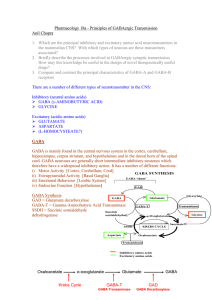
Pharmacology 18a – Priciples of GABAergic Transmission
... GABA is stored in vesicles in nerve terminals (like any other neurotransmitter) and is released by exocytosis upon influx of calcium ions. GABA Receptors There are 2 types of GABA receptor: GABAA Generally POSTsynaptic When activated by GABA cause influx of Cl- ions This causes the cell to hyp ...
... GABA is stored in vesicles in nerve terminals (like any other neurotransmitter) and is released by exocytosis upon influx of calcium ions. GABA Receptors There are 2 types of GABA receptor: GABAA Generally POSTsynaptic When activated by GABA cause influx of Cl- ions This causes the cell to hyp ...
D2 receptor overexpression in the striatum leads to a deficit in
... This article contains supporting information online at www.pnas.org/lookup/suppl/doi:10. 1073/pnas.1109718108/-/DCSupplemental. ...
... This article contains supporting information online at www.pnas.org/lookup/suppl/doi:10. 1073/pnas.1109718108/-/DCSupplemental. ...
Document
... important for understanding the functional role of this network during normal circumstances and under pathophysiological conditions, for example in the case of epilepsy. How the properties of neurons and synapses within area CA3 change in aged animals. It is well known that aged animals are cognitiv ...
... important for understanding the functional role of this network during normal circumstances and under pathophysiological conditions, for example in the case of epilepsy. How the properties of neurons and synapses within area CA3 change in aged animals. It is well known that aged animals are cognitiv ...
A tale of two stories: astrocyte regulation of
... and frequency of prior activity at that same synaptic terminal [5]. One widely studied mechanism responsible for the dependence of synaptic transmission on past activity has been dubbed presynaptic short-term plasticity [6]. Upon repetitive action potential stimulation, the response of a presynaptic ...
... and frequency of prior activity at that same synaptic terminal [5]. One widely studied mechanism responsible for the dependence of synaptic transmission on past activity has been dubbed presynaptic short-term plasticity [6]. Upon repetitive action potential stimulation, the response of a presynaptic ...
Synapses formed by normal and abnormal hippocampal mossy fibers
... established with the complex spines of the postsynaptic pyramidal cell protruding deeply into the presynaptic bouton. Chicurel and Harris (1992) have found 37 such contacts in a serially reconstructed mossy fiber bouton. Asymmetric synaptic contacts are rarely observed on dendritic shafts, and these ...
... established with the complex spines of the postsynaptic pyramidal cell protruding deeply into the presynaptic bouton. Chicurel and Harris (1992) have found 37 such contacts in a serially reconstructed mossy fiber bouton. Asymmetric synaptic contacts are rarely observed on dendritic shafts, and these ...
62 Cranial Nerve VII: The Facial Nerve And Taste
... and palatine glands (via the greater superficial petrosal nerve) and (b) the submandibular and sublingual salivary glands (via the chorda tympani nerve) . 2 . The gustatory (solitary) nucleus in the medulla supplies sensory fibers . These fibers go to taste buds on the anterior two-thirds of the ton ...
... and palatine glands (via the greater superficial petrosal nerve) and (b) the submandibular and sublingual salivary glands (via the chorda tympani nerve) . 2 . The gustatory (solitary) nucleus in the medulla supplies sensory fibers . These fibers go to taste buds on the anterior two-thirds of the ton ...
Mapping synaptic pathology within cerebral cortical circuits in
... Relative strengths of the spinning disk confocal microscope include having more photons reach the detector than in a typical LSCM setup (i.e., a pinhole of 1 Airy unit) (Sandison and Webb, 1994), providing greater fidelity of quantification of fluorescent intensity. Spinning disk confocals also use ...
... Relative strengths of the spinning disk confocal microscope include having more photons reach the detector than in a typical LSCM setup (i.e., a pinhole of 1 Airy unit) (Sandison and Webb, 1994), providing greater fidelity of quantification of fluorescent intensity. Spinning disk confocals also use ...
A1 - 58 - University of Pittsburgh
... is sustained, however, if the action potentials are ceased, then the myosin can detach from the action and the muscle will quickly relax and elongate. The goal of myoelectric devices is to register the frequency and number of action potentials, and then interpret them in the same way that sarcomeres ...
... is sustained, however, if the action potentials are ceased, then the myosin can detach from the action and the muscle will quickly relax and elongate. The goal of myoelectric devices is to register the frequency and number of action potentials, and then interpret them in the same way that sarcomeres ...
Energy balance
... Now, back to caffeine. • Caffeine binds to the receptors for adenosine, but has no effect on the receptors. • When caffeine is bound, adenosine can’t bind. Adenosine Caffeine ...
... Now, back to caffeine. • Caffeine binds to the receptors for adenosine, but has no effect on the receptors. • When caffeine is bound, adenosine can’t bind. Adenosine Caffeine ...
Spasticity after stroke: Physiology, assessment and treatment
... of both the agonist and antagonist muscles resulting from an abnormal pattern of commands in the descending supraspinal pathway), extensor or flexor spasms, clonus, exaggerated deep tendon reflexes and associated reaction [4, 5]. On the other hand, negative signs are muscle weakness, loss of dexteri ...
... of both the agonist and antagonist muscles resulting from an abnormal pattern of commands in the descending supraspinal pathway), extensor or flexor spasms, clonus, exaggerated deep tendon reflexes and associated reaction [4, 5]. On the other hand, negative signs are muscle weakness, loss of dexteri ...
Synaptic Pruning in Development: A Novel Account in Neural Terms
... frontal order [Rakic et al., 1994]. Larger temporal di erences were found between species; in some species, the peak level of synaptic density is obtained at a very early age after birth (e.g. 2 weeks for the macaque monkeys [Bourgeois, 1993]). The changes in synaptic density are not a result of cha ...
... frontal order [Rakic et al., 1994]. Larger temporal di erences were found between species; in some species, the peak level of synaptic density is obtained at a very early age after birth (e.g. 2 weeks for the macaque monkeys [Bourgeois, 1993]). The changes in synaptic density are not a result of cha ...
Slide 1
... Chemical synapse The synaptic terminal releases a neurotransmitter that binds to the postsynaptic plasma membrane Produces temporary, localized change in permeability or function of postsynaptic cell Changes affect cell, depending on nature and number of stimulated receptors ...
... Chemical synapse The synaptic terminal releases a neurotransmitter that binds to the postsynaptic plasma membrane Produces temporary, localized change in permeability or function of postsynaptic cell Changes affect cell, depending on nature and number of stimulated receptors ...
The contribution of intrinsic membrane dynamics to fast network
... of networks of inhibitory LIF neurons depends on the time constants of the recurrent synaptic currents. With physiologically reasonable time constants, the population frequency is ⬎100 Hz and can be as high as 300 Hz, whereas single cells fire irregularly and at a much lower rate than the population ...
... of networks of inhibitory LIF neurons depends on the time constants of the recurrent synaptic currents. With physiologically reasonable time constants, the population frequency is ⬎100 Hz and can be as high as 300 Hz, whereas single cells fire irregularly and at a much lower rate than the population ...
Insights into Rapid Modulation of Neuroplasticity by Brain Estrogens
... (e.g., cortex and hippocampus); 2) describe the mechanisms that control the bioavailability of active estrogens within discrete regions of the brain, in particular focusing on the ability to synthesize estradiol in nervous tissue; 3) examine the cellular consequence of rapid estrogenicsignaling on p ...
... (e.g., cortex and hippocampus); 2) describe the mechanisms that control the bioavailability of active estrogens within discrete regions of the brain, in particular focusing on the ability to synthesize estradiol in nervous tissue; 3) examine the cellular consequence of rapid estrogenicsignaling on p ...
The Dialectics of Hebb and Homeostasis within
... plasticity, synaptic scaling, that operates in a global manner to homeostatically adjust the postsynaptic weights of excitatory synapses (Turrigiano, 2008). In reduced systems one can demonstrate that this form of plasticity operates in a global and multiplicative manner, in effect ‘scaling” postsyn ...
... plasticity, synaptic scaling, that operates in a global manner to homeostatically adjust the postsynaptic weights of excitatory synapses (Turrigiano, 2008). In reduced systems one can demonstrate that this form of plasticity operates in a global and multiplicative manner, in effect ‘scaling” postsyn ...
AANEM Glossary of Terms in Neuromuscular
... The field of neuromuscular and electrodiagnostic medicine requires a universal language to communicate effectively. This glossary is the cumulative effort of many individuals over the past several decades. With added knowledge gained through research and innovation, the need to update the extensive ...
... The field of neuromuscular and electrodiagnostic medicine requires a universal language to communicate effectively. This glossary is the cumulative effort of many individuals over the past several decades. With added knowledge gained through research and innovation, the need to update the extensive ...
Print
... this structural identification and allowed the characterization of its pharmacological properties (112). In vitro and in vivo tests showed a great similarity of actions between anandamide and cannabinoid drugs. Anandamide reduced the electrogenic contraction of mouse vas deferens and closely mimicke ...
