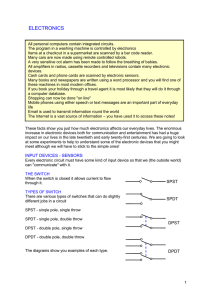
Electronic Circuits
... measured in Henries. If a speaker is placed in the circuit, it will generate sound at this frequency. For an audible sound must be in the range of 30-20,000 Hz. Since inductors always have resistance, which dissipates power a source of power must also be included in the circuit, or the sound will ...
... measured in Henries. If a speaker is placed in the circuit, it will generate sound at this frequency. For an audible sound must be in the range of 30-20,000 Hz. Since inductors always have resistance, which dissipates power a source of power must also be included in the circuit, or the sound will ...
HIGH VOLTAGE IGNITION COIL DRIVER POWER IC
... Information furnished is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, STMicroelectronics assumes no responsibility for the consequences of use of such information nor for any infringement of patents or other rights of third parties which may result from its use. No license is granted by implicatio ...
... Information furnished is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, STMicroelectronics assumes no responsibility for the consequences of use of such information nor for any infringement of patents or other rights of third parties which may result from its use. No license is granted by implicatio ...
ScienceHelpNotes-UnitD2 - JA Williams High School
... A switch can be used to control the flow of electricity through a circuit by turning it on or off. When the switch is open, the conducting points are not in contact with each other, and no current con flow through. When the switch is closed, however, the conducting points are connected, and curren ...
... A switch can be used to control the flow of electricity through a circuit by turning it on or off. When the switch is open, the conducting points are not in contact with each other, and no current con flow through. When the switch is closed, however, the conducting points are connected, and curren ...
Summary Notes - Login Page for Xphysics
... 10. State that the voltage pushes the electrons round the circuit. 11. Describe how a voltmeter is used to measure the voltage across components in a circuit. 12. State that the unit of voltage is the volt (V). 13. Draw the symbols for an ammeter and a voltmeter 14. Recognise and build a series circ ...
... 10. State that the voltage pushes the electrons round the circuit. 11. Describe how a voltmeter is used to measure the voltage across components in a circuit. 12. State that the unit of voltage is the volt (V). 13. Draw the symbols for an ammeter and a voltmeter 14. Recognise and build a series circ ...
DS2000UBLA-1HS v3.4.2016
... Fluxgate, closed loop compensated technology with fixed excitation frequency and second harmonic zero flux detection for best in class accuracy and ...
... Fluxgate, closed loop compensated technology with fixed excitation frequency and second harmonic zero flux detection for best in class accuracy and ...
Ringing Phenomenon during Recovery of Power Diodes
... and the inductance (L) of the external circuit. It is important to keep the inductance (L) small by laminating electric wiring. If forward current is small or Δt is short, the holes stored in the n region will be low. In that case the reverse current after t4 will becomes small allowing the depleted ...
... and the inductance (L) of the external circuit. It is important to keep the inductance (L) small by laminating electric wiring. If forward current is small or Δt is short, the holes stored in the n region will be low. In that case the reverse current after t4 will becomes small allowing the depleted ...
RESISTANCE/VOLTAGE RELATIONSHIP
... • As the resistance increases, the voltage across the resistor increases, and the voltage across the lamp decreases. ...
... • As the resistance increases, the voltage across the resistor increases, and the voltage across the lamp decreases. ...
Ham Radio Kit Building Class
... Conduction begins when forward bias is applied which exceeds a fairly low threshold (0.5 - 1 V). If reverse bias is applied, no current flows until reverse bias voltage exceeds the breakdown voltage, at which point current increases with reverse voltage. ...
... Conduction begins when forward bias is applied which exceeds a fairly low threshold (0.5 - 1 V). If reverse bias is applied, no current flows until reverse bias voltage exceeds the breakdown voltage, at which point current increases with reverse voltage. ...
Combining Light Bulbs in Parallel
... 1. Build a circuit with one light bulb and observe its brightness. 2. Add a second bulb in parallel. Observe or infer what happens to the: Power of an individual bulb (= brightness) Total power of the circuit Resistance of an individual bulb Total resistance of the circuit Total potential difference ...
... 1. Build a circuit with one light bulb and observe its brightness. 2. Add a second bulb in parallel. Observe or infer what happens to the: Power of an individual bulb (= brightness) Total power of the circuit Resistance of an individual bulb Total resistance of the circuit Total potential difference ...
FDC658P Single P-Channel, Logic Level, PowerTrench MOSFET
... This P-Channel Logic Level MOSFET is produced using Fairchild Semiconductor's advanced PowerTrench process that has been especially tailored to minimize the on-state resistance and yet maintain low gate charge for superior switching performance. These devices are well suited for notebook computer ap ...
... This P-Channel Logic Level MOSFET is produced using Fairchild Semiconductor's advanced PowerTrench process that has been especially tailored to minimize the on-state resistance and yet maintain low gate charge for superior switching performance. These devices are well suited for notebook computer ap ...
AMS2115 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... The AMS2115 is a single IC controller that drives an external N channel MOSFET as a source follower to produce a fast transient response, low dropout voltage regulator. The fast transient load performance is obtained by eliminating expensive tantalum or bulk electrolytic output capacitors in the mos ...
... The AMS2115 is a single IC controller that drives an external N channel MOSFET as a source follower to produce a fast transient response, low dropout voltage regulator. The fast transient load performance is obtained by eliminating expensive tantalum or bulk electrolytic output capacitors in the mos ...
Document
... interleaved structure is employed in the input side, which not only reduces the current stress through each power switch, but also constrains the input current ripple. In addition, the reverserecovery problem of the diodes is alleviated, and the efficiency can be further improved. The operating prin ...
... interleaved structure is employed in the input side, which not only reduces the current stress through each power switch, but also constrains the input current ripple. In addition, the reverserecovery problem of the diodes is alleviated, and the efficiency can be further improved. The operating prin ...
BarkerSwansonMorgan_Lab3-+BJT
... family of curves of Ic vs. VCE for different values of IB Thus, we will have to add to the DC sweep analysis another source that will sweep between 1uA to 8uA in steps of 1uA. This will give us a family of 8 curves. ...
... family of curves of Ic vs. VCE for different values of IB Thus, we will have to add to the DC sweep analysis another source that will sweep between 1uA to 8uA in steps of 1uA. This will give us a family of 8 curves. ...
TRIAC
TRIAC, from triode for alternating current, is a genericized tradename for an electronic component that can conduct current in either direction when it is triggered (turned on), and is formally called a bidirectional triode thyristor or bilateral triode thyristor.TRIACs are a subset of thyristors and are closely related to silicon controlled rectifiers (SCR). However, unlike SCRs, which are unidirectional devices (that is, they can conduct current only in one direction), TRIACs are bidirectional and so allow current in either direction. Another difference from SCRs is that TRIAC current can be enabled by either a positive or negative current applied to its gate electrode, whereas SCRs can be triggered only by positive current into the gate. To create a triggering current, a positive or negative voltage has to be applied to the gate with respect to the MT1 terminal (otherwise known as A1).Once triggered, the device continues to conduct until the current drops below a certain threshold called the holding current.The bidirectionality makes TRIACs very convenient switches for alternating-current (AC) circuits, also allowing them to control very large power flows with milliampere-scale gate currents. In addition, applying a trigger pulse at a controlled phase angle in an AC cycle allows control of the percentage of current that flows through the TRIAC to the load (phase control), which is commonly used, for example, in controlling the speed of low-power induction motors, in dimming lamps, and in controlling AC heating resistors.