Rapid Translocation of Zn 2+ from Nerve Terminals
... FIG. 2. Stimulation-induced release of Zn . A: images of the hilus of hippocampal dentate gyrus perfused with 20 M NG dipotassium salt before (1) and 0.5 s after (2) electrical stimulation (200 s, 0.5-mA pulses at 100 Hz for 5 s). 4 in 1 and 2, placement of the stimulation electrodes. Scale bars a ...
... FIG. 2. Stimulation-induced release of Zn . A: images of the hilus of hippocampal dentate gyrus perfused with 20 M NG dipotassium salt before (1) and 0.5 s after (2) electrical stimulation (200 s, 0.5-mA pulses at 100 Hz for 5 s). 4 in 1 and 2, placement of the stimulation electrodes. Scale bars a ...
TESIS DOCTORAL Dynamics and Synchronization in Neuronal Models
... Chapter 2 investigates the role of noise acting on neurons. The phenomenon of stochastic resonance is characterized on an ensemble of neurons of the motor system. After the introduction of the appropriate model describing the neuron dynamics and the numerical integration details, stochastic resonanc ...
... Chapter 2 investigates the role of noise acting on neurons. The phenomenon of stochastic resonance is characterized on an ensemble of neurons of the motor system. After the introduction of the appropriate model describing the neuron dynamics and the numerical integration details, stochastic resonanc ...
Depolarization stimulates lamellipodia formation and
... stained cells were quickly pelleted for 10 s in an eppendorf centrifuge and washed three times by resuspension in 1 ml GCM containing 0.2% bovine serum albumin ŽBSA. and centrifugation. After the last centrifugation step, the cells were resuspended in 1 ml GCM and counted. The stained cells were dil ...
... stained cells were quickly pelleted for 10 s in an eppendorf centrifuge and washed three times by resuspension in 1 ml GCM containing 0.2% bovine serum albumin ŽBSA. and centrifugation. After the last centrifugation step, the cells were resuspended in 1 ml GCM and counted. The stained cells were dil ...
Coupling in Networks of Neuronal Oscillators (Spring 2015)
... In each of these equations, all the parameters have been nondimensionalized. Equation (1) is a current balance equation for the cellular membrane potential. V is the cellular membrane potential, and C is the membrane capacitance. (1) balances an applied current Iapp with three ionic currents: ICa - ...
... In each of these equations, all the parameters have been nondimensionalized. Equation (1) is a current balance equation for the cellular membrane potential. V is the cellular membrane potential, and C is the membrane capacitance. (1) balances an applied current Iapp with three ionic currents: ICa - ...
Acetylcholine Facilitates Recovery of Episodic Memory after Brain
... acetylcholine innervation (for review, see Bartus, 2000). However, systemic administration of acetylcholinesterase inhibitors produces only small acute improvements in memory (Sahakian et al., 1993). Despite the lack of evidence that procholinergic therapies in Alzheimer’s disease lead to lasting im ...
... acetylcholine innervation (for review, see Bartus, 2000). However, systemic administration of acetylcholinesterase inhibitors produces only small acute improvements in memory (Sahakian et al., 1993). Despite the lack of evidence that procholinergic therapies in Alzheimer’s disease lead to lasting im ...
The Peripheral Nervous System
... categorized as somatic or visceral • Sensory inputs also classified as general or special ...
... categorized as somatic or visceral • Sensory inputs also classified as general or special ...
Ion Channels in Bursting Neurons
... This experimental preparation was chosen by Hodgkin and Huxley principally because the giant size of the squid’s axon made the insertion of multiple electrodes possible. However, there is another reason that the choice of the squid axon was fortuitous. It turns out that the conductances found in thi ...
... This experimental preparation was chosen by Hodgkin and Huxley principally because the giant size of the squid’s axon made the insertion of multiple electrodes possible. However, there is another reason that the choice of the squid axon was fortuitous. It turns out that the conductances found in thi ...
Ascending Sensory Pathways
... vary according to their morphology, the velocity of conduction, and the modality to which they respond, as well as to their location in the body, they generally all function in a similar fashion. The stimulus to which a specific receptor responds causes an alteration in the ionic permeability of the ...
... vary according to their morphology, the velocity of conduction, and the modality to which they respond, as well as to their location in the body, they generally all function in a similar fashion. The stimulus to which a specific receptor responds causes an alteration in the ionic permeability of the ...
Quantity and Three-Dimensional Position of the Recurrent and
... Quantity and Three-Dimensional Position of the Recurrent and Superior Laryngeal Nerve Lower Motor Neurons in a Rat Model ...
... Quantity and Three-Dimensional Position of the Recurrent and Superior Laryngeal Nerve Lower Motor Neurons in a Rat Model ...
studying the isolated central nervous system
... important role for metabolic pumps in nerve and muscle activity. The role of the electrogenic sodium pump in nerve and muscle tissues (especially mammalian cardiac muscle) is now more fully appreciated. ...
... important role for metabolic pumps in nerve and muscle activity. The role of the electrogenic sodium pump in nerve and muscle tissues (especially mammalian cardiac muscle) is now more fully appreciated. ...
Excitatory and Inhibitory Synaptic Placement and Functional
... synapses, classified as type 1 synapses, are innervated by axons of glutamatergic neurons (Baude et al. 1993). While there are a few reports of specific cell regions on particular types of neurons where type 1 synapses are localized directly on the dendritic shaft (Megias et al. 2001; Parnavelas et ...
... synapses, classified as type 1 synapses, are innervated by axons of glutamatergic neurons (Baude et al. 1993). While there are a few reports of specific cell regions on particular types of neurons where type 1 synapses are localized directly on the dendritic shaft (Megias et al. 2001; Parnavelas et ...
Soghomonian J.J., Sethares C., and Peters, A
... cortex and, as shown previously, about 30% of asymmetric (excitatory) and symmetric (inhibitory) axodendritic synapses are lost from the neuropil of layer 2/3 in prefrontal area 46 with age (Peters et al., 2008). Whether there is a similar loss of inhibitory axosomatic synapses from this cortex has ...
... cortex and, as shown previously, about 30% of asymmetric (excitatory) and symmetric (inhibitory) axodendritic synapses are lost from the neuropil of layer 2/3 in prefrontal area 46 with age (Peters et al., 2008). Whether there is a similar loss of inhibitory axosomatic synapses from this cortex has ...
Ultrastructural Characterization of Gerbil Olivocochlear Neurons
... acid (D-ASP) and wheatgerm agglutinin-horseradish peroxidase conjugate (WGA/ HRP) from the cochlear perilymph. While both populations are capable of uptake and retrograde uptake of WGAIHRP, one population accumulates and retrogradely transports D-ASP (D-ASP OC neurons) and the other does not (non-DA ...
... acid (D-ASP) and wheatgerm agglutinin-horseradish peroxidase conjugate (WGA/ HRP) from the cochlear perilymph. While both populations are capable of uptake and retrograde uptake of WGAIHRP, one population accumulates and retrogradely transports D-ASP (D-ASP OC neurons) and the other does not (non-DA ...
Neurophysiologic markers in laryngeal muscles indicate functional
... Stimulation was applied while subjects were engaged in the visual object-naming task. The methodology for visually presented objects (VPOs)/pictures were taken from a normative study by Brodeur et al. (2010). Fifty pictures were presented during measurement in a randomized manner in one session. The ...
... Stimulation was applied while subjects were engaged in the visual object-naming task. The methodology for visually presented objects (VPOs)/pictures were taken from a normative study by Brodeur et al. (2010). Fifty pictures were presented during measurement in a randomized manner in one session. The ...
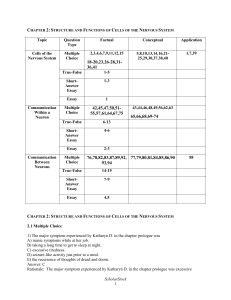
Sample
... 11) The portion of a neuron that carries a signal toward the cell body is the A) soma. B) axon terminal. C) presynaptic membrane. D) dendrite. E) glial membrane. Answer: D Diff: 1 Page Ref: 21-22 Objective: Factual LO: 2.1 APA:1.1 12) The physical gap between two nerve cells across which messages a ...
... 11) The portion of a neuron that carries a signal toward the cell body is the A) soma. B) axon terminal. C) presynaptic membrane. D) dendrite. E) glial membrane. Answer: D Diff: 1 Page Ref: 21-22 Objective: Factual LO: 2.1 APA:1.1 12) The physical gap between two nerve cells across which messages a ...
A Model of a Segmental Oscillator in the Leech Heartbeat Neuronal
... 1983a, 1983b). The coordinating interneurons do not initiate spikes in their ganglion of origin; instead spikes are initiated at sites in either the third or fourth ganglion (Peterson, 1983b). The coordinating neurons burst in alternation with their ipsilateral oscillator neuron (Fig. 1B). These neu ...
... 1983a, 1983b). The coordinating interneurons do not initiate spikes in their ganglion of origin; instead spikes are initiated at sites in either the third or fourth ganglion (Peterson, 1983b). The coordinating neurons burst in alternation with their ipsilateral oscillator neuron (Fig. 1B). These neu ...
Nicotine addiction and comorbidity with alcohol abuse and mental
... postsynaptic DA neurons is sufficient to produce LTP when paired with the boosted glutamate release caused by presynaptic α7* nAChRs. While those nicotine-induced mechanisms enhance glutamatergic excitation of DA neurons, related mechanisms decrease the inhibition from GABAergic interneurons in the ...
... postsynaptic DA neurons is sufficient to produce LTP when paired with the boosted glutamate release caused by presynaptic α7* nAChRs. While those nicotine-induced mechanisms enhance glutamatergic excitation of DA neurons, related mechanisms decrease the inhibition from GABAergic interneurons in the ...
Descending Pathways in Motor Control
... not to cross the midline, to find its target neurons, and to avoid others. The neuropharmacological features include the neurotransmitter and neuromodulators released at the pathway’s terminals. Finally, we need to add the neuroinformatic features: the activity/information that the pathway transmits ...
... not to cross the midline, to find its target neurons, and to avoid others. The neuropharmacological features include the neurotransmitter and neuromodulators released at the pathway’s terminals. Finally, we need to add the neuroinformatic features: the activity/information that the pathway transmits ...
Neonatal Ethanol Exposure Impairs Trace Fear Conditioning and
... in the encoding and consolidation of TFC. For instance, pretraining infusions of an NMDAR antagonist into either region impairs TFC, as evidenced by reduced freezing behavior during context and CS retention testing (Gilmartin and Helmstetter, 2010; Quinn et al., 2005). DuPont and colleagues (2014) a ...
... in the encoding and consolidation of TFC. For instance, pretraining infusions of an NMDAR antagonist into either region impairs TFC, as evidenced by reduced freezing behavior during context and CS retention testing (Gilmartin and Helmstetter, 2010; Quinn et al., 2005). DuPont and colleagues (2014) a ...
Analysis of Firing Correlations Between Sympathetic Premotor
... Recent intracellular recordings from rat RVLM sympathetic premotor neurons in vivo demonstrate that under normal experimental conditions, action potentials in sympathetic premotor neurons invariably arise from depolarizing events with the characteristics of excitatory synaptic inputs (Lipski et al. ...
... Recent intracellular recordings from rat RVLM sympathetic premotor neurons in vivo demonstrate that under normal experimental conditions, action potentials in sympathetic premotor neurons invariably arise from depolarizing events with the characteristics of excitatory synaptic inputs (Lipski et al. ...
Taste Physiology - Viktor`s Notes for the Neurosurgery Resident
... produced by Ebner glands. SWEET - at tongue tip. most sweet substances are organic: sucrose, maltose, lactose, glucose, polysaccharides, glycerol, some alcohols and ketones, chloroform, beryllium salts, various amides of aspartic acid. artificial sweeteners (saccharin and aspartame) produce sati ...
... produced by Ebner glands. SWEET - at tongue tip. most sweet substances are organic: sucrose, maltose, lactose, glucose, polysaccharides, glycerol, some alcohols and ketones, chloroform, beryllium salts, various amides of aspartic acid. artificial sweeteners (saccharin and aspartame) produce sati ...
Enhanced intrinsic excitability and EPSP
... increase the frequency, but not amplitude, of miniature excitatory postsynaptic currents. ...
... increase the frequency, but not amplitude, of miniature excitatory postsynaptic currents. ...
Neuromuscular junction

A neuromuscular junction (sometimes called a myoneural junction) is a junction between nerve and muscle; it is a chemical synapse formed by the contact between the presynaptic terminal of a motor neuron and the postsynaptic membrane of a muscle fiber. It is at the neuromuscular junction that a motor neuron is able to transmit a signal to the muscle fiber, causing muscle contraction.Muscles require innervation to function—and even just to maintain muscle tone, avoiding atrophy. Synaptic transmission at the neuromuscular junction begins when an action potential reaches the presynaptic terminal of a motor neuron, which activates voltage-dependent calcium channels to allow calcium ions to enter the neuron. Calcium ions bind to sensor proteins (synaptotagmin) on synaptic vesicles, triggering vesicle fusion with the cell membrane and subsequent neurotransmitter release from the motor neuron into the synaptic cleft. In vertebrates, motor neurons release acetylcholine (ACh), a small molecule neurotransmitter, which diffuses across the synaptic cleft and binds to nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) on the cell membrane of the muscle fiber, also known as the sarcolemma. nAChRs are ionotropic receptors, meaning they serve as ligand-gated ion channels. The binding of ACh to the receptor can depolarize the muscle fiber, causing a cascade that eventually results in muscle contraction.Neuromuscular junction diseases can be of genetic and autoimmune origin. Genetic disorders, such as Duchenne muscular dystrophy, can arise from mutated structural proteins that comprise the neuromuscular junction, whereas autoimmune diseases, such as myasthenia gravis, occur when antibodies are produced against nicotinic acetylcholine receptors on the sarcolemma.