Ohm`s Law
... and resistance was discovered by Georg Simon Ohm. The relationship and the unit of electrical resistance were both named for him to commemorate this contribution to physics. One statement of Ohm’s law is that the current through a resistor is proportional to the voltage across the resistor. In this ...
... and resistance was discovered by Georg Simon Ohm. The relationship and the unit of electrical resistance were both named for him to commemorate this contribution to physics. One statement of Ohm’s law is that the current through a resistor is proportional to the voltage across the resistor. In this ...
Chapter 7: Current Electricity End of Chapter Questions
... How does the sum of the currents though the branches of a simple parallel circuit compare to the current that flows through the voltage source? As more lines are added at a fast food restaurant, the resistance to people getting served is reduced. How is this similar to what happens when more branche ...
... How does the sum of the currents though the branches of a simple parallel circuit compare to the current that flows through the voltage source? As more lines are added at a fast food restaurant, the resistance to people getting served is reduced. How is this similar to what happens when more branche ...
Electrical Networks
... Typically, as p and q move along lines, the potential difference between p and q doesn’t change except when p or q move through a circuit element such as a resistor or voltage source. Voltage is measured in volts. If V is the potential difference between two points, then the electric field transfers ...
... Typically, as p and q move along lines, the potential difference between p and q doesn’t change except when p or q move through a circuit element such as a resistor or voltage source. Voltage is measured in volts. If V is the potential difference between two points, then the electric field transfers ...
KTA-304 Solar Radiation Sensor Transducer 4
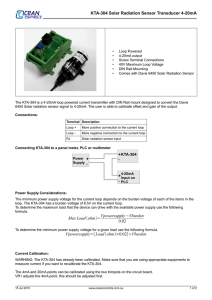
... The minimum power supply voltage for the current loop depends on the burden voltage of each of the items in the loop. The KTA-304 has a burden voltage of 8.5V on the current loop. To determine the maximum load that the device can drive with the available power supply use the following formula. ...
... The minimum power supply voltage for the current loop depends on the burden voltage of each of the items in the loop. The KTA-304 has a burden voltage of 8.5V on the current loop. To determine the maximum load that the device can drive with the available power supply use the following formula. ...
... the nominal 48 V. Once this voltage exceeds the sum of Q3’s gate threshold and D2’s Zener voltage, Q3 will start to turn on. It will not turn on abruptly, however, but will operate in its linear region momentarily due to the RC time constant created by R6 and C2. The momentary operation in the linea ...
Practice Electricity Questions
... You may want to color code the circuits to get a better idea of what’s going on… ...
... You may want to color code the circuits to get a better idea of what’s going on… ...
Kirchhoff`s Laws and Circuit Analysis (EC 2) • Circuit analysis
... Kirchhoff's Laws and Circuit Analysis (EC 2) • Circuit analysis: solving for I and V at each element • Linear circuits: involve resistors, capacitors, inductors • Initial analysis uses only resistors • Power sources, constant voltage and current • Solved using Kirchhoff's Laws (Current and Voltage) ...
... Kirchhoff's Laws and Circuit Analysis (EC 2) • Circuit analysis: solving for I and V at each element • Linear circuits: involve resistors, capacitors, inductors • Initial analysis uses only resistors • Power sources, constant voltage and current • Solved using Kirchhoff's Laws (Current and Voltage) ...
2SB1731
... VCB=−30V VEB=−6V IC=−1A, IB=−50mA VCE=−2V, IC=−100mA ∗ VCE=−2V, IE=100mA, f=100MHz ∗ VCB=−10V, IE=0A, f=1MHz ...
... VCB=−30V VEB=−6V IC=−1A, IB=−50mA VCE=−2V, IC=−100mA ∗ VCE=−2V, IE=100mA, f=100MHz ∗ VCB=−10V, IE=0A, f=1MHz ...
Electrical Engineering / Electromagnetics Plot voltage versus time
... 35. Describe the difference between an AC and DC motor. Solution: There are direct current or DC and alternating current or AC motors. The reference of DC or AC refers to how the electrical current is transferred through and from the motor. Both types of motors have different functions and uses. DC ...
... 35. Describe the difference between an AC and DC motor. Solution: There are direct current or DC and alternating current or AC motors. The reference of DC or AC refers to how the electrical current is transferred through and from the motor. Both types of motors have different functions and uses. DC ...
Notebook Pages – Binary (day 3)
... Practice with the NAND logic gate: 1) Place the 74LS00 in the breadboard. 2) Connect Pin7 (GND) to 0V and Pin14 (Vcc) to +5V. 3) According to circuit shown on the next page, connect the Input "A" to Data Switch SW4 and the Input "B" to Data Switch SW2 (or any other switchers of your choice) and conn ...
... Practice with the NAND logic gate: 1) Place the 74LS00 in the breadboard. 2) Connect Pin7 (GND) to 0V and Pin14 (Vcc) to +5V. 3) According to circuit shown on the next page, connect the Input "A" to Data Switch SW4 and the Input "B" to Data Switch SW2 (or any other switchers of your choice) and conn ...
Shaker Flashlight - University of Michigan SharePoint Portal
... Figure 5: Measuring the voltage of the AC circuit The signal is green, and we see that the voltage is alternating between positive and negative as a sine wave. It spends half the time positive, and half the time negative. This means that the current flows in one direction, slows down, flows in the ...
... Figure 5: Measuring the voltage of the AC circuit The signal is green, and we see that the voltage is alternating between positive and negative as a sine wave. It spends half the time positive, and half the time negative. This means that the current flows in one direction, slows down, flows in the ...
TRIAC
TRIAC, from triode for alternating current, is a genericized tradename for an electronic component that can conduct current in either direction when it is triggered (turned on), and is formally called a bidirectional triode thyristor or bilateral triode thyristor.TRIACs are a subset of thyristors and are closely related to silicon controlled rectifiers (SCR). However, unlike SCRs, which are unidirectional devices (that is, they can conduct current only in one direction), TRIACs are bidirectional and so allow current in either direction. Another difference from SCRs is that TRIAC current can be enabled by either a positive or negative current applied to its gate electrode, whereas SCRs can be triggered only by positive current into the gate. To create a triggering current, a positive or negative voltage has to be applied to the gate with respect to the MT1 terminal (otherwise known as A1).Once triggered, the device continues to conduct until the current drops below a certain threshold called the holding current.The bidirectionality makes TRIACs very convenient switches for alternating-current (AC) circuits, also allowing them to control very large power flows with milliampere-scale gate currents. In addition, applying a trigger pulse at a controlled phase angle in an AC cycle allows control of the percentage of current that flows through the TRIAC to the load (phase control), which is commonly used, for example, in controlling the speed of low-power induction motors, in dimming lamps, and in controlling AC heating resistors.