Ohm`s Law
... Apparatus: DC power supply, connecting wires-5 (banana plug), 2-alligator clips, 5-ohm resistor, 10-ohm resistor, light bulb (6.3A, 0.5A), P-N junction diode (Si), and 2- digital multi meters. Theory: Georg Simon Ohm (1787-1854), a German physicist, discovered Ohm’s law in 1826. This is an experimen ...
... Apparatus: DC power supply, connecting wires-5 (banana plug), 2-alligator clips, 5-ohm resistor, 10-ohm resistor, light bulb (6.3A, 0.5A), P-N junction diode (Si), and 2- digital multi meters. Theory: Georg Simon Ohm (1787-1854), a German physicist, discovered Ohm’s law in 1826. This is an experimen ...
Intermediate 1/Access 3 Physics
... a) Describe what is meant by a series circuit. b) Describe what is meant by a parallel circuit. ...
... a) Describe what is meant by a series circuit. b) Describe what is meant by a parallel circuit. ...
Presentation: Comparison of Strategies for Redundancy to
... During operation: generation of overlapping traps Poly Silicon ...
... During operation: generation of overlapping traps Poly Silicon ...
Electric Circuits
... • Batteries increase the potential energy of charges in a circuit. A battery acts like a pump by increasing the energy of charges, much like a water pump gives water potential energy by pumping it to a higher level. Electric potential is the electrical potential energy per unit charge, measured ...
... • Batteries increase the potential energy of charges in a circuit. A battery acts like a pump by increasing the energy of charges, much like a water pump gives water potential energy by pumping it to a higher level. Electric potential is the electrical potential energy per unit charge, measured ...
DN505 - Dual Controller Provides 2μs Step
... transient detect feature. The DTR pin indirectly monitors the output voltage by looking at the AC-coupled ITH signal. If the inferred overshoot exceeds a user set value, the bottom FET turns off. This allows the inductor current to slew down at a faster rate, which in turn reduces the overshoot. Per ...
... transient detect feature. The DTR pin indirectly monitors the output voltage by looking at the AC-coupled ITH signal. If the inferred overshoot exceeds a user set value, the bottom FET turns off. This allows the inductor current to slew down at a faster rate, which in turn reduces the overshoot. Per ...
Strand 1 Electricity Review 022412
... Read the following information to answer questions number one and two. A group of students carried out the following investigation. “Our hypothesis is that the greater the wire diameter used in a toaster, the greater the resistance in the wire.” 1. We took a 4-meter length of wire with a diameter of ...
... Read the following information to answer questions number one and two. A group of students carried out the following investigation. “Our hypothesis is that the greater the wire diameter used in a toaster, the greater the resistance in the wire.” 1. We took a 4-meter length of wire with a diameter of ...
package ruggedness absolute maximum ratings features description
... ASI Semiconductor, Inc. (ASI) reserves the right to make changes to information published in this document at any time and without notice. This document supersedes and replaces all information supplied prior to the publication hereof. Information in this document is believed to be accurate and relia ...
... ASI Semiconductor, Inc. (ASI) reserves the right to make changes to information published in this document at any time and without notice. This document supersedes and replaces all information supplied prior to the publication hereof. Information in this document is believed to be accurate and relia ...
Int. Sci. 9 - Electricity Powerpoint
... 3) Induction (a neutral object acquires a charge from a charged object close by ...
... 3) Induction (a neutral object acquires a charge from a charged object close by ...
Physics I - East Syracuse-Minoa Central School District
... In the circuit at right, Rx is the unknown resistance to be measured; R1, R2 and R3 are resistors of known resistance and the resistance of R2 is adjustable. If the ratio of the two resistances in the known leg (R2 / R1) is equal to the ratio of the two in the unknown leg (Rx / R3), then the voltage ...
... In the circuit at right, Rx is the unknown resistance to be measured; R1, R2 and R3 are resistors of known resistance and the resistance of R2 is adjustable. If the ratio of the two resistances in the known leg (R2 / R1) is equal to the ratio of the two in the unknown leg (Rx / R3), then the voltage ...
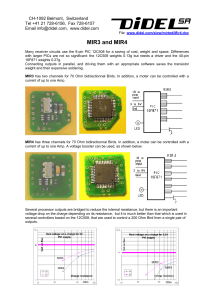
Mir4
... should be between 3 and 5 Volts. It is safe to have an A-meter connected. In case of excessive current (> 100 mA), switch off immediately and check. The processor should survive a 1-2 second inversion of polarity. A high current may also be due to a transistor with a bad input connection. Both trans ...
... should be between 3 and 5 Volts. It is safe to have an A-meter connected. In case of excessive current (> 100 mA), switch off immediately and check. The processor should survive a 1-2 second inversion of polarity. A high current may also be due to a transistor with a bad input connection. Both trans ...
POWER ELECTRONICS NOTES 10ES45
... A single phase full wave ac voltage controller circuit (bidirectional controller) with an RL load using two thyristors T1 and T2 (T1 and T2 are two SCRs) connected in parallel is shown in the figure below. In place of two thyristors a single Triac can be used to implement a full wave ac controller, ...
... A single phase full wave ac voltage controller circuit (bidirectional controller) with an RL load using two thyristors T1 and T2 (T1 and T2 are two SCRs) connected in parallel is shown in the figure below. In place of two thyristors a single Triac can be used to implement a full wave ac controller, ...
TRIAC
TRIAC, from triode for alternating current, is a genericized tradename for an electronic component that can conduct current in either direction when it is triggered (turned on), and is formally called a bidirectional triode thyristor or bilateral triode thyristor.TRIACs are a subset of thyristors and are closely related to silicon controlled rectifiers (SCR). However, unlike SCRs, which are unidirectional devices (that is, they can conduct current only in one direction), TRIACs are bidirectional and so allow current in either direction. Another difference from SCRs is that TRIAC current can be enabled by either a positive or negative current applied to its gate electrode, whereas SCRs can be triggered only by positive current into the gate. To create a triggering current, a positive or negative voltage has to be applied to the gate with respect to the MT1 terminal (otherwise known as A1).Once triggered, the device continues to conduct until the current drops below a certain threshold called the holding current.The bidirectionality makes TRIACs very convenient switches for alternating-current (AC) circuits, also allowing them to control very large power flows with milliampere-scale gate currents. In addition, applying a trigger pulse at a controlled phase angle in an AC cycle allows control of the percentage of current that flows through the TRIAC to the load (phase control), which is commonly used, for example, in controlling the speed of low-power induction motors, in dimming lamps, and in controlling AC heating resistors.