes and actions. There are four major subtypes α1α2β1 and β2. Adrenoceptors respond to catecholamines in an order of potency; for alpha adrenoceptors ...
Bio_246_files/Motor Control
... afferent neuron which sends information about the length of a muscle and the speed at which the length changes during ...
... afferent neuron which sends information about the length of a muscle and the speed at which the length changes during ...
Fundamentals of the Nervous System and
... Electrical synapses have neurons that are electrically coupled via protein channels and allow direct exchange of ions from cell to cell. ...
... Electrical synapses have neurons that are electrically coupled via protein channels and allow direct exchange of ions from cell to cell. ...
Nervous Systems
... Propagation of Action Potential • Action potential are very localized events • DO NOT travel down membrane • Are generated anew in a sequence along the ...
... Propagation of Action Potential • Action potential are very localized events • DO NOT travel down membrane • Are generated anew in a sequence along the ...
Lecture 048 - Neurons and Nervous Systems
... Ion channels open & close in response to changes in charge across membrane Na+ ...
... Ion channels open & close in response to changes in charge across membrane Na+ ...
Neuromuscular junction

A neuromuscular junction (sometimes called a myoneural junction) is a junction between nerve and muscle; it is a chemical synapse formed by the contact between the presynaptic terminal of a motor neuron and the postsynaptic membrane of a muscle fiber. It is at the neuromuscular junction that a motor neuron is able to transmit a signal to the muscle fiber, causing muscle contraction.Muscles require innervation to function—and even just to maintain muscle tone, avoiding atrophy. Synaptic transmission at the neuromuscular junction begins when an action potential reaches the presynaptic terminal of a motor neuron, which activates voltage-dependent calcium channels to allow calcium ions to enter the neuron. Calcium ions bind to sensor proteins (synaptotagmin) on synaptic vesicles, triggering vesicle fusion with the cell membrane and subsequent neurotransmitter release from the motor neuron into the synaptic cleft. In vertebrates, motor neurons release acetylcholine (ACh), a small molecule neurotransmitter, which diffuses across the synaptic cleft and binds to nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) on the cell membrane of the muscle fiber, also known as the sarcolemma. nAChRs are ionotropic receptors, meaning they serve as ligand-gated ion channels. The binding of ACh to the receptor can depolarize the muscle fiber, causing a cascade that eventually results in muscle contraction.Neuromuscular junction diseases can be of genetic and autoimmune origin. Genetic disorders, such as Duchenne muscular dystrophy, can arise from mutated structural proteins that comprise the neuromuscular junction, whereas autoimmune diseases, such as myasthenia gravis, occur when antibodies are produced against nicotinic acetylcholine receptors on the sarcolemma.