... this structural identification and allowed the characterization of its pharmacological properties (112). In vitro and in vivo tests showed a great similarity of actions between anandamide and cannabinoid drugs. Anandamide reduced the electrogenic contraction of mouse vas deferens and closely mimicke ...
tracts - Anatomický ústav 1. LF UK
... foramen ganglion spinale , conditional pseudounipolar sensitive neurons whose axons enter back into the roots of the spinal cord. ...
... foramen ganglion spinale , conditional pseudounipolar sensitive neurons whose axons enter back into the roots of the spinal cord. ...
Serotonin 1B Receptor Modulates Frequency Response Curves and
... Auditory stimuli were created and data were collected with the custom software package Batlab (Dr. Donald Gans, Kent State University). Stimuli were regulated in intensity through a PA5 attenuator and were filtered through an FT-6 antialias filter (TDT; Alachua, FL). Stimuli were played through eith ...
... Auditory stimuli were created and data were collected with the custom software package Batlab (Dr. Donald Gans, Kent State University). Stimuli were regulated in intensity through a PA5 attenuator and were filtered through an FT-6 antialias filter (TDT; Alachua, FL). Stimuli were played through eith ...
Focal local field potential (LFP) signature of the single
... to relate the signal to the underlying activity of neurons (Einevoll et al., 2013). Here we model and investigate one type of such recordings, i.e., the spike-trigger-averaged LFP (stLFP) of monosynaptic connections from single thalamocortical (TC) neurons impinging onto neuronal populations in cort ...
... to relate the signal to the underlying activity of neurons (Einevoll et al., 2013). Here we model and investigate one type of such recordings, i.e., the spike-trigger-averaged LFP (stLFP) of monosynaptic connections from single thalamocortical (TC) neurons impinging onto neuronal populations in cort ...
Focal local field potential (LFP) signature of the single
... to relate the signal to the underlying activity of neurons (Einevoll et al., 2013). Here we model and investigate one type of such recordings, i.e., the spike-trigger-averaged LFP (stLFP) of monosynaptic connections from single thalamocortical (TC) neurons impinging onto neuronal populations in cort ...
... to relate the signal to the underlying activity of neurons (Einevoll et al., 2013). Here we model and investigate one type of such recordings, i.e., the spike-trigger-averaged LFP (stLFP) of monosynaptic connections from single thalamocortical (TC) neurons impinging onto neuronal populations in cort ...
Recruitment properties of intramuscular and nerve
... synaptic inputs [1], [2]. Normally, the smaller motoneurons innervating small numbers of slow, fatigue-resistant muscle fibers are recruited first [3]. They provide stable and finely controlled force for small, precise, and frequently needed movements. The larger motoneurons innervating larger numbe ...
... synaptic inputs [1], [2]. Normally, the smaller motoneurons innervating small numbers of slow, fatigue-resistant muscle fibers are recruited first [3]. They provide stable and finely controlled force for small, precise, and frequently needed movements. The larger motoneurons innervating larger numbe ...
Neuromuscular junction

A neuromuscular junction (sometimes called a myoneural junction) is a junction between nerve and muscle; it is a chemical synapse formed by the contact between the presynaptic terminal of a motor neuron and the postsynaptic membrane of a muscle fiber. It is at the neuromuscular junction that a motor neuron is able to transmit a signal to the muscle fiber, causing muscle contraction.Muscles require innervation to function—and even just to maintain muscle tone, avoiding atrophy. Synaptic transmission at the neuromuscular junction begins when an action potential reaches the presynaptic terminal of a motor neuron, which activates voltage-dependent calcium channels to allow calcium ions to enter the neuron. Calcium ions bind to sensor proteins (synaptotagmin) on synaptic vesicles, triggering vesicle fusion with the cell membrane and subsequent neurotransmitter release from the motor neuron into the synaptic cleft. In vertebrates, motor neurons release acetylcholine (ACh), a small molecule neurotransmitter, which diffuses across the synaptic cleft and binds to nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) on the cell membrane of the muscle fiber, also known as the sarcolemma. nAChRs are ionotropic receptors, meaning they serve as ligand-gated ion channels. The binding of ACh to the receptor can depolarize the muscle fiber, causing a cascade that eventually results in muscle contraction.Neuromuscular junction diseases can be of genetic and autoimmune origin. Genetic disorders, such as Duchenne muscular dystrophy, can arise from mutated structural proteins that comprise the neuromuscular junction, whereas autoimmune diseases, such as myasthenia gravis, occur when antibodies are produced against nicotinic acetylcholine receptors on the sarcolemma